Read the boundary 2 special issue “Charles Bernstein: The Poetry of Idiomatic Insistences” (volume 48, issue 4), which features Runa Bandyopadhya’s essay “Pataquericalism: Quantum Coherence between the East and West,” among others.

Read the boundary 2 special issue “Charles Bernstein: The Poetry of Idiomatic Insistences” (volume 48, issue 4), which features Runa Bandyopadhya’s essay “Pataquericalism: Quantum Coherence between the East and West,” among others.

by Sora Han
Res Nulla Loquitur: A Multimedia Essay in Seven Parts is an experiment in the study of how sound decomposes the words of law. The sound recordings used here were taken from evidence collected during investigations into the deaths of Sandra Bland, Michael Brown, Jamar Clark, Terence Crutcher, Samuel Debose, Eric Garner, Freddie Gray, Walter Scott, and Alton Sterling. While legal interpretation of these recordings strip them of self-evidentiary meaning, their recomposed repetition here force an encounter with a form of evidence I call, res nulla loquitur, ‘the no-thing speaks.’ Their indestructible questions refuse to settle for and in whatever the law offers as justice.
Click on the image below to use the essay:
Res Nulla Loquitur is a prelude to the article, “North County Jail,” forthcoming in boundary 2.
Sora Han is Chair of the Department of African American Studies, and Associate Professor of Criminology, Law & Society, the Culture & Theory Ph.D. Program and the School of Law at UC Irvine. She is the author of Mu: 49 Lines of Flight (forthcoming) and Letters of the Law (2015), and a co-author of Lacan and Mahayana Buddhist Thought (2022) and the law casebook, Comparative Equality and Anti-Discrimination Law, 3rd Edition (2020).

This article has been peer-reviewed by the b2o editorial board.
“Je suis oiseau, voyez mes ailes. Vive la gent qui fend les air!
… Je suis souris: vivent les rats!”[1]
A pigeon in a mural. In early August 2011, the American street artist Shepard Fairey paints a mural in Copenhagen, Denmark, on a wall adjacent to the “ground zero” of a recently demolished squat called Ungdomshuset (the Youth House). Fairey could hardly have chosen a worse spot in the city to sport his ready-made design of a pigeon hovering over the word “peace”: shortly after the mural’s completion, graffiti writers defaced what Fairey refers to as “my Peace Dove mural.”[2] Their message was clear: “no peace” and “go home yankee hipster.” To make matters worse, Fairey ended his trip to Copenhagen with a “black eye and a bruised rib” after a violent assault.[3]
Today, Fairey’s pigeon—a take on Picasso’s famous peace dove—is still aloft in the mural high above the vacant lot, a serene emblem of triumphant peace. Unlike Hito Steyerl’s parable of contemporary art in “A Tank on a Pedestal”—where she recounts how pro-Russian separatists drove a Soviet battle tank “off a World War II memorial pedestal” to use it in guerilla warfare—the pigeon was never hijacked from its mural and redeployed as a war machine.[4] Or was it? Considering Fairey’s controversial mural from the combined perspective of art history, the history of counterinsurgency, and late-modern warfare prompts a series of questions that pertain to our “hypercontemporary” moment in much the same way that Steyerl’s example of a tank on a pedestal does: is the mural a theater of war? Picasso’s peace dove, a drone?
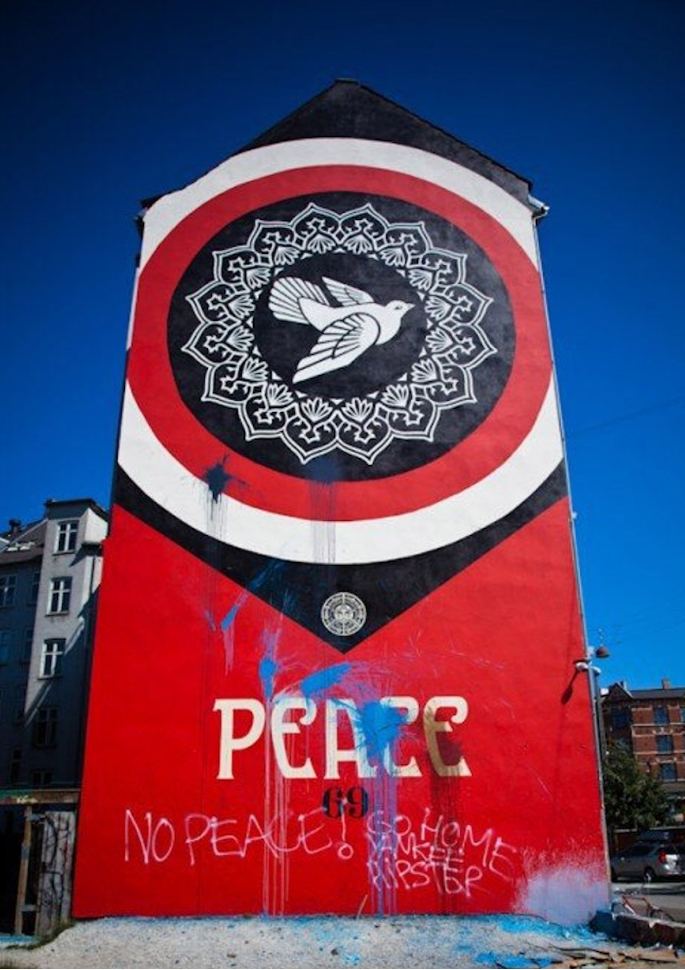

In this essay, I consider Fairey’s pigeon in a mural as an art-historical index for the “bodies of beliefs, images, values and techniques of representation” that characterize the “historical situation” of US drone warfare under the Obama administration.[5] By analyzing the peace-dove motif, and situating it in the broader context of drone warfare, I argue that the pigeon-cum-peace-dove emerges as an instrument of war alongside its mechanical double, the drone. The pigeon in the mural, then, is more than some helpless animal caught in the crossfire of a chance conflict: it is also a cipher for late capitalist war.
In what follows, I begin from the controversy surrounding Fairey’s Copenhagen peace dove mural before zooming out to reconsider how the peace dove motif relates to the conduct of war and politics from the end of the Second World War to the age of drone warfare—and beyond. As I show, the peace dove motif is historically at the center of an “image war” in which opposing political ideologies struggle for mastery in the realm of representations.[6] The story of the peace dove from Picasso through to Fairey, in other words, is the story of how an “icon of the left” was detached from its origins and aligned with a triumphant conception of liberal peace: one that effectively helped obscure US military aggression in the era of drone warfare.[7] Ultimately, then, the image conflict traced and contextualized in this essay points toward the historical limits of what the German philosopher Immanuel Kant, in a seminal essay from 1795, called the “sweet dream of perpetual peace.”[8]
I
“You don’t have to be Picasso, you just need to be inspired by Barack Obama.”[9]
To the Copenhagen Youth House activists, Fairey’s artistic peace statement was unwanted because it literally and symbolically erased the traces of conflict from the site of a year-long struggle that revolved around systemic dynamics of capitalist gentrification, political repression, and police violence. But the activists’ fury—as the tag line “go home yankee hipster” suggests—was equally fueled by their perception that Fairey’s peace message converged with President Obama’s rhetoric in the US-led war on terror by other supposedly more “peaceful” means, mostly drones.
On the street address Jagtvej 69 in Copenhagen where the Youth House once stood, there is now an empty, graffiti-covered lot. The house that once stood there, by contrast, was a vibrant hub for radical politics and dissidence for more than a century. Historical figures like Rosa Luxemburg and Lenin would pass through to give political speeches and conspire with local revolutionaries and exiled comrades. It was also here, in August 1910, that the German Marxist Clara Zetkin proposed the annual celebration of what is now known as the International Women’s Day.
After the eclipse of the historical workers’ movement, the building was temporarily abandoned. In 1982, in the wake of severe street confrontations, the Copenhagen municipality surrendered the disused building to the “BZ-movement” of young squatters, dropouts, and punks.[10] People started referring to the building as Ungdomshuset (the Youth House), which became a crucial countercultural node for the European punk movement and radicals of various stripes.
Around the turn of the millennium, the Copenhagen municipality sold off the estate to a Christian sect. The sale technically turned the building into an illegal “squat,” as its users refused to acknowledge the change of ownership. Instead, existing tensions rose, and conflicts about “the right to the city” developed into riots. The militants responded to eviction notices and a sensation-hungry press by hanging a banner from the windows of the occupied building, reading: “For sale, including 500 autonomist stone-throwing violent psychopaths from hell.”[11]
Early one morning in March 2007, one of the most carefully planned and most spectacular police operations ever carried out in Denmark took place. In scenes resembling a film, police helicopters lowered a team of special operations agents onto the Youth House, broke through barricaded windows with power tools, and filled the house with tear gas to evict the militants and clear the house for demolition. As news of the eviction spread, Copenhagen’s streets became ablaze with anger. Hundreds of militants from all over Europe joined the struggle. In their effort to “keep the peace,” while facing some of the most severe riots Denmark had ever seen, the Copenhagen police department mustered reinforcements from neighboring districts, and even neighboring countries.[12]
The state forces far outnumbered protesters and rioters, who could not prevent the Youth House’s eventual demolition.[13] Still, the riots, protests, and demonstrations carried on relentlessly after the demolition, and every single Thursday for several years, thousands of protesters would ritually march through the city. Even though in 2008 the municipality yielded to the pressure and allotted another building in the city’s outskirts to activist purposes, the Thursday protests carried on unrelentingly for several years. The original battle cry—nothing forgotten, nothing forgiven—still resounded among a discontented youth when Shepard Fairey made his cameo appearance in 2011.
When Fairey flew in to decorate the city—Fairey’s stint as a Copenhagen street artist included an art show at the self-styled “street art gallery,” V1, and no fewer than seven murals in prime locations across the city—the Youth House struggles were still recent memory. In a blog post, Fairey recalls being aware that “the mural location in question had a controversial history” but says he thought to himself: “what a shame, I hope I can do something that is a symbolically positive transformation.”[14] Apparently, some activists thought differently. Even before the mural was completed it was destroyed by graffiti.
The destruction of the Copenhagen mural and the ensuing image conflict soon attracted international media attention. The Guardian, for instance, reported that Fairey’s mural “appeared to reopen old wounds, with critics accusing Fairey of peddling government-funded propaganda.”[15] Fairey, in turn, insisted that his mural was non-political, stressing that he was merely promoting a universal message of peace, and went back to restore his mural. Just as quickly as he restored it, however, someone destroyed it anew.
V1, Fairey’s local art gallery, stepped in to mediate by inviting some artists, who supposedly represented the Youth House, to repaint the bottom half of the mural in a design of their own choice. Fairey recalls:
It was a powerful scene of hostile riot police like those who had evicted the Youth House dwellers and it incorporated one of the paint bombs on the mural as if it had been thrown by a riot cop. I thought it was a brilliant solution reflecting the history of the site and keeping my pro-peace message intact, but adding additional emphasis to the idea that peace is always facing attack from injustice that I felt was already more subtly implied by placing the dove in a target.[16]
These changes did little to help, and the mural kept getting attacked. And so too, unfortunately, did the artist. Soon, a mock version of the famous Obama posters the artist created for the 2008 US presidential election appeared on Copenhagen street corners. Instead of a picture of Obama, the poster now featured Fairey, with a bruised eye, over the familiar caption: HOPE. But why such vehement opposition? And “how”—as the artist asked—“is a mural advocating global peace inflammatory”?[17]
To understand the antagonism toward Fairey, one needs to consider how Fairey glossed over decades of struggles between local activists and a repressive state apparatus parading as the apotheosis of liberal democracy. As the mock poster amply suggests, the activists’ perception of Fairey as a useful idiot for American cultural imperialism originates in the street artist’s world-renown campaign to help elect Obama for president.
In 2008, Fairey created and distributed thousands of stickers, posters, T-shirts, and other merchandise to support the future president. Fairey even painted an “Obama mural” in Hollywood, photographed from a spectacular bird’s eye view. Across these images, the graphic form of Obama’s face is invariant. Fairey’s instantly recognizable aesthetic, which borrows in equal parts from political propaganda, pop art, and advertising, led The New Yorker’s art critic, Peter Schjeldahl, to extol Fairey’s Obama HOPE poster as “the most efficacious American political illustration since ‘Uncle Sam Wants You.’”[18]
Obama too, recognized the poster’s political efficacy. In a letter of appreciation to the street artist, Obama said: “I would like to thank you for using your talent in support of my campaign. […] Your images have a profound effect on people, whether seen in a gallery or on a stop sign. I am privileged to be a part of your artwork and proud to have your support.”[19] Soon after, with a little help from his “poster boy,” as the media later dubbed Fairey, Obama was elected. He was sworn into office on January 20, 2009. The rest is history. A history of hope, among other things.
Looking back from the recent Trump era, Obama’s presidency might appear to embody the progressive march towards what Kant, in 1795, had called “perpetual peace.” But the “sweet dream of perpetual peace,” as Kant stressed—to shield himself from allegations of subversive intent—remains precisely that: a philosopher’s dream, to which the “worldly statesman” does not need to “pay […] any heed.”[20] And though the worldly statesman Obama rhetorically advocated peace, he didn’t shy back from using military force.
One of President Obama’s first military campaigns, what became known as the “Obama-surge,” consisted in ramping up US troops in Afghanistan by an additional 17.000 soldiers. Later Obama’s military strategy shifted toward a series of so-called “small wars” or military interventions in Libya, Iraq, and Afghanistan, among other places, that most certainly violated key philosophical articles in Kant’s treatise on peace – e.g. intervening forcibly in another state and employing “assassins.”[21] Advanced weapon technologies or “drones” for carrying out assassinations were instrumental to what some would describe as the Obama administration’s transformation of “the whole concept of war,” along with its attendant relationship to peace.[22]
However, Obama was not yet another “war president” but rather an example of a statesman who carefully paid heed to the dream of lasting peace and whose chief political task, accordingly, was to engineer this peace by all means necessary. One of the most potent tools that Obama inherited and redefined was the infamous US drone program. However, while new technology may have changed the reality of warfare, it takes more than technical advances to change social conceptions of war. Critics have rightly exposed the ambiguities in Obama’s peace rhetoric.[23] But which other “instruments” may have helped transform our understanding of war and its relationship to peace?
Key here, I believe, is how state and non-state actors ideologically supercharge artworks to wage “image war.”[24] One of the most famous examples of image war occurred when US officials, prior to the invasion of Iraq in 2003, deemed the reproduction of Picasso’s Guernica that was hanging in the UN Security Council chamber an inappropriate backdrop and ordered it to be concealed behind a curtain before the media arrived. According to the Retort collective’s analysis, this incident illustrates how states “struggle for mastery in the realm of the image.”[25] Can we pursue this analysis one step further to explore forms of image war that do not directly involve the state’s micromanagement of the “means of symbolic production”?
The advent of blogs, social media, and algorithms has challenged traditional top-down approaches to the politics of representation. As the Situationist Guy Debord pointed out at the dawn of our networked era, new decentralized or “diffuse” forms of control in the realm of the image exist side by side with more “concentrated” forms of spectacular representation.[26] State power no longer relies to the same extent on micromanaging appearances. Instead, as in the case of the Obama administration’s quasi-official endorsement of Fairey’s artwork, state power now benefits equally from artists-as-influencers who more or less wittingly align their aesthetics with the ideological exigencies of those in power.
Fairey placing his pigeon in a target to “subtly” imply, in his own words, “that peace is always facing attack from injustice” is an example of how ideology exists, independently of overt state control, in the expanded realm of art.[27] Fairey’s idea of a fragile and easily victimized peace—as not-so-subtly underscored by the white-feathered creature placed in a target—thus readily exposes a key ideological component of the liberal reasoning behind late-modern warfare: that perpetual peace requires an advanced pre-emptive “security” regime to ward off potential attacks from the enemies of peace.
In the liberal conception of peace, “keeping the peace” does not mean waging war indiscriminately but protecting the international community’s fragile state of equilibrium from external threats. What the US-led international community refers to as “peace” is not just a misnomer for perpetual war but also, in a historically specific sense, the precondition for newfangled forms of pre-emptive state violence, the urbanization of drone warfare, and the policing of racialized “surplus populations.”[28] From war power to police power, in other words.[29]
From such a perspective, Fairey’s pigeon dovetails with what Mark Neocleous calls the “liberal peace thesis.”[30] Now “a standard trope in the political discourse of international theory,” Neocleous argues, the liberal peace thesis is an untenable “claim for capitalism’s essentially pacific grounds.”[31] Since its inception in eighteenth-century political philosophy, the proponents of the liberal peace thesis have ignored evidence that contradicts the idea that free markets are an effective antidote to armed conflict. The constitutive violence at the heart of the liberal peace thesis, Neocleous notes, is encapsulated in ahistorical interpretations of Kant’s essay:
Liberalism, and thus many international lawyers, like [sic] to cite Kant’s essay ‘Perpetual Peace’ as a key philosophical document outlining the liberal foundations of peace, yet usually omit the fact that the essay was published in October 1795, just one month after the military suppression of the revolt in Poland led by Tadeusz Kosciuszko and Poland’s partition by Russia and Prussia, and about which Kant had nothing to say.[32]
Likewise, proponents of the liberal peace thesis in the age of drone warfare typically have little to say about the lethal violence undergirding the “peace” discourse of the Global North. Obama is, again, a case in point. As one of the most popular American presidents ever, Obama was—and to some extent still is—primarily perceived as the embodiment of liberal democracy. In terms of US politics, Obama is something close to the incarnation of the liberal peace thesis: a champion of the most politically progressive values, with “peace” chief among them.
Eleven months into his presidency, in December 2009, Obama was awarded the Nobel Peace Prize for helping the US to play a more constructive role in world politics and for preferring “dialogue and negotiations” as “instruments for resolving even the most difficult international conflicts.”[33] The news that the 44th American president had received the world’s most prestigious peace prize resonated globally. Prefiguring Fairey’s pigeon mural, the Spanish newspaper El Pais published a cartoon picturing Obama as a “black peace dove.”[34]
But the 2009 Nobel Peace Prize laureate admitted to having “instruments” other than just “dialogue and negotiations” in his peace arsenal. In his acceptance speech, Obama acknowledged that, as “the Commander-in-Chief of the military of a nation in the midst of two wars,” he was “filled with difficult questions about the relationship between war and peace.”[35] The answer to these “difficult questions,” as is now well known, took the form of the drone.
As Daniel Klaidman stated in his contemporaneous bestselling book Kill or Capture: the War on Terror and the Soul of the Obama Presidency, “[b]y the time Obama accepted the Nobel Peace Prize in December 2009, he had authorized more drone strikes than George W. Bush had approved during his entire presidency.”[36] According to estimates produced by the Bureau of Investigative Journalism, Obama oversaw “ten times more” air strikes than his predecessor, amounting to “a total of 563 strikes, largely by drones,” in Pakistan, Somalia, and Yemen among other places. The corresponding death-by-drone casualties logged by the bureau amount to somewhere “between 384 and 807 civilians,” and counting.[37]
In his Nobel Peace Prize remarks, Obama gauged the “costs of armed conflict” in relation to the “imperatives of a just peace” and concluded: “So yes, the instruments of war do have a role to play in preserving the peace.”[38] Obama’s closing remark?
Clear-eyed, we can understand that there will be war, and still strive for peace. We can do that—for that is the story of human progress; that’s the hope of all the world; and at this moment of challenge, that must be our work here on Earth.[39]
Leaving aside the question of whether the US-led, drone-based peace campaign is the story of human progress, it is clear that Obama’s work on Earth changed how we think about war and international conflict. Touting promises of “hope,” “progress,” and “change” (incidentally, the words that Fairey interchangeably used on his iconic HOPE posters), the Obama administration helped transform the concept of warfare into a logic of global “security.” As Grégoire Chamayou, in his instant classic of the drone age, pointed out, “in the logic of this security, based on the preventive elimination of dangerous individuals, ‘warfare’ takes the form of vast campaigns of extrajudiciary executions.”[40] As Chamayou remarks, “the names given to the drones—Predators (birds of prey) and Reapers (angels of death)—are certainly well chosen.”[41] So, is the pigeon in Fairey’s mural a bird of prey? The peace dove, an angel of death? Let’s examine in more detail the history of this magically ambiguous motif.
II
In 2010, the year before Fairey painted his “Peace Dove mural” in Copenhagen, there had been a global celebration of Picasso’s work. The temporary closure of the Picasso Museum in Paris, which sent many of Picasso’s works on tours of the global museum circuit, enabled major Picasso retrospectives in Moscow, New York, Münster, Seattle, Zürich, Vienna, and Liverpool.[42] The Liverpool exhibition, which took place at the Tate Liverpool gallery, was called Picasso: Peace and Freedom.
The exhibition frontispiece sported one of the artist’s iconic peace dove designs. According to the exhibition statement, this would be the first exhibition “to examine in depth the artist’s engagement with politics and the Peace Movement,” and it would “reflect a new Picasso for a new time.”[43] A new Picasso for a new time—but what “new time,” exactly? A time before Brexit, Boris Johnson, and Trump. A time of “hope,” for sure. A time that embodied all the most progressive values and hopes of Western liberal democracies. But how did Picasso’s peace dove become an emblem for an overarching liberal narrative of progress, peace and freedom?

While the dove has been a symbol of peace since ancient times, it was in the hands of the twentieth century’s most famous artist, Pablo Picasso, that it acquired its status as the quasi-official symbol of world peace. Appropriately to our story, Picasso’s peace dove originated, it is not often noted, as a fusion of street art avant la lettre and political propaganda. According to art historian Sarah Wilson, Picasso’s peace dove first appeared on the world stage in a poster on the streets of Paris announcing the World Congress for Peace, Paris-Prague, in 1949. It was the French communist and founding member of Surrealism, Louis Aragon, who, during a visit to Picasso’s studio, had chosen “Picasso’s pigeon—a soft wash drawing on a black ground” as a symbol for the upcoming international peace congress.[44]
Thanks to mechanical reproduction techniques, Picasso’s pigeon or La Colombe (1949)—originally intended as a limited edition lithograph of 50 prints—was being churned out by the thousands. Under the French Communist Party (PCF) auspices, Picasso’s delicate peace dove motif thus evolved into what specialist in political imagery Zvonimir Novak fittingly describes as a machine de guerre graphique, a graphical war machine.[45]
In response to the PCF’s “extremely successful billboard campaign,” French anti-communists, covertly sponsored by the CIA, formed a movement called Paix et Liberté (peace and freedom), with the sole purpose of discrediting the communist peace campaign that symbolically centered on Picasso’s wildly popular peace dove motif.[46] Did the 2010 Tate exhibition, Picasso: Peace and Freedom, perhaps intend some historical pun by alluding to the anti-communist propaganda of Paix et liberté in their exhibition title? It is difficult to tell, especially given that there was also a pacifist communist group with that name in the interwar years.[47] The changing ideological valence of the terms “peace and freedom” notwithstanding, the recuperation of Picasso’s peace dove exemplifies how art and politics intertwine in ways that exceed artistic intent. Much like Picasso’s Guernica was detached from its historical origins in “exchange for its continuing topicality”—as O.K. Werckmeister argued in his seminal book Icons of the Left—so too did his peace dove evolve into an all-purpose image of a politically non-descript peace. [48]
The original Paix et liberté group is an essential component in the history of Picasso’s peace dove. It was the French socialist politician, Jean-Paul David, who in 1950 founded Paix et liberté together with fellow partisans of the North Atlantic Treaty. To their concern, the signing of the treaty had been “effectively eclipsed” in France by the press coverage of the first communist peace congress.[49] The group’s aesthetic counter-offensive launched a flood of “posters supplemented by newsletters, brochures, pamphlets, stickers, and tracts that used the words, themes and symbols of the Communist Party to counter their message.”[50] In the climate of tense ideological antagonism that characterized the early phases of the Cold War, Novak recalls, the Parisian “walls were a site for a permanent war between billposters, the streets a battlefield scattered with paper tracts.”[51] A recurrent feature of the anti-communist campaign was how it exploited a deep-seated cultural sense of ambiguity about birds to draw attention to the two-faced nature of the communist peace symbol.
In a popular fable by Jean de La Fontaine, “The Bat and The Weasels,” a bat is caught by a weasel with an appetite for mice. The poor creature cunningly escapes death by convincing the predator that it is “not of that species” at all: “I, a mouse? No, no, some people must have told you merely out of malice. Thanks to the creator of the universe, I am a bird: behold my wings. Long live the nation that skims the air.” A little later, the same bat is caught again by another weasel, this time one that harbors an “enmity” toward birds. Again, the clever bat escapes. But this time by refusing to be a bird, insisting that, surely, it is the feathers that make the bird, not the mere ability to fly. La Fontaine’s fable—which, as one can imagine, also lent itself to French anti-Semitic political caricatures—was used against the communists to present them as morally suspect.
Because much of the support for the PCF in the 1940s and 1950s stemmed from the glory of the communist resistance movement’s fight against fascism during the Second World War, the Fontainesque anti-communist propaganda centered on undermining the idea that communists could be French republican patriots. One particular tract, a precursor to the Paix et liberté variations that followed in its path, gets this message across: recto, there is a winged creature draped in the French colors, with a caption that reads “I am bird, behold my wings”; verso, the creature reveals its true colors, a deep communist red, hammer and sickle on its chest, with the caption now reading “I am a mouse! Long live the rats!”
Perhaps the most successful attack of this kind was the poster, La colombe qui fait boum, which ingeniously transformed Picasso’s peace dove into an explosive device. According to Wilson, “the explosive slogan was soon pasted all over the walls of Paris as Picasso’s Dove had been: the print run was purportedly 300,000.”[52] As Wilson notes, Picasso’s voluminous FBI file references the satirical poster along with a press clipping from The Washington Post, February 17, 1952:
The back, the pouting breast and the belly made the form of a tank: the tail feathers were exhaust fumes. The head was a turret and the beak a cannon, the hammer and sickle brand was on the shoulder. There was a simple five word caption: ‘The Dove that goes Boom’. All Paris laughed and the Communists were ridiculed.[53]

The satirical attacks may have harmed the PCF’s image momentarily, but Picasso’s peace dove took off to become the quasi-official mascot of the world peace movement. From today’s perspective, however, the peace dove of the Picasso: Peace and Freedom exhibition at Tate Liverpool Gallery stands, along with Fairey’s peace dove mural, at the end of the historical arc of triumphant liberalism.
Retrospectively, 1989 was a hinge moment. On this crucial threshold from the “modern” to the “contemporary,” Francis Fukuyama famously trumpeted the “end of history” based on the alleged “fact that ‘peace’ seems to be breaking out in many regions of the world.”[54] In the prominent political scientist’s global peace narrative, “Western liberal democracy” had revealed itself to be the “endpoint of mankind’s ideological evolution.”[55] The future, from this perspective, was canceled. The only significant task left to humankind would be to come to terms with the past, a perpetual historical curating. Or, in Fukuyama’s own words: “In the post-historical period there will be neither art nor philosophy, just the perpetual caretaking of the museum of human history.”[56] But the “modern” constraints and contradictions of the pigeon-cum-peace-dove were carried over into the age of drone warfare and continues to shape our hypercontemporary—and oddly Fontainesque—condition.
III
Imagine this. Just as Shepard Fairey puts the finishing touches to his mural in Copenhagen, a mysterious mechanical bird crashes to the ground. But Fairey, in deep concentration, perhaps mulling over whether to include an olive branch in the pigeon’s beak, doesn’t notice it at all. The street artist is so immersed in his work that he forgets where he is. Los Angeles, New York, Reykjavik, or perhaps Tel Aviv? When Fairey looks around to see what the commotion is about, it is nightfall in Balochistan Province, Pakistan. A man, lit up by the headlights of a parked car, holds up what “looks a bit like a silver bird,” while another man stands guard with a Kalashnikov.[57] What’s going on here? Is it a bird? Is it a plane? A toy? No, it’s “a small combat-proven spy drone.”[58]
Of course, Fairey painting his peace dove mural and the “weird, birdlike mystery drone” falling from the sky were two separate events that happened in two different places. Fairey wasn’t magically beamed into Pakistan. Sheer historical coincidence brings these two birds to the fore at this exact historical moment (August 2011). But there is something uncanny about these twin events that brings to mind the work of the Egyptian artist Heba Y. Amin, who in As Birds Flying (video, 2016) and The General’s Stork (mixed media, 2016–ongoing), mines the contemporary drone imaginary through an aesthetic exploration of the historical and ideological overlaps between birds and drones.
Amin does not discuss Shepard Fairey’s peace dove, but she does refer to the Pakistan “mystery drone” as an example of how drones are nested in deep-seated cultural imaginaries about birds flying. In The Generals Stork, Amin relates the crashed mystery drone to its commercial twin, the then much-hyped “SmartBird” by Festo engineering, and brings these two birds-as-drones into a larger media narrative about how, in 2013, Egyptian authorities detained a migratory stork on suspicions of espionage because it was equipped with an electronic tracking device. A device that, as it transpired, merely registered the bird’s migratory patterns.
To Amin, the Pakistan spy-drone crash highlights the progressive obscuring of the boundaries between natural beings and military artifacts that characterize situations of drone warfare and creates the conditions of possibility not only for storks being detained but also for generalizing a sense of paranoia that pervades everyday life under drone surveillance: “Imagine the confusion of finding such an object in a place where people are so accustomed to drone attacks. What happens when we can no longer differentiate a machine from a living thing?”[59]
Amin critically addresses the projected drone future where birds-as-drones and other similar creatures “naturally” circle the sky above. And Festo’s “smart bird,” to be sure, marks a historical threshold. The “SmartbBird” has since inspired a flock of cheaply available “bionic” or “bio-mimetic” drones, so called because they are engineered to mimic birds and other living creatures. In 2016, for instance, Amazon patented new drone technology that would allow future delivery drones to perch “like pigeons” on streetlights, church steeples, and other vertical urban structures.[60] When the world’s largest online retailer jumps on the bionic drone bandwagon, we can start to imagine what the drone future might bring.
Indeed, if one is to believe the media hype, bio-inspired drones might be the next big thing. One 2019 NBC news report rubric reads: “Inspired by the aerial abilities of birds, bats and insects, researchers are crafting a new generation of ultralight drones that lack propellers and are equipped not with fixed wings but with flapping ones.”[61] More recent examples confirming this trend are legion. In contemporary robotics, common pigeons of the kind that inspired Picasso’s peace dove motif are being anatomically dissected to teach semi-autonomous machines to perform more like their feathered brethren.[62] The common pigeon that inspired Picasso’s peace dove is, essentially, a proto-drone.[63]
Amin’s art project, As Birds Flying, further instructs us about the historical and symbolic crossovers between birds and their mechanical counterparts, the drones, and crucially brings colonialism into the frame. Amin’s film is based on found drone footage of locations in the Middle East, including views of Israeli settlements, and poetically reinterprets how religious myths, colonial wars, airpower, spy birds, surveillance technologies, and late-modern drone warfare historically interlock.
In the artistic research project The General’s Stork, Amin recalls the story of Lord Allenby’s seizure of Jerusalem from the Ottoman Turks in 1917 to show how deep the bird-as-drone imaginary reaches into the historical texture of orientalism and colonialism:
[Lord Allenby] launched an attack based on a biblical prophecy found in the book of Isaiah 31:5, which states: “As birds flying, so will the Lord of hosts defend Jerusalem; defending also he will deliver it; and passing over he will preserve it.” By reason of this prophecy, he sent as many planes as possible to fly over Jerusalem, forcing the Turks to surrender the city. So, when Allenby marched into Jerusalem, it was seen as a prophecy fulfilled. Right at the core of this prophetic figure, or augury, is the symbolic and actual presence of the avian, the prophecy of the birds flying over Jerusalem, the birds mutating into airplanes, the airplanes mutating into drones, and the menace of predictive drone technology metastasizing into the specter of aerial bombardment. This prophecy has become predictive in terms of drone technology, envisioning what will be and what is yet to come.[64]
Amin’s examination of “the symbolic and actual presence of the avian” in the historical ascendance of the drone underscores how the realms of the symbolic and the real overlap. Just as the biblical prophecy helped Lord Allenby visualize and ultimately legitimize Jerusalem’s destruction, the liberal peace thesis provides ideological justification for the US-led drone program. Lord Allenby’s prophecy materialized as mechanical birds flying over Jerusalem dropping bombs while Picasso’s peace dove, in turn, participates in an ongoing image war with no less deadly consequences. As diverse as these different historical contexts of killing may be, they are equally grounded in deep-seated cultural narratives with a near palpable orientalist subtext.

Seen from an art-historical perspective, the migration of the common pigeon (Colombia livia)—from Picasso’s 1949 ink-wash drawing through to Fairey’s 2011 peace dove mural and further still—forms an irregular pattern across history that culminates symbolically at the height of the age of drone warfare and resonates into our present moment. Today, there is a more-than-symbolic sense in which Picasso’s peace dove mutates into a drone—or a swarm of drones, to be exact.
In December 2016, as Obama’s presidency was coming to an end, the skies above the Disney World theme park “dazzled with drones” in a spectacular night-time show: “For Starbright Holidays’ finale, the drones form a dove. With the music swelling, the sequence packs an emotional punch.”[65] In an article in USA Today, Ayala, one of Disney’s so-called Imagineers (that is, an imagination engineer) notes that “his team originally animated the word, ‘peace,’ but later removed it. The dove, the Imagineers figured, transcends language and culture. ‘We have the symbol of peace,’ notes Ayala. ‘What better way to show it than from the stars themselves—from the universe?’”[66]
Although arbitrary to the events recounted in this essay, the Disney show appears as a grand finale of the ideology of liberal peace as epitomized by the drone. It also bespeaks what Andrea Miller calls the “specter of the drone,” an example of how “diffuse histories and geographies of war are folded into the sign of the drone” in new forms of entertainment.[67] The proliferation of drones as a tool of entertainment since 2016 practically refutes its reputation as an aggressive instrument of US neo-imperialist war in ways that are most certainly conducive to the drone industry. President-elect Joe Biden’s drone fireworks celebration in November 2020 testifies to this historical shift—and raises important questions about what the drone future might hold.[68] So where are we now? And what happened to the pigeon in the mural?
*
In 2013, Shepard Fairey fell out of love with his former political icon, Obama, and became an outspoken critic of drone warfare (if not of liberal peace).[69] As Fairey’s criticism of Obama’s use of drones became known to the public, one blogger quipped: “End of a Fairey Tale: Poster Artist Says Obama’s Drones Killed ‘Hope’.”[70] A 2015 Washington Post op-ed took a similar line: “Obama’s done. It’s the perfect metaphor for the Obama administration for Republicans. That widespread enthusiasm for Obama in 2008 has eroded, and with less than two years left in office, one of his most visible supporters, the guy who made the most iconic image of the Obama years has even turned on him.”[71] The commentator turned out to be correct: Obama was done. The Fairey Tale of perpetual peace ended, as we now know, with the brutal awakening in 2017 to the Trump era and the spectacular rise of late-capitalist fascism.[72]
The story about the destruction of Fairey’s peace dove mural in Copenhagen now belongs in a backroom of Fukuyama’s “museum of human history.” And no one paid much attention to Shepard Fairey’s peace dove after its attempted assassination by graffiti writers in 2011. After Fairey returned to the US, the partly destroyed mural was left to its own devices; an aesthetic prop in the staging of a “radical chic” image that accompanies Copenhagen’s ongoing gentrification. To this day, Fairey’s pigeon remains intact in its mural, hovering peacefully above street level commotion. Its mechanical double, however, is as busy as a bee.
The Covid 19-pandemic has rekindled interest in “bionic” drones inspired by flying creatures such as birds, bats, and bees. In China, for instance, drones disguised as white doves surveil the population, firing up the imagination of conspiracy theorists worldwide.[73] In the US and in many other countries, a new breed of Fontainesque drones with and without feathers are operating daily outside of the military context. In addition to commercial drones and drones operated by amateur hobbyists, so-called “pandemic drones” are now performing various roles: delivering medical supplies, sanitizing streets, or “shouting” at people to keep their distance.
According to statistics from the Bard College Drone Center, more than 500 public safety agencies acquired drones between 2018 and 2020, bringing their total number close to 1,600—and counting. If the US is a bellwether of a global tendency for public safety agencies to add drones to their “peace arsenal,” the question remains whether this peace is preferable to what was called, once upon a time, by a more recognizable name: war.
Taking recent political unrest in the US and elsewhere into consideration one can fear that the mainstream adoption of drones—under continuing capitalist relations of production—will reinforce rather than challenge existing systems of technologically enabled oppression. It is crucial to remember, as scholar of surveillance Simone Brown notes, that oppressive forms of surveillance did not arrive with new technologies such as drones. Instead, drone surveillance is but a new expression of the same racism and anti-blackness that undergird existing power structures.[74] Whether we are dealing with “ghetto birds” or drones disguised as white peace doves, racist police power is still, to paraphrase James Baldwin, policing black communities like occupied territories.[75] The “sweet dream of perpetual peace,” in other words, still weighs heavily on the brains of the living.[76]
_____
Dominique Routhier is a postdoctoral researcher affiliated with the research project Drone Imaginaries and Communities (Independent Research Fund Denmark) at the University of Southern Denmark. His first book With and Against: the Situationist International in the Age of Automation, is forthcoming with Verso Books in 2023.
_____
[1] Jean de La Fontaine, Fables choisies, mises en vers par J. de La Fontaine, vol. 1 (Paris: Desaint and Saillant, 1755), 53, https://gallica.bnf.fr/ark:/12148/bpt6k1049428h.
[2] Shepard Fairey, “Obey Copenhagen Post 1 (Good),” Obey Giant (blog), August 11, 2011, https://obeygiant.com/obey-copenhagen-post-1-good/.
[3] Xan Brooks, Dominic Rushe, and Lars Eriksen, “Shepard Fairey Beaten up after Spat over Controversial Danish Mural,” The Guardian, August 12, 2011, http://www.theguardian.com/artanddesign/2011/aug/12/shepard-fairey-beaten-danish-mural.
[4] Hito Steyerl, Duty Free Art (New York: Verso, 2017), 1–8.
[5] T. J. Clark, “The Conditions of Artistic Creation,” Times Literary Supplement, May 24, 1974, 562.
[6] The term “image war” has been used in various theoretical contexts since the Gulf War. Perhaps most famously, Jean Baudrillard theorized “the birth of a new kind of military apparatus which incorporates the power to control the production and circulation of images” in a series of essays that appeared in English translation under the title The Gulf War did not take place (Bloomington IN: Indiana University Press, 1995), 5. Dora Apel in War Culture and the Contest of Images (New Brunswick: Rutgers Univeristy Press, 2012), W.J.T. Mitchell in Cloning Terror: The War of Images (Chicago: Chicago University Press, 2011), and, of course, the Retort collective in Afflicted Powers: Capital and Spectacle in a New Age of War (New York: Verso, 2005) all use the term (or corelates) in their analysis of the spectacular nature of late modern warfare.
[7] In terms of methodology, I rely on Otto Karl Werckmeister, Icons of the Left: Benjamin and Eisenstein, Picasso and Kafka after the Fall of Communism (Chicago: The University of Chicago Press, 1999).
[8] Immanuel Kant, “Toward Perpetual Peace: A Philosophical Sketch,” in Immanuel Kant, Toward Perpetual Peace and Other Writings on Politics, Peace, and History, ed. Pauline Kleingeld, trans. David L. Colclasure (New Haven: Yale University Press, 2006), 67.
[9] Shepard Fairey, “Manifest Hope,” Obey Giant (blog), August 11, 2008, https://obeygiant.com/manifest-hope/.
[10] For a more detailed historical contextualization of the Youth House, see René Karpantschof and Flemming Mikkelsen, “Youth, Space, and Autonomy in Copenhagen: the Squatters’ and Autonomous Movement, 1963-2012,” in The City is Ours: Squatting and Autonomous Movements from the 1970s to the Present, eds. Bart van der Steen, Ask Katzeff, and Leendert van Hoogenhuijze (Oakland: PM Press, 2014), 179-206.
[11] As chronicled by CrimethInc Ex-Workers Collective, “CrimethInc. : The Battle for Ungdomshuset : The Defense of a Squatted Social Center and the Strategy of Autonomy,” CrimethInc., April 7, 2021, https://crimethinc.com/2019/03/01/the-battle-for-ungdomshuset-the-defense-of-a-squatted-social-center-and-the-strategy-of-autonomy. The following description of the Youth House events relies partly on the account by CrimetInc.
[12] Anna Ringstrom, “Danish Police Battle Protesters,” Reuters, March 3, 2007, https://www.reuters.com/article/us-danish-clashes-1-idUSL0349757520070303.
[13] Kate Connolly, “Tearful Protesters Fail to Save Historic Centre,” The Guardian, March 6, 2007, http://www.theguardian.com/world/2007/mar/06/topstories3.mainsection.
[14] Shepard Fairey, “Obey Copenhagen Post 2 (Bad),” Obey Giant (blog), August 12, 2011, https://obeygiant.com/obey-copenhagen-post-2-bad/.
[15] Brooks, Rushe, and Eriksen, “Shepard Fairey Beaten up.”
[16] Fairey, “Obey Copenhagen Post 2 (Bad).”
[17] Ibid.
[18] Peter Schjeldahl, “Hope And Glory,” The New Yorker, February 23, 2009, https://www.newyorker.com/magazine/2009/02/23/hope-and-glory.
[19] Shepard Fairey, “Thank You, from Barack Obama!,” Obey Giant (blog), March 5, 2008, https://obeygiant.com/check-it-out/.
[20] Kant, “Toward Perpetual Peace: A Philosophical Sketch,” 67.
[21] “Targeted killing” using drone airstrikes is arguably state assassination by another name. Thanks to Tim Carter for helping me clarify my argument here.
[22] Christi Parsons and W. J. Hennigan, “President Obama, Who Hoped to Sow Peace, Instead Led the Nation in War,” Los Angelses Times, January 13, 2017, http://www.latimes.com/projects/la-na-pol-obama-at-war/.
[23] See, for instance, Joshua Reeves and Matthew S. May, “The Peace Rhetoric of a War President: Barack Obama and the Just War Legacy,” Rhetoric and Public Affairs, Vol. 16, No. 4, 2013, pp. 623-650.
[24] For an excellent discussion of this term in relation to the task of art history, see James Day, “Review Essay: Art History in Its Image War: Ten Recent Publications on Image-Politics in Relation to the Possibility of Art Historical Analysis,” The Nordic Journal of Aesthetics 24, no. 48 (2015), doi:10.7146/nja.v24i48.23071.
[25] Iain Boal, T. J. Clark, Joseph Matthews, and Michael Watts (Retort), Afflicted Powers: Capital and Spectacle in a New Age of War (New York: Verso, 2005), 19.
[26] See Guy Debord, Comments on the Society of the Spectacle, trans. Malcolm Imrie (London ; New York: Verso, 1990).
[27] Fairey, “Obey Copenhagen Post 2 (Bad).”
[28] See Ian G. R. Shaw, “The Urbanization of Drone Warfare: Policing Surplus Populations in the Dronepolis,” Geographica Helvetica 71, no. 1 (February 15, 2016): 19–28, doi:10.5194/gh-71-19-2016.
[29] Mark Neocleous, War Power, Police Power (Edinburgh: Edinburgh University Press, 2014).
[30] Ibid., 90.
[31] Ibid., 90.
[32] Ibid., 221n3.
[33] “The Nobel Peace Prize 2009,” NobelPrize.Org, accessed February 2, 2021, https://www.nobelprize.org/prizes/peace/2009/press-release/.
[34] Stephanie Busari and Claire Barthelemy, “Obama Peace Prize Win Polarizes Web,” CNN World, accessed April 21, 2021, https://edition.cnn.com/2009/WORLD/europe/10/09/obama.nobel.peace.reaction/index.html.
[35] Barack Obama, “Remarks by the President at the Acceptance of the Nobel Peace Prize” (Oslo City Hall, Oslo, Norway, December 10, 2009), https://obamawhitehouse.archives.gov/the-press-office/remarks-president-acceptance-nobel-peace-prize.
[36] Daniel Klaidman, Kill or Capture: The War on Terror and the Soul of the Obama Presidency (Boston: Houghton Mifflin Harcourt, 2012), 117.
[37] Jessica Purkiss and Jack Serle, “Obama’s Covert Drone War in Numbers: Ten Times More Strikes than Bush,” The Bureau of Investigative Journalism, January 17, 2017, https://www.thebureauinvestigates.com/stories/2017-01-17/obamas-covert-drone-war-in-numbers-ten-times-more-strikes-than-bush.
[38] Barack Obama, “Remarks by the President at the Acceptance of the Nobel Peace Prize,” December 10, 2009, https://obamawhitehouse.archives.gov/the-press-office/remarks-president-acceptance-nobel-peace-prize.
[39] Ibid.
[40] Grégoire Chamayou, A Theory of the Drone, trans. Janet Lloyd (New York: The New Press, 2015), 35.
[41] Ibid.
[42] Ina Cole, “Pablo Picasso and the Development of a Peace Symbol,” Art Times, May/June 2010, https://www.arttimesjournal.com/art/reviews/May_June_10_Ina_Cole/Pablo_Picasso_Ina_Cole.html.
[43] Tate, “Picasso: Peace and Freedom – Exhibition at Tate Liverpool,” Tate, accessed April 21, 2021, https://www.tate.org.uk/whats-on/tate-liverpool/exhibition/picasso-peace-and-freedom.
[44] Sarah Wilson, Picasso/Marx and Socialist Realism in France (Liverpool: Liverpool University Press, 2013), 131.
[45] Zvonimir Novak, Agit tracts: un siècle d’actions politique et militaire (Les Éditions L’échapée, 2015), 210.
[46] Anastasia Karel, “Brief History of Paix et Liberté,” Princeton University Libraries, accessed February 11, 2021, http://infoshare1.princeton.edu/libraries/firestone/rbsc/mudd/online_ex/paix/.
[47] Novak, Agit tracts, 210.
[48] See Otto Karl Werckmeister, Icons of the Left: Benjamin and Eisenstein, Picasso and Kafka after the Fall of Communism (Chicago: The University of Chicago Press, 1999), 78.
[49] Wilson, Picasso/Marx, 132.
[50] Karel, “Brief History of Paix et Liberté.”
[51] Novak, Agit tracts, 207.
[52] Wilson, Picasso/Marx, 142.
[53] Ibid., 122.
[54] Francis Fukuyama, “The End of History?,” The National Interest, no. 16 (1989): 3.
[55] Ibid., 4.
[56] Ibid., 18.
[57] Spencer Ackerman, “Weird, Birdlike Mystery Drone Crashes in Pakistan,” Wired, August 29, 2011, https://www.wired.com/2011/08/weird-birdlike-mystery-drone-crashes-in-pakistan/.
[58] David Cenciotti, “New Images of the Mystery Bird-like Drone Crashed in Pakistan. Taken in Iraq,” The Aviationist, September 14, 2012, https://theaviationist.com/2012/09/14/bird-drone/.
[59] Heba Y. Amin, General’s Stork (Berlin: Sternberg Press, 2020), 137.
[60] Kelsey D. Atherton, “Amazon Patent Lets Drones Perch On Streetlight Recharging Stations | Popular Science,” Popular Science, July 20, 2016, https://www.popsci.com/amazon-patent-puts-drones-on-streetlight-recharging-stations/.
[61] Kate Baggaley, “Forget Props and Fixed Wings: New Bio-Inspired Drones Mimic Birds, Bats and Bugs,” NBC News, July 30, 2019, https://www.nbcnews.com/mach/science/forget-props-fixed-wings-new-bio-inspired-drones-mimic-birds-ncna1033061.
[62] Eric Chang et al., “Soft Biohybrid Morphing Wings with Feathers Underactuated by Wrist and Finger Motion,” Science Robotics 5, no. 38 (January 16, 2020), doi:10.1126/scirobotics.aay1246.
[63] The “animal prehistory” of drone technology is comparatively well-rehearsed, see Stubblefield, Drone Art, especially chapter 4, “The Animal Remainder: Excavating Nohuman Life from Contemporary Drones.”
[64] Anthony Downey, “Drone Technologies and the Future of Surveillance in the Middle East” (interview with Heba Y. Amin), The MIT Press Reader, January 6, 2021, https://thereader.mitpress.mit.edu/drone-technologies-future-of-surveillance-middle-east/.
[65] “Drones Dazzle at Disney World in a New Holiday Show,” USA Today, accessed April 14, 2021, https://www.usatoday.com/story/travel/experience/america/theme-parks/2016/12/20/disney-springs-holiday-drone-show-starbright-holidays/95628500/.
[66] Ibid.
[67] Andrea Miller, “Shadows of War, Traces of Policing: The Weaponization of Space and the Sensible in Preemption,” in Captivating Technology: Race, Carceral Technoscience, and Liberatory Imagination in Everyday Life, ed. Ruha Benjamin (Durham: Duke University Press, 2019), 86.
[68] For an excellent analysis of Joe Biden’s drone fireworks in the shifting historical context of drones, see Caren Kaplan “Everyday Militarisms: Drones and the Blurring of the Civilian-Military Divide During COVID-19” Forthcoming in Drone Aesthetics: War, Culture, Ecology, eds. Michael Richardson and Beryl Pong, Open Humanities Press.
[69] A more recent incident in France testifies to Fairey’s continued commitment to the liberal cause and his knack for appealing to world leaders with his propaganda art. Briefly told, Fairey painted a gigantic Marianne-mural, that, in an echo of the 2011 Copenhagen incident, was destroyed by anonymous graffiti artists. See HIYA! Rédaction, “Un Crew Anonyme Fait «pleurer» La plus Grande Marianne de France! #MariannePleure,” HIYA!, December 14, 2020, https://hiya.fr/2020/12/14/inedit-un-crew-anonyme-fait-pleurer-la-plus-grande-marianne-de-france-mariannepleure/.
[70] Warner Todd Huston, “End Of a Fairey Tale: Poster Artist Says Obama’s Drones Killed ‘Hope,’” Wizbang, October 1, 2013, https://www.wizbangblog.com/2013/10/01/end-of-a-fairey-tale-poster-artist-says-obamas-drones-killed-hope/.
[71] Hunter Schwarz, “The HOPE Poster Guy is Done with Obama. And Republicans Now Have Their Metaphor,” Washington Post, May 28, 2015, https://www.washingtonpost.com/news/the-fix/wp/2015/05/28/the-hope-poster-guy-just-handed-republicans-their-ideal-metaphor-for-obamas-presidency/.
[72] For a forthcoming analysis of “late capitalist fascism,” see Mikkel Bolt Rasmussen, Late Capitalist Fascism (Cambridge: Polity Press, 2022).
[73] See for instance the self-declared international movement “Birds Aren’t Real,” which absurdly claims that all birds are government-controlled drones. Whether or not these “activists” are serious about their claims is hard to tell.
[74] Simone Browne, Dark Matters: On the Surveillance of Blackness (Durham: Duke University Press, 2015), 8.
[75] James Baldwin, “A Report from Occupied Territory,” July 11, 1966, https://www.thenation.com/article/archive/report-occupied-territory/.
[76] I would like to thank the two anonymous reviewers for their thoughtful comments and insightful criticisms that have helped me greatly improve this essay.
_____
Works Cited

a review of Anustup Basu, Hindutva as Political Monotheism (Duke, 2020)
This article was peer-reviewed by the boundary 2 Editorial Collective.
“In studying its (Hindutva as political monotheism) long genesis, my objective is not to advance toward a prognostic reading of the present…My purpose will instead be to explore, with some degree of speculation, the ground of the present.”
(Anustup Basu, Hindutva as Political Monotheism, 10)
The sentences above are crucial for approaching the novelty of Anustup Basu’s approach in his monograph Hindutva as Political Monotheism. Studies of Hindutva usually focus on its historical geneses, its sociological impact, and its anthropological dimensions.[1] Basu’s monograph is a path-breaking attempt to trace its genealogy as a political monotheism. This effort, he says, is not “a presentist elaboration of what we are witnessing now, but a deep search of its (Hindutva’s) historical origins” (2). The key analytical optic he deploys to understand Hindutva as a political monotheism, as an ideology that seeks a “unifying ethnocultural consistency rather than a theological unity,” and as “a monotheme of religiosity rather than religion itself” are the works of the hard-right thinker and one-time Nazi jurist Carl Schmitt (5). Schmitt’s theses on the concept of the political assists Basu in drawing out a “tacit monotheistic imperative in European organic theories of religious and ethnocentric nationhood” that he explores in detail in his first chapter (5). This monotheistic impulse utilizes the colonial epistemological category of “Hinduism” to invent it as a “jealous” political and national identity that eventually colonizes the apparatus of the post-colonial state. In an introduction and four subsequent chapters, Basu traces the development of this monotheistic impulse as a literary and cultural project in the nineteenth and twentieth centuries to its eventual replacement by “Hindutva 2.0”—an advertised and informational experience of urban modernity—in the contemporary period. Basu does not conduct this inquiry by presenting a chronological narrative of the development of core Hindutva ideas; rather, the word “speculation” in the epigraph above signals his eclectic and creative juxtaposition of multiple primary sources to trace a genealogy of Hindutva as a political monotheism.
Hindutva as Political Monotheism (henceforth Hindutva) locates the search for a fully developed political monotheism in India in relation to two dimensions of inquiry. The first is the colonial epistemological invention of “Hinduism,” the larger arcs of modernity in India, and the drafting and implementation of post-colonial India’s constitution in 1950. The second places the contemporary rise of Hindutva within the broader global crisis of liberalism and the concomitant rise of ethic-national chauvinisms. Two conceptual terms serve as touchstones in the four chapters. The first is axiomatic that is derived from William Connolly’s work on American evangelical-capitalism in Capitalism and Christianity, American Style (2008). The axiomatic, Basu writes, is a “singular religious passion that does not necessarily depend on theological consistency” (5). This observation connects with his argument broached earlier that Hindutva is more about religiosity than about religion per se. He further specifies that the axiomatic is “a techno-social regime of governmentality than simply a theologico-pastoral formation” (5). The second term is parabasis, which he draws from Gayatri Spivak’s Critique of Postcolonial Reason (1999). This term emerges from classical Greek theater and refers to the duration in the play when the actors leave the stage, and the chorus addresses the audience. Basu deploys parabasis to explore the “historical roots of a relatively recent voice of a wider urban consensus beyond usual suspects such as the ardent disciple of (M.S.) Golwalkar or the angry foot soldier of (Narendra) Modi” (9).[2] This urban consensual voice, while constituted by dissonant timbres, converges in crucial aspects to consolidate and sustain “the increasing metropolitan revision of regional eccentricities and the fervor for security and techno-financial growth” (10). The genealogical precedents and rise to prominence of this “electronic Hindu political monotheism,” which surpasses the older impasses of print capitalism, is the central knowledge-object Basu focuses on in Hindutva.
Chapter One—“Questions Concerning the Hindu Political”—lays the theoretical foundations by elaborating some key concepts from Schmitt’s The Concept of the Political (2007) and Political Theology (2006). The key extension that he makes to Schmitt’s vitalistic conceptualization of the political as the realm defined by the friend-enemy antagonism is by reading it as a “fundamentally monotheistic calling” and not via the German thinker’s observation that all secular concepts are at their base sublimated religious ones (14). This austere notion of the political is a “mythopoetic automaton” that enables the imagination of a unified people and the state only after having “categorically distinguished the believer from the infidel” (14). This “passion” is monotheistic by “secular transposition, because it has to be a singular impelling of devotion to the nation and the state” (14). In the colonial/post-colonial Indian context, this monotheism is conceived by the Hindu right as constitutively Hindu, an axiomatic that is then opposed to rival monotheistic axiomatics like Islam and, to a lesser extent, Christianity. A fiction of a primordial, prepolitical Hindu India is, thus, disseminated which has supposedly survived and persisted despite Islamic, and later, British colonization of what is now a nation-state.
Basu states that he isn’t interested in an “instrumental” reading of the Indian context in Schmittian terms (23). Schmitt’s theorizations are not used as a mechanical explanatory model applied to the Indian context; rather, his “sparse” invocation is useful in highlighting three important themes of particular pertinence to nation-thinking and imaginaries of sovereignty: “the modern understanding of religion, the romance of the past, and the concomitant monotheistic imperative of political theology” (14). Basu is interested in mining the connection between Schmitt’s notion of the political and Hindutva for three specific reasons. First, there has been a consistent monotheistic impulse in the discursive invention of “Hinduism” from the nineteenth century onwards. The Abrahamic cast endowed to Hinduism from that period paves the way for its consolidation as a political and nationalist identity that desires the state form. Second, Hindu nationalism is thoroughly Eurocentric and Orientalist at its core, a fact underscored rather risibly, as reported in the news portal The Wire (2021), in a recent revision to the history curriculum of Delhi University where the Mughal emperor Babur’s entry into India is termed “invasion” while the East India Company’s rule is couched under the more benign term “territorial expansion.” Third, when Hindu nationalism became institutionalized as a political movement in the 1920s and 30s, it was directly influenced by European fascisms and Herderian romantic-organicist formulations (17). But what makes Schmitt particularly relevant to Basu’s project is his identification of the passion of “jealousy” as the core of the monotheistic distinction between friend and enemy in the realm of the political. This passion facilitates the imagination of a Hindu India as “an organic whole rather than an associational pact” and is often summoned to judge the contrarian pressures of regionalism or to condemn secularism and federalism in the Indian context (151).
Let us tarry with some of the distinctive features of Basu’s reading of the passion of “jealousy” in Schmitt awhile. In The Concept of the Political, Schmitt argues that the friend-enemy distinction is the central antagonism in the political sphere. Given Basu’s focus on “grounds,” it is crucial to note the way he distinguishes Schmitt’s friend-enemy antagonism and its relation to sovereign decisionism from the Hobbesian model of decisionism. Hobbes begins from the contractualist fiction and not the primordial time-space that precedes the contract. In contrast, for Schmitt, this primordial is the settlement of the question of friend and enemy. Thus, the friend-enemy antagonism and its settlement prior to social contracts or associations constitutes the very grounds of the political. Basu writes:
The political is decided by a primal pathology prior to self-conscious peopleness; it…has to be an already-there organic unity. It cannot be associational or contractual precisely because it must express a singular and undivided will before reason and talk can proceed. Schmitt’s political theology therefore necessarily defines the bearer of the political as a monotheistic congregation, jealous of any apostates, pagans or heretics in its midst. (18)
The passion of jealousy points us towards the chilling imperative that a war for extermination between both parties is possible at any time. The purpose of the state is to respond to this fear at every step. When the juridical resources of the state cannot fulfil this expectation, a “secular miracle” is called for—the exception.[3] This sovereign decision can either be a war against “internal” enemies or a “perpetual civil war as an index of relentless determination or purification” (18). The chilling imperatives of Hindutva as political monotheism, which can be conducted both as a war on internal enemies and a permanent civil war, echo these Schmittian postulations.
Chapter Two (“The Hindu Nation as Organism”) is the core of Hindutva. This chapter juxtaposes philosopher Bimal Krishna Matilal’s work on Indic “little traditions” with modern Hindutva’s organismic invented “grand” tradition that attempts to subsume a massive plurality of identities via a “unifying ethnocultural consistency rather than a theological unity” (5). Basu deploys Aamir Mufti’s Enlightenment in the Colony (2007) to caution that there is no “pristine truth of pluralism” to contrast with the pristine truth of monotheism—both desires are sullied by the colonial modern. They gesture to a lost excess beyond the organizing frames of colonial taxonomies. But what is missing, Basu writes, in Hindutva discourses is the “critical admission of irony and amnesiac mourning—an understanding of the bygone as necessary fiction with a phantom aspect…” (34). This differentiates Hindutva’s monotheistic search for lost origins from the double consciousness that marks scholars like Matilal, Mufti, and, indeed, works like Hindutva itself.
In contrast to Hindutva’s modernist desire for a theistic unity and consistency in line with the Abrahamic traditions, Matilal’s works on “little traditions” show that while the numerous South Asian scriptural traditions have “involved themselves with logic and epistemology, religious duties and rituals, metaphysics and soteriology,” they have hardly ever “furnished a constitutive moral worldview” (38). This seeming lack of a constitutive, coherent moral worldview and a massive polyphony of voices within what is called the Hindu tradition has led many Western thinkers to posit that “Indian religion was inseparable from Indian mythology” (Hegel) or that there was “no concept of morality in Sanskrit” (Max Weber) (39-41). To make Hinduism “necessarily Brahminical and resolutely monolingual,” as Hindutva attempts to do, would involve the negation of the dynamic osmosis among the tremendous babble of “little traditions” into a “manufactured and jealous ‘Epic of Traditions’…in order to institute a masculine, Savarna national morality robbed of all errant and queering energies” (41). This is a project still in the making, but one which has become more prominent and public in recent times.
The other insuperable bottleneck that Hindutva faces is that of caste. While Hindutva discourse insists on the “original Varna as a recognition of merit over birth,” the questions of Jati and Varna are always complicated by plural traditions that are “artisanal, ecological, and based on everyday customs and pieties” (44-6). The problem here lies in Hindutva’s uncritical adoption of the Western anthropological category of religion itself. As Basu says, quoting Matilal: “‘The social reality [called] religion did not exist in ancient or classical India’—at least in a core, etymological root sense of the word, as reliq, or that which binds and relegates” (47). Responding to this absence, Hinduism is invented as a monotheism and as resolutely monolingual by Hindutva. The valorization of Brahminical theodicy in this monolingual reformulation is a manifestation of the desperate desire of Hindutva historicism to respond to and rectify the purported lack posited by the Orientalizing gaze of the big colonizing Other.
The tour de force in this chapter is Basu’s analysis of the “pieties” of Hindutva discourse and the problems it encounters in endowing the nation an organismic cast. For Hindutva thinkers like MS Golwalkar and Deen Dayal Upadhyay, the Hindu nation in its essence is paradoxically predicated on “terrestrial homogeneity as well as cosmogonic inequity” (32). Once this promised Hindu punyabhumi (consecrated land) is achieved via the revival of Hindu virtue:
…this nation, in its perfection, will be marked by a balanced metabolism of natural caste patrimony and a principled docility of the lower orders. Citizenship shall be defined by selfless service and sacrifice, not by individual rights and interests. The state here can only be an organic expression of an originary Brahminical peace; it may not be a profane artifice to ward off a natural state of (caste) war. (32)
This invocation of Brahminical peace and caste war leads directly to Basu’s fascinating consideration of Hindutva’s “primal origin myth” and evocation of “deep time” that he conducts via an elaboration of four themes: “Time and Origins,” “Race and Law,” “Territory, Imaginative Geography, Identity,” and “Language, Countermemory, and Culture.” I won’t go into the details of each theme but will explicate Basu’s theorization of Hindutva “deep time” through a contrast with an interesting moment in a well-known South Asian fictional text. Nirmal, a central character in Amitav Ghosh’s The Hungry Tide (2006), tries to explain how he will attempt to communicate the vastness of geological timescales to a group of rural children in Bengal:
It’s not just the goddesses—there’s a lot more in common between myth and geology. Look at the size of their heroes, how immense they are—heavenly deities on the one hand, and on the other the titanic stirrings of the earth itself—both equally otherworldly, equally remote from us…And then, of course, there is the scale of time—yugas and epochs, Kaliyug and the Quaternary. And yet—mind this!—in both, these vast durations are telescoped in such a way as to permit the telling of a story. (150)
Nirmal’s homology between myth and geology shows how the vastness of geological time is conceptualized by different epistemological formations in varied yet comparable ways. As the medievalist Jeffrey J. Cohen (2015) writes—“Every historical period works with the conceptual tools it inherits but is never bound by that heritage to the replication of that which is already known” (83). Nirmal seems to intuitively understand the connection between such different epistemological attempts at comprehending the vastness of temporal scales. He uses this understanding and tries to channel it creatively towards a pedagogical goal—how to make his students grasp the vastness of the temporal scales of geohistory.
Is the Hindutva homology, or rather the erasure of the gap between myth and history the same as what Nirmal institutes between myth and geology? Time, as Basu says, in its Hindu-Aryan naissance “is geological” (49). Basu succinctly distinguishes imaginaries of temporal scale in Puranic cosmologies and the way Hindutva banalizes them for statist ends. Deep time in Puranic texts is not quantifiable in literal terms, and function as “pure magnitudes to invoke fear, shame and reverence…” (51). Such pure magnitudes create an “existential distance between humans of the present and the Dharmic exemplum” (52). Time-reckoning in the ancient era could simultaneously exist as cyclical in terms of cosmology and linear in terms of the moment of the here and now. The problem with Hindutva thinking lies in “making the two identical, and then vectorizing the whole thing in terms of statist mythography” (52). The complexities of the temporal imaginaries that so invigorate Nirmal to help his students encounter questions of geological scale is rerouted via colonial historiography by Hindutva discourse into “coarse positivisms of rise and fall” (53). Invocations of deep time in Hindutva discourse is not a contention with different timescales, but a negation of timeliness and metric history, as for example in Golwalkar’s rhetorical flourish that Hindus ruled India for ten thousand years before a “foreigner” set foot in it (54-5). Metric time and history are conceptualized as a form of rupture. The original period of Hindu glory cannot be located within temporal frameworks; instead, history begins with a curving towards Kaliyuga (end times). Secular history is a fall from a myth of origins, while the myth of the golden Hindu past exists in a time before time.
This conceptualization of deep time before historical time proper is also imagined as a period of Brahminical peace. The invocation of a mythic past in terms of Varna is necessary for Hindutva because it is predicated “in the form of a Jati revenge against Islam, not Jati parity within Hinduism” (56). The monotheme of a jealous Hindu identity ranged against rival axiomatics can only be consolidated by “foreclosing the emergence of countermemories and competing fictions of Jati identity” (56). Deploying Michel Foucault’s ideas on race war from Society must be Defended (2003), Basu argues that for this Hindu monotheme to emerge and to anticipate a possible future when this essence is restored, the link between history and caste-war must be actively denied or forgotten:
No matter how far back one goes, profane historical knowledge does not present nature, right, order, or peace for Hindutva. Hindutva’s historicism is therefore founded on an idealism that knowledge and truth belong to the order of Brahminical peace; that they cannot belong to the side of violence, miscegenation, and relentless caste war. (62)
Besides the potential extermination of the enemy and forgetting of caste war, this narrative of Hindu redemption is predicated on the concurrent remembering of an ideal Hindu subject that is “apparently different from the profane, modern one, yet one that is lost in an ever-receding past that in itself cannot be viewed other than through the prism of the modern” (86). This ideal Hindu subject, simultaneously ancient and modern, must be reinstated as sovereign among the plurality of identities in the subcontinent. This is one of the core elements of the Hindutva project.
Chapter Three—“The Indian Monotheism”—moves away from Hindutva discourse to an analysis of “normative Hinduism,” a secularized, albeit Hinduized, sensus communis that has been the bedrock of the post-colonial nation-state. This discourse of “soft” Hinduness ranges across a spectrum from “benign to sharp.” It also oscillates between a patronizing benevolence towards Islam and a paranoid hauteur directed towards the jealous monotheism of Hindutva (124). In recent decades, Basu writes, this “apparently benign Hinduness has increased its powers as a psychological parabasis for a majoritarian nation” (88). Chapter Three looks at “discursive antecedents” in the “broader nineteenth-century Indological identification of ‘Hinduism’ and the discourses of Hindu reform, Hindu anthropology, jurisprudence, and history” (7). This “benign” discursive trajectory of a Hindu monotheme has increasingly been replaced with “ritualized pathological expressions” (88). The fact that benign Hinduness and ritualized pathological Hindutva are often substitutable with each other reveal that they are secret sharers drawing from the same wellspring of the Hindu monotheme.
In terms of specifics, “The Indian Monotheism” considers a broad “constellation of moments”—the Vedantic reform of Raja Rammohan Roy, the literary moment of Bankimchandra Chattopadhyay, Sarvepalli Radhakrishnan’s universalization of the caste question, and the “pacific paternalism” of M.K. Gandhi (146). Crucial to this discursive project of a “monothematic Hindu becoming in anticipation of the nation-state” is the furnishing of “imagined communities and personages with a subjectivity and a historical agency pertinent to the overall invention of a Hindu past” (147). This occurred in several ways—the elevation of neo-Vedantic monism as a counter to the messy facts of polytheism in Hindu practices (evident, for instance, in the literary interventions of Roy), the institutionalization of the Bhagawad Gita as the holy book of the Hindu people (a reading very prominent in Bankim), and the portrayal of figures like Rama and Krishna as prophetic personages greater than Christ or the Buddha. In each case, the development of the Hindu monotheme necessitated arguments with colonial Reason and the subsumption of ambiguous and scattered elements within the ambit of “antiquarian or monumental” histories that corresponded to nationalistic desires (147). All these moments of argumentation had major differences with Hindutva—for instance, Rammohan Roy’s Hindu monism as universal religion bypassed the passion of jealousy altogether, while Radhakrishnan’s pragmatic defense of Varna differs from the theologico-cosmogonic cast that Hindutva ideologues like Golwalkar posited. What unites them though is the deep desire for a quintessentially Hindu-Indian axiomatic.
The discussion of the trajectory from Roy to Radhakrishnan is bookended by Hegel’s philosophical critique of the Gita on the one hand and B.R. Ambedkar’s critique of Hinduism on the other. Hegel’s 1827 civilizational diagnosis that the “absence of a monotheistic esprit de corps” in the Gita compromises the nation’s “security in a world of lordship and bondage,” serves as a foil for the intellectual ripostes by Rammohan Roy and Bankim (101). Much more interesting though is Basu’s discussion of Ambedkar’s Jacobin critique of Hinduism. I will highlight one aspect of Ambedkar’s radical critique of Hindu monotheism through a contrast with Radhakrishnan. For Radhakrishnan, caste became a means to contain race conflict in India. The genius of the Indian caste system, for Radhakrishnan, was the prevention and containment of race war (which was supposedly common in all societies) via a process of harmonization rather than the alternatives of enslavement or extermination (129). Caste, thus, is presented as not ontologically unique to Indian society. According to Radhakrishnan, it is a feature of all societies. It is just that it happened to be a practical and harmonious way to stave off race war perfected in the Indian context. This universalization of the caste question and its specific flowering in Indian climes produced a “democracy of spirit,” although it was not amenable to the accumulation of wealth or political power (129).
Ambedkar, Basu says, rejects the “naturalistic, race-based exoneration” of caste in the Gandhi-Radhakrishnan trajectory of Hindu reformism. The caste imaginary’s strict adherence to notions of purity and endogamous marriage went against a phenomenology of biological race—a fair-skinned lower caste person would still be ostracized while a dark-skinned Brahmin would not (136). From a political economic perspective, caste was not division of labor, but “a calibrated division of laborers” that could not be encompassed by economism alone (137). The essence of caste does not depend on a naturalistic explanation but is a “sublimation in time” (137). It shifts and mutates in a historical field “pertaining to shifts in custom, culture, production, theology, or the aesthetics of self-making” (137). Caste discrimination was a disciplinary framework that combines “a libidinal economy of desire with a political one of interest” (140). This notion of disciplining the caste other is fundamentally inimical to the idea of democracy that Ambedkar draws from his teacher John Dewey—“…a mode of associated living, of conjoint communicated experience” (142). The problem with Indian nationalism, suffused by reformism of the Gandhi-Radhakrishnan type, is that it short-circuited social revolution in favor of a political one (143). In doing so, “soft” Hinduism suffused with the “lure of temperate Brahminism” became the raison d’etre of the post-colonial state. This constituted the “parabasis of the new Hindu normal” whose affective power rendered the “Indian constitutional revolution passive by foreclosing a constitutional morality” (145). Hegemonic Indian nationalism viewed the spiritual work of the nation as already complete millennia ago—all that was necessary was reform and revival (149). Rare exceptions like Ambedkar and Rabindranath Tagore, whom Basu considers briefly at the end of this chapter, went against the grain of this Hindu-normative common sense.
Chapter Four—“Hindutva 2.0 as Advertised Monotheism”—considers Hindutva monotheism from the other end of the temporal spectrum: “in terms of millennial mutations in the era of information and globalization” (7). This chapter is a return to familiar turf for readers familiar with Basu’s earlier work on film and media cultures. The two key conceptual terms in this chapter—“Hindutva 2.0” and “advertised modernization”—fuses the analysis of contemporary media ecologies with considerations of affect. Thus, the assemblage of Hindutva 2.0 presumes a “neuropolis of populations” and sustains itself on “industrialized instincts of jealousy and anxiety” (166). As a mediatized phenomenon, predicated on the rapid proliferation of cellphones, the internet and digital technology, it does not depend on some of the established avenues of modernity like newspapers, books or university spaces. It is not dependent on “traditional” orders like shakhas or temples either. Instead, it works “primarily by way of loose, fungible distributions of affect, spectacle and…the substance of the advertised” (158). In an age of Whatsapp forwards, or what is colloquially called the “Whatsapp University,” it hollows out historical consciousness and reduces it to the syncopated form of a meme or a short message that can be forwarded virally. Hindutva 2.0 also establishes new synergies between “being Hindu and neoliberalism, one taking place on a plane of marketable desires and terrors” (158). In doing so, it spreads both soft and hard versions of the Hindu normal across the entire digital spectrum.
The other key term—advertised modernization—draws on trajectories of affect studies that point towards “a neuropolitics of the twenty-first century in which multidirectional stimulations, attention spans, diversions, ennui, or boredom become potent political factors” (180). “Advertised” is a conceptual metaphor which goes beyond questions of truth and falsehood; instead, it renders “an innocuous ‘take away,’ a ‘feel good’ sensation, or in some cases, a consumable fear” (180). In such an advertised scenario, which is also necessarily majoritarian, there is “no narrative obligation to truth or closure”; rather, it is the affect it evokes and the sense of belonging it creates to a particular brand that counts (180). Probably its most well-known global manifestation in recent times is the “pure gesture” of the Trumpian lie. As is obvious, most of what Trump (or Modi) utter in public can be debunked with minimal fact-checking; yet, for the devout Trump or Modi follower, they operate as “pure gestures advertising a new covenant between tradition and modernity, rather than as dialectical matters of an Aristotleian politics aimed at virtue…” (181). The Trumpian statement itself may be outrageously false, but it comes straight from the heart for legions of acolytes.
The Trump-Modi performatives also thrive in a changed scenario of the advertisement. The older model of the fifteen to thirty second advertisement emerging from “vertical models of mass culture” is passé. What has taken its place is an “order of convergence marked by nondirectional flows between platforms, instant audience migrations, and corporate cooperation” (181). In this changed scenario, political campaigning itself becomes interactive and is constituted by feedback loops and the processing of data that occur 24/7—consider here, for instance, the use of holograms and selfies during Modi’s 2014 campaign. The political personality becomes a brand that proliferates across a wide mediaverse circumnavigating a multidirectional circuit of affect. Branding, in Basu’s words, “becomes a matter of controlled chaos, leveraged in order to achieve critical densities of affect, recall value, or regularities of reference” (182). In this altered mediascape, the monotheme of Hindutva does not operate through a straightforward invocation of jealousy against the infidel; instead, congregations of believers coalesce in “virtual affinity spaces” that cut across older divides of city and country.
Basu also provides a contrast between two different historical constellations to outline the specificity of Hindutva 2.0. This contrast is set up through his discussion of the journalist Akshaya Mukul’s book Gita Press and the Making of Hindu India (2015) at the beginning of the chapter. Mukul’s fascinating book received a fillip when he came across the “Poddar papers,” a massive archive of correspondence, pamphlets and manuscripts by, on or written to Hanuman Prasad Poddar, who along with Jaydayal Goyandka founded the Gita Press in Gorakhpur in 1923. Mukul writes:
As Gita Press stands within striking distance of a century, the only organization that may be said to parallel its success is the Bible Society. No other publishing house in India has marketed religion so successfully. (430)
Through cheap editions of Hindu religious texts in multiple languages, its Hindi monthly Kalyan (first published in 1927) and its English avatar Kalyana-Kalpataru (first published in 1934), Gita Press made deep inroads throughout India, even into Hindu homes that wouldn’t identify necessarily with Hindutva. Espousing conservative upper caste-Hindu values and functioning as a foot-soldier of the Sangh Parivar, despite its claims that it maintains a safe distance from politics, Gita Press also managed to get a wide spectrum of notable figures of varying ideological proclivities, ranging from Golwalkar to Gandhi, to write for Kalyan. The notable absentee unsurprisingly was Ambedkar, a figure Kalyan was scathingly critical of. Often deploying what Basu calls a “paranoid style” (155), Gita Press at various times has also effectively deployed the language of hate and insular religious identity.
While Gita Press is still influential, Basu extensively discusses Mukul’s book to show how Hindutva 2.0 is a massive shift in amplitude in the era of new media forms and the neoliberal order. This is especially evident with the rise of Narendra Modi as a media phenomenon—a process that demonstrated “the advertised realignment of tradition and modernity” for a “virtual Hindu congregation” (182). In this new distributional matrix of information, the divergent energies constituting the virtual Hindu congregation could touch the “Brahminical sensible” [a term Basu reworks from Jacques Ranciere’s idea of the distribution of the sensible from Dissensus (2015)] at various points without being subsumed within a monolingual Hindutva discourse. Basu concretizes the difference between Hindutva 2.0 and the older model of print capitalism thus:
That older revivalist discourse, as have seen in the case of Gita Press…struggled to subsume the modern disciplines and the physical sciences into an apex Hindu vision. It had to world the caste question afresh in an altered universe of rights, freedoms and irreverent democratic tempers. It attempted, at every turn, to reconcile mythology with history, science and realism, or theodicy with justice. Such discursive efforts—rarely sublime, often ludicrous—have had a long history and continue to this day. However, in this new ecology, they acquire fresh powers of particularization and shooting through. (183)
The neuropolitical dimension in this new informational ecology enables the collapse of traditional distinctions between city and country and epistemologies like Vedic cosmogony and astrophysics. The public this ecology subsumes can react in a variety of ways within the frame of this Hindu normativity—ranging from indulgence to outright dismissal, from neurosis to humor. But the key difference between this moment and the “traditional” print capitalist one, as Basu says, is that “it can bravely ‘touch upon,’ without obligation, many matters that traditional Hindu nationalist discourse has either avoided or approached gingerly” (183).
In a broader spectrum of culture, advertised modernity is also evident in the shifts in the fantasy machine of Bollywood in the era of neoliberalization. Basu’s earlier work on the “geo-televisual aesthetic” (2010) is particularly relevant here in mapping these shifts.[4] On the one hand, post-1990 Bollywood films are marked by the gradual disappearance of the rural sphere, the poor, Dalit or Muslim character, and an obliteration of what film scholar Ranjani Mazumdar (2007) calls, the presence of the street; on the other hand, we notice the gradual rise to prominence of what Mazumdar calls the “lifestyle mythology” of the urban elite (143). Basu argues in Hindutva that advertised modernization operates at “the level of colors, saturations, textures, magical transportations, luminosities, and sonorous resonances” by which the “new, urban Hindu elite…[presents]…its life and aspirations as artwork” (191-2). Vedic and Puranic cosmologies exist side by side with a muscular patriotism and an open (and opulent) celebration of right-wing mythologies as in Sanjay Leela Bhansali’s controversial film Padmavat (2018).
The underside of this glossy normative Hindu advertised fantasy is the proliferation of gritty, stylish films usually about Bombay’s underbelly. The “encounter” film—which revels in vigilante justice and extrajudicial killing meted out to characters from the underworld—has become a sub-genre in its own right. Basu reads it as a symptom of a persisting fascination with sovereign decisionism and of vigilante violence (especially against Muslims and Dalits, phenomena that spill from reel to real life) in the Indian context. A good example here would be Shimit Amin’s 2004 noir film Ab Tak Chappan (Till Now Fifty-six), which valorizes the life of the “encounter specialist” of the Mumbai Police Force, Daya Nayak. The title refers to the “encounter score” of fifty-six extrajudicial killings that Nayak purportedly participated in.
This acceptance of extrajudicial violence, of course, is not a new phenomenon in Indian public life as the long and controversial histories of legal instruments like the AFSPA (Armed Forces Special Powers Act) and TADA (Terrorist and Disruptive Activities Act) easily illustrates. What the contemporary “encounter” film does though is to stage the majoritarian desire for sovereign decisionism with a “cool” dressing of the gritty, seductive style of noir. At the level of cultural fantasy, the proliferation of such films signals two things. First, it “presents a metropolitan caste Hindu existence as the only form of life worth living” (199). Islam enters this cultural fantasy only when assimilated into “an overall civic religiosity of the (Hinduized) market” as in the celebration of figures like former President APJ Abdul Kalam or the three superstar Khans—Shahrukh, Aamir and Salman—of Bollywood (199). Otherwise, the Muslim is completely othered. Second, such fantasies also present the “urban caste Hindu existence as the only secure form of life worth living” (200). In this variation of the fantasy, the Muslim becomes the security threat against which society must be defended. As Basu writes, this “perception of Islam as an absolutist ethics is important for the cult of the encounter because it authorizes the state to respond with fearful symmetry and an instant theodicy of its own” (200). The bleed between reel and real could not be more chilling than this.
No account of the urban Indian fascination with sovereign decisionism can be complete without reference to the current Prime Minister Narendra Modi. In one respect, Modi represents the open vocalization of certain desires that lay immanent before 2014: the fascination with a strong leader, alternative history scenarios where Vallabhbhai Patel or Subhash Chandra Bose led India instead of the “soft” Nehru, and the long-standing admiration for Hitler’s works in many middle-class Indian homes. Basu’s focus, however, is only incrementally with the personality of Modi and more with the images projected of Modi as a media phenomenon. What interests Basu is how the new “congregational plane” of advertised modernization “animated by instantaneous and wide dissemination” effectively negated an old truism about India as a coalition at the altar of Modi’s charismatic aura. At another level, this proliferating form of advertised modernization also brought together two elite urban population categories that had hitherto remained apart. Basu calls these two population subsets the Gentoo (the colonial term for “Hindu” that draws on the Portuguese gentio—pagan) and the Dehat (the Hindi term for rustic). The Gentoo is the technocratic elite enamored with neoliberal development. Within this category there is a spectrum of possibilities: the Gentoo wedded to hard Hindutva, the Gentoo who imagined the metropolitan good life as indistinguishable from Hinduness, and finally, the secular-neoliberal who conditionally supported Modi’s economic “reform” persona without going the whole hog with his cultural nationalist project. The Dehat, on the other hand, was the vernacular elite that emerged from the rich farming and privileged caste groups.
Before 2014, at best only a provisional and uneasy Gentoo-Dehat coalition could be imagined. The media phenomenon that Modi became from around 2006 onwards with the celebration of the mythologized “Gujarat model of development” brought these two subsets together on the congregational plane. For the Gentoo especially, “Modi was a Dehat who could talk the talk of the Chicago boys and talk it well” (173). The public personality of Modi that was projected coalesced the images of the neoliberal messiah who would turbocharge the Gentoo model of development, the “strong” and decisive Hindu leader who would not compromise on national security against internal and external enemies, and the “saintly” man of sewa (service) who rose above petty politicking and remained untouched by the profanity of corruption. This could not have happened without the new media ecology that was “marked by speedy informational flows and feedback loops independent of traditional institutions of news and veracity” and where “one could freely disperse affects and expressions without disciplinary enunciation or narrative form” (170). In short, Hindutva 2.0 as advertised monotheism.
Hindutva is an eclectic and multidimensional work that makes major interventions in multiple knowledge-fields like media and cinema studies, religious studies, postcolonial studies, South Asian studies, studies of nationalism and affect studies. Readers of Carl Schmitt can also deploy Basu’s reading of “jealousy” to read the mutation of the German thinker’s later work such as his theorization of the “absolute enemy” in The Theory of the Partisan (2007). Schmitt’s work, written in the wake of guerrilla movements and anticolonial revolutions during the Cold War period, prefigures how the contemporary juridical category of the “terrorist” envisaged as a figure relegated outside the sphere of the law, follows the tracks of earlier legal categorizations like “pirate” or “guerrilla.” Schmitt’s underlying argument that the contemporary partisan (or “terrorist”) is no longer an enemy, but a “satanic pursuer” who attempts to create ex nihilo (quoted in Ulmen 2007, xviii), would be useful to analyze via Basu’s categories of the passion of jealousy and its relation to the primordial settlement of the political.
Moreover, while anchored strongly in the Indian context, Hindutva also has global relevance. While analyses of phenomena like the Trumpian lie clearly illustrates the broad reach of Basu’s work, his conclusion clearly shows how the insights of Hindutva can be utilized to contend with our current global conjuncture. I highlight one passage from the conclusion as an illustration:
In a world dominated by a cartel of international banks, a transnational plutocracy, and North Atlantic military powers and their constable states, the nation is no longer the seat of those two immense themes of the liberal tradition: self-determination and the rights of the people. Yet paradoxically, and perhaps precisely because of this, the nation has to be defined as a progressively more insular cosmology of justice. It has to be relentlessly purified and made to close in upon itself; the country has to be at once achieved and repeatedly taken back. (206)
This paradoxical movement of simultaneous achievement and the repeated taking back of the spectral nation is not limited to Hindutva 2.0 and the rise of Narendra Modi alone. With proper contextualization, these insights can also apply to Trumpian America, Bolsonaro’s Brazil, Duterte’s Philippines, Orban’s Hungary, Putin’s Russia and Erdogan’s Turkey among others. Indeed, as Basu writes, twenty-first century “fascism is about focalizing…intense localisms and threading them into a nationalist politics of rage and revenge banks” (206). The strongman (and it is usually a man, with Marine Le Pen one of the exceptions) is he who cuts through the patina of incessant talk (what Schmitt in an earlier Fascist conjuncture criticized about procedural liberalism) by monopolizing widespread public skepticism about corruption and about information culture. He promises to replenish the masculinity of the nation by simplifying discourse and identifying the enemy clearly.
That said, I advance one critique of Hindutva from my own location as a scholar of the borderland region of Northeast India. While I grant that Northeast India isn’t the focus of Hindutva, there is a missed opportunity here for framing a more complicated account of the political in the South Asian context. In the first chapter, Basu writes that the specter of the concentration camp “hovers around the National Register of Citizens (NRC) project that the present Hindu nationalist government in India has reactivated in the Indian northeastern state of Assam” (19). I do not disagree that the ruling BJP (Bharatiya Janata Party) has weaponized the NRC as a pan-Indian phenomenon, and that detention centers are a grim reality in Assam today. But the word “reactivated” above, to use Basu’s own terms against himself, seems to make Hindutva the only player in town in Assam (204). The BJP is a relative late entrant into the NRC process. The genealogy of the NRC predates the BJP becoming a major player in this borderland state and has to be located in the complex politics of what the political essayist Sanjib Baruah in In the Name of the Nation (2020) calls a “settlement frontier” of the erstwhile colonial state (47-75). As Ornit Shani (2018) writes in her book on the creation of independent India’s first set of electoral rolls:
In Assam…ethno nationalist attitudes manifested particularly towards the non-Assamese ‘floating population,’ many of whom are Bengali speaking Hindus from East Pakistan. Local authorities expressed a view of membership from a state that was defined by a descent group and delimited to ‘children of the soil,’ who were eligible to have full rights. Thus, ethno nationalist conceptions were not necessarily on the basis of religion. (72)
This long history shapes the institutionalization of the NRC as a discriminatory citizenship regime. These facts show that the grounds of the political in such borderland contexts are not exclusively determined by religious binaries and its attendant passion of jealousy familiar to scholars of mainland South Asia.
To be sure, there have been synergies between ethnonationalism and Hindutva in recent times. But the completion of the NRC process also reveals the faultlines between Hindutva and ethnonationalist politics. When the NRC was published in 2019, for instance, the BJP was disappointed that many Hindus were included in the list. They have recently promised a new, updated NRC. This faultline between Hindutva and ethnonationalism has hardened with the implementation of the CAA (Citizenship Amendment Act) in December 2019 which proposes to give citizenship to Hindu refugees, even though the BJP went on to win a majority in the state elections in 2021. None of these complexities are however mentioned in Basu’s account. In fact, in footnote twenty-five of Chapter One, the only source Basu cites about the NRC is an NPR report. He also writes in that same footnote that after “lying dormant for decades, it (the NRC) became politically relevant once more after Modi came to power” (213). Anyone familiar with Assam’s political scenario would be quick to point out that this discourse has not been dormant in the region at all, and that while Modi’s coming to power may have made it visible to mainstream Indian political discourse, the Northeastern borderlands have long been wrestling with this issue prior to 2014. In comparison to the eclectic historical and theoretical sketch of Hindutva, one is left wishing for a more complex rendering of the political in a borderland space such as Assam in this portion of Basu’s book.
By way of a conclusion and drawing further from my own location in Northeast Indian studies, I initiate a brief conversation between Basu’s book and another major book on Hindutva that was published recently: Arkotong Longkumer’s ethnographic study The Greater India Experiment (2021). Hindutva is essentially correct, I think, in drawing a genealogy of an urban Hindu normativity. But what about Hindutva’s spread in locales beyond the Gentoo-Dehat urbanscape, especially in places that have been to a large extent inimical to the idea of India such as the borderland Northeastern region? In his fascinating discussion of Hindutva worldings in the Northeastern region, Longkumer shows how within the larger monotheme of Hindu religiosity that Basu identifies, actual Hindutva practices are defined by shape-shifting and flexible positionalities as it tries to draw the divergent cosmologies of “tribal” religions within its fold. Of particular interest here is how Hindutva actors in Northeast India deploy the language of global indigeneity, polytheism and paganism to show connections between indigenous religions in the region and Hinduism. For instance, Longkumer writes that a 2005 BJP party document titled “Evolution of the BJP,” draws on the works of anthropologists on local and global aspects of indigeneity to argue that:
…paganism relates, crucially, to local gods and ancestors of the land based on ideas of polytheism…In summing up the basic overlap between paganism and Hinduism, the BJP text says: ‘In a sense at the basic level Hinduism is a pagan religion. As Paganism allows for evolution Hinduism too allows for evolution. Since Paganism is belief in many Gods there is generally no fight over Gods. This is the greatest virtue of Polytheism…Once Hinduism is expressed along these lines, then, it has the potential to relate with other native traditions that are intimately connected to land. (115-16)
While Hindutva proselytization in Northeast India is still an ongoing and contested process, such sentiments about polytheism are often invoked by Hindutva activists on the field to contest the animosity that monotheistic faiths like Christianity display against “pagan” and animist belief systems. An urban Hindu monotheme that has become dominant with advertised modernity and a flexible deployment of polytheism as a proselytizing strategy in the borderlands—these are two torn halves that do not constitute a whole, but gesture towards a larger and still developing story of why Hindutva has become the dominant political discourse in India today.
_____
Amit R. Baishya is Associate Professor of English at the University of Oklahoma. He is the author of Contemporary Literature from Northeast India: Deathworlds, Terror and Survival (Routledge, 2018) and the co-editor of Northeast India: A Place of Relations (Cambridge University Press, 2017), Postcolonial Animalities (Routledge, 2019), and a special issue of the journal Postcolonial Studies titled “Planetary Solidarities: Postcolonial Theory, the Anthropocene and the Nonhuman” (2021-22).
_____
Notes
[1] For examples, see Jaffrelot (1995); Hansen (1999); Vanaik (2017).
[2] M.S. Golwalkar (1906-73) was a prominent early ideologue of the RSS (Rashtriya Swayamsevak Sangh), the apex body in what is called the “Sangh Parivar.”
[3] Schmitt’s views on the connection between exception and miracles comes out most clearly in his reading of Chapter 37 of Hobbes’ Leviathan in The Leviathan in the State Theory of Thomas Hobbes (1996). Schmitt says—“A miracle is what the sovereign state authority commands its subjects to believe to be a miracle; but also—and here the irony is especially acute—the reverse: Miracles cease when the state forbids them” (55).
[4] Basu defines the geo-televisual as a cinematic idiom that emerged from the mid-90s onwards and which cannibalized and combined heterogenous elements (MTV, video games, international travel, spiritualism et al) in a “fungible yet sensuous style—one that begins to operate at the level of the tissue and the nerve” (7). We notice an early intimation of the neuropolitical here.
_____
Works Cited

a review of Jed Rasula, History of a Shiver: The Sublime Impudence of Modernism (Oxford, 2016) and Acrobatic Modernism from the Avant-Garde to Prehistory (Oxford, 2020)
by Nathan Brown
This essay has been peer-reviewed by the b2o: An Online Journal editorial board.
Jed Rasula’s doctoral dissertation, submitted in 1989 for a Ph.D. in History of Consciousness at UC Santa Cruz, is titled “The Poetics of Embodiment: A Theory of Exceptions.” His forthcoming book with Oxford University Press is titled The Lower Frequencies: Genre and Extravagance in the Novel. From exception to extravagance: that relay offers an apt resumé of Rasula’s critical oeuvre, which has been consistently devoted to the discrepant, the illegible, the exorbitant, the eccentric, and the superfluous. Rasula’s first critical book, The American Poetry Wax Museum, studies the “reality effects” of anthologization and canon formation from 1940-1990. But while this is indeed a work of literary history and sociology, it amounts to a reckoning with the metaphysics of genteel cultural coercion, a study of “canontology” as that which signifies “the criteria for existence—the modes of being and appearing” that are stipulated by canons (471).
Rasula is himself an anthologist of another stripe. Imagining Language (MIT, 2001), coedited with Steve McCaffery, convenes a vast assembly of linguistic deviation, experiment, and expansion across three millennia, organized conceptually and thematically so as to produce discordant congruities brought into theoretical and contextual focus by rigorously rhapsodic section introductions. Burning City: Poems of Metropolitan Modernity (Action Books, 2012), coedited with Tim Conley, assembles a vertiginous array of efforts by international modernists to include the cacophonous provocations of urban experience within the field of the poem through parataxis, visual forms, and aural effects. These are anthologies that do not reproduce canontology but rather explode its parameters.
It is in his book This Compost: Ecological Imperatives in American Poetry (University of Georgia Press, 2002) that Rasula goes farthest toward undoing distinctions between the roles of literary critic, anthologist, and poet. The book traverses the sweep of American poetry from Whitman through Pound, Olson, and Zukofsky to such contemporary figures as Susan Howe, Nathaniel Mackey, and Rachel Blau DuPlessis, while referring to dozens of poets along the way. As it does so, This Compost deploys a unique style of quotation whereby texts are woven together in compound threads, constructing associative bonds between passages from different poets distinguished only by a tilde (~), with names and titles cited sequentially in endnotes. Amid these we find passages of Rasula’s poetic prose, distributed across subsections of a continuous essay and thinking with rather than interpreting the poetry—drawing out conceptual, historical, imaginative implications and consequences with often startling lucidity:
The peculiar skill of any art is in making all that is available of itself be surface; even its depths (like the picaresque profundities of Moby-Dick) are disclosed only as surface events. This puts writer and reader on more or less equal footing, because although each has a different approach to the text, once the text is in place the surface it makes available is haunted or shadowed by an obverse, the obvious perversity by which it affords glimpses of eaches and anys where every and all appear to lurk. Both sides are never visible at once, although a fundamental tropical urge is to make both sides available in such rapid succession that, like a coin trick, a continuity of the alternating surfaces blends into one demonic animated texture that is posed as identity and surplus indistinguishably. (71)
In This Compost, it is as though the surfaces of poems had descended into the darkness of the underworld along with their reader (or wreader, as Rasula sometimes writes, emphasizing the co-implication between reading and writing) before emerging once more into the light, now transfigured by their passage into possibilities of relation they always harbored among themselves.
Rasula’s work cannot be subsumed under a “methodology,” but if there is one word that captures the enabling condition of his mode of thought it would modernism. The exceptions his work theorizes and the extravagance it displays are akin to the exteriorizing force of modernist rupture, to the self-surpassing energies that go by the name of modernism and continue to agitate the present. Imagining Language delves into three thousand years of the archive, but the inspiration for that transhistorical editorial labor stems from the revolution of the word carried out by modernism, projected forward and backward from the rift it opens in the history of the letter, the line, and the law of genre. In The Shadow Mouth: Modernism and Poetic Inspiration (Palgrave, 2009) and Destruction was my Beatrice: Dada and the Unmaking of the Twentieth Century (Basic Books, 2015), Rasula turns his attention directly toward this subject matter, but it is only in his two most recent volumes that the full scope of his immersion in modernism across the arts comes into focus. History of Shiver: The Sublime Impudence of Modernism (Oxford University Press, 2016) and Acrobatic Modernism from the Avant-Garde to Prehistory (Oxford University Press, 2020) are companion volumes carving forking paths from early German Romanticism through Wagnerism to the proliferation of international avant-gardes and the global convulsions of jazz before following the ungrounding of these upheavals back to prehistoric precedents in cave painting, reading modernism as a “renaissance of the archaic.” With the prodigious and perhaps unprecedented range and variety of materials these volumes convene across nine hundred pages, Rasula has demonstrated that it is indeed possible to develop a research practice and a prose style adequate to the sheer profusion of modernist precedent—if not through an unattainable approximation of totality then by producing a sufficiently complex experience of its irreducible inventions.
The signal claim of History of a Shiver is that “the first modernism was Romanticism” (73). If the eighteenth century querelle between the ancients and the moderns remained “a neoclassical affair” (73), we might deduce from this claim that modernism emerges within modernity not through the rupture between the classical and the modern, but rather between the classical and the romantic. The impetus of modernism—its sublime impudence—stems from the self-conscious affirmation of this break, signaled in particular by a movement beyond classical genres. Rasula argues that modernism might be “understood in broad historical terms as the self-overcoming of genres in all the arts, for it’s this above all that illuminates the distinguishing trait of modernism while making legible its basis in Romanticism” (74). The specific Romanticism to which Rasula refers is the circle of writers concentrated in Jena, Germany, in the late 1790s, including Friedrich Schlegel, A.W. Schlegel, Novalis, Friedrich Schleiermacher, and Ludwig Tieck. Through their journal, Athenaeum, the Jena Romantics made the overcoming of separations between genres and art forms their explicit project through such keywords as Romantische Poesie, Mischgedicht, or Roman, which constellate their ambition to inaugurate forms of writing, thought, and sociality fusing art, science, philosophy, and politics while displacing the opposition of literature and criticism. “To affirm creative activity in terms of perpetual expansion and self-overcoming,” writes Rasula, “is not so much to envision the completion of a work as to valorize a project exceeding any momentary incarnation in a particular work” (56). Through this “feeling for projects” affirmed by Friedrich Schlegel, Jena circa 1800 becomes a fragment of the future it anticipates and constructs, with unclassifiable works like Novalis’s Das Allgemeine Brouillon making manifest a mode of striving not only metaphysical or historical, but above all formal—a demand that forms become adequate to all that exceeds them.
History of a Shiver coalesces around the recognition that such striving involves a passion for synesthesia: “The Mischgedicht—or blended composition—fanned the flames of an ambitiously synesthetic compulsion revisited with increasing urgency throughout the nineteenth century” (61). Moreover, in Rasula’s account the vehicle of this synesthetic compulsion was music. Due to an ineffability apparently exceeding that of other arts, and “because music was the art form least encumbered by mimetic criteria” (61), it served as an endlessly mutable locus of synesthetic reverie, such that experiences of “seeing music” or “listening to incense” pass over from idle analogy to transgenerational project, conveyed by the Wagnerian Gesamtkunstwerk from Romantische Poesie to early twentieth century avant-garde experimentation. Rasula is attentive to the irony of one particular art form taking on, through synesthetic revery, the burden of overcoming particular art forms—but what is irony? And how are we to understand the specific nature of this particular irony? It is by posing and indeed answering questions like this—which up the ante of art historical observation—that Rasula is able to illuminate the undercurrents of a century’s obsessions with an order of metaphysical insight equal to his objects of study, here in response to a fragment by Schlegel:
“Irony is the clear consciousness of eternal agility, of an endlessly abundant chaos”—in short, the primordial cosmic potentiality from which art (and all creative effort) derives. Irony is the romantic salutation of a finite being greeting the infinite cosmos, graced by reciprocal genuflections of cricket and leviathan. According to the principle of the fragment, every creative act leaves some trace of its “infinitely teeming” energy in the domain of the possible. Although the romantic concept of irony was mostly applied to literature, its artistic consequences are closely linked to the increasing eminence of music during the nineteenth century. Disclosing patterns of “eternal agility,” accompanied by an ironic awareness of the fragility of musical forms, music became the Trojan horse that smuggled Romanticism into modernism. (58-59)
It is not only ironic that music is positioned as the art capable of overcoming divisions among the arts; music is the irony which bears and conveys that Romantic imperative through the nineteenth century: the eternal agility of a medium with no object and no delimited spatial frame, temporally restless and composed of fleeting tones that die upon the air into which they are born and within the senses they populate. It is the clear consciousness of endlessly abundant chaos, communicated by music, from which modernism draws its sublime impudence from Romanticism, an ironic consciousness that extends to the dialectical relation between medium specificity and interarts experimentation, each pole of that relation propelling the other into generative contradictions. Taking up Carl Dalhaus’s notion of the “pathos of emancipation” (23) implicit in the contradictions of medium specificity and synesthetic yearning, the first half of History of a Shiver tracks tantalizing efforts to “surmount the input/output ratio of sense-specific arts” (24) from the throes of melomania and the delirium of Wagnerism through the subtractive operations of symbolism, the untimely pastorals of pageantry, pictorialism, and dance in California, invocations of a fourth dimension and a sixth sense, and a theoretical excursion through the ideal of endless melody.
Chapters on symbolism and on pictorialism and dance exemplify Rasula’s discrepant approaches to defamiliarizing modernism. “Drawing a Blank: Symbolist Retraction” is a beautiful, fluent meditation upon the “propensity to vacate the stage, reconvene space as magnitude, and generally clear the ground in order to start from scratch” (116). This “particular motif of retraction or clearing a blank,” Rasula argues, “is the salient feature of symbolism that persisted into modernism” (116). It’s not only the argument itself but also a subtle appreciation of the complex emotional textures of this subtractive operation that lend Rasula’s account its singularity. “I feel myself more trusting of the nameless,” Rilke intones, and as we read, that feeling of trust enters into the vacancies of Hammershøi’s interiors; into the “simple feelings” of Maeterlink’s plays and puppet theater (137); into the ghostly evanescence of Fernand Khnopff’s paintings, or their serial repetition of figures upon undeveloped ground; into portraits by Auguste Levêque, Mieczyslaw Jakimowicz, Odilon Redon, and Dante Gabriel Rossetti, wherein closed eyes bespeak a silent inner life; into Mallarmé’s compositions in which the lines “mustn’t be composed of words; but of intentions, and all the words must fade before the sensation” (121). Moving among so many names—some familiar, others less so—Rasula helps us sense the nameless blank of indeterminate meaning in the background or below the surface of what we thought we knew, of what we have been looking at for a long time:
Symbolist painting exudes a kind of thematic huddling, suggesting the predatory nature of certain subjects, as though the subjects chose the painters and not the other way around. So those scenarios of silence and absence seem on the verge of releasing some sound, like the skittering of rats or a sudden flutter of pigeons. (145)
To see sight renounced is to be asked to consider another sense (143); to trust the nameless is to let the object sink into indeterminacy, into resonance with undefined attributes—so symbolist retractions fertilize synesthesia and merge with the ineffability of music by evoking interiorities or elsewheres subtracted from recognition, suggesting reminiscence, and suffused with significance.
The following chapter on pictorialism and dance in turn-of-the-century America follows such obscure figures as photographer Arnold Genthe into the neo-Hellenic fantasies of Carmel by the Sea, or poets Bliss Carman and Richard Hovey onto the open road in their Songs from Vagabondia (1894). Rasula reconstructs affinities between the bucolic idylls, hieratic poses, flowing gowns, and pagan mysteries of American pageantry and Pacific arts colonies with fin-de-siècle Europe through such transatlantic crossover figures as Isadora Duncan and Loie Fuller, imbibing and interpreting Wagner, praised by Mallarmé. Photography not only documented the bodily postures and physical mystique of such figures, it also sculpted, curated, and framed their production according to the contrasting subjective ideals looking both forward and backward at the switching point between centuries:
Photography provides a vivid study of contrasts at that fin de siècle moment when Jean-Martin Charcot was documenting the convulsions of his hysterics for scientific purposes, while dance and body culture manuals were deploying a similar range of corporeal expressivity to illustrate modern standards of healthy living. In the genteel and ultimately redemptive petition to art by pictorial photography, the female form emerged as a tasteful return to Hellenistic animation—animus tamed by anima. (183)
Moving from Muybridge and Étienne-Jules Marey’s experiments with the photographic documentation of movement to Diana Watts’s The Renaissance of the Greek Ideal and Genthe’s photographs of Duncan, his collaboration with Percy Mackay (leader of the American pageantry movement), and his link to the photographic pictorialism of Stieglitz’s Camera Work, to Edward Steichen’s affiliation with the same journal, Rasula tracks the curious capacity of burgeoning art photography to shuttle between pastoral bohemia, mechanical scientism, nostalgic Hellenism, and Hollywood glitz. Formal problems of lighting and pose link these apparently discrepant photographic worlds with symbolism, while documentation of outdoor dance links pictorialism to the “barefoot modernism” of Duncan and the Arcadian dream of Vagabondia. Anne Brigman would photograph a series of wilderness nudes posed on outcroppings in the high Sierras, evocative of H.D.’s poems in Sea Garden and of “new dimensions” of “the human form as part of tree and rock rhythms” (198). Such projects exemplify Rasula’s reminder that “the influential view of modernism as a series of formal advances in various arts has obscured the extent to which such advances were stations in a spiritual quest.” “It has been too easy,” he notes, “to recognize formal issues from outside, while the tangle of hunches and beliefs that actually drove someone’s engagement with his or her art can seem inscrutable and messy. Once something like an idea emerges, it seems to have little to do with the plangent psychological and material muck out of which it arose” (189-190). Rasula’s rare gift is his capacity to make that plangent substance and that tangle of hunches manifest, not only prior to but in the ideas they generate and by which they are displaced.
The arabesque associations between major and minor streams of incipient modernism in History of a Shiver flow into Acrobatic Modernism like elaborately winding tributaries into a vast river, itself composing manifold currents. Understanding the structure of the book is crucial to grasping its method. We find three central chapters—“Make it New,” “Jazzbandism,” and “Multiplied Men”—constructed as something like encyclopedic catalogues. Here the task is to track down and include as many nodes in these thematic networks as possible: the writing moves briskly between names, practices, movements, and contexts, enumerating and briefly characterizing declarations of fidelity to the new in all its forms; the international scope and protean reception of jazz as a global phenomenon; invocations of plural selves and heteronymic displacements of identity. The sheer profusion of these chapters is at once exhausting and exhilarating, as the Preface anticipates:
My advice to the reader, then, is to regard the text like a big crowd on Times Square, Berlin’s Alexanderplatz, Mexico City’s Zócalo, or Trafalgar Square in London. As you venture into the swarm, let the kaleidoscope spin. After a while patterns will emerge in prismatic rotation, and the poor old tired horse of modernism may turn out to be a zebra after all. Count the stripes, if you will, or at any rate, saddle up. (vii)
One might add “buckle up,” in preparation for a ride that charges onward with the velocity of Marinetti’s automobile retrofitted for the freeway.
Yet these three central chapters are bookended by five others which proceed at a somewhat more reflective pace, and which pursue more or less continuous lines of investigation through the opening and closing sections of the volume. The first three chapters—“The Ache of Modernism,” “Luminous Sores,” and “Gathering Hay in a Thunderstorm”—elaborate an approach to artworks as “pathic receptacles,” compounds of thought and feeling deposited by making, poiesis. “Signs in any medium,” Rasula notes, “propagate more signs even as they purport to close in on the object of representation or on some intended meaning.” Thus,
To speak of an artwork as a pathic receptacle indicates this migratory propensity, this condition by means of which our sentience gets the better of us, as it were, thanks to which artifacts attain a life of their own. The transfigured object harbors a twofold pathos: on the one hand, like a corporeal dismemberment, the work is poignantly removed from the body that nourished it; on the other hand, in defiance of the medical model, the work itself (the disjected member) becomes the phantom sensation. (61)
The notion of artworks as phantom sensations, and of prosthesis as constitutive of embodied apprehension and production, is theorized in greater detail and with striking insight in Rasula’s dissertation on “The Poetics of Embodiment.” Here it offers an approach to artworks traversing apparently discrete forms or distinct media and attentive to “a biomorphic insistence, a biologically exigent extension of corporeality” attending the work of artists whose “generative impulse is profoundly embedded in a somatic manifold” (62).
In “Luminous Sores: The Pathic Receptacles of Modernism,” this approach enables a deep reckoning with the impact of the Great War on the relation between modernism and modernity. What distinguishes Rasula’s treatment of this well-worn topic is a concept of the artwork adequate to understanding how the war brought into “cataclysmic focus” (64) a wrenching recalibration of sensory ratios and a thoroughgoing displacement of generic norms that was already well underway. The “acute materialization of pathic intensity” focalized by the war is “a rupture that tells us, poignantly, that art is of the body and the body’s traumas extend to art” (115)—“that art’s receptacles hurt when they undergo transformation” (114). From the perspective of the synesthetic dialectic developed in History of Shiver—wherein synesthetic yearning becomes lodged in particular artforms, transgressing their distinctions precisely through intensifications of their address to particular sensory channels—we are in a position to understand how Nietzsche’s response to the Wagnerian Gesamtkunstwerk registers the pain of modernism in the element of both formal and historical transformation, given the body’s inadequacy to the demands of reception: “the absolute arts tear us to pieces, as it were, and we also enjoy only by bits, now as ear-people, now as eye-people, etc” (qtd on 115). “The siren call of ‘absolute art,’” writes Rasula, “endowed each sense with an enhanced perspective of loss—what it had to shed to partake of the absolute—as well as the advantages of further refinements along the paths of ‘eye-people’ and ‘ear-people’” (115).
This clarification illuminates not only anticipations by artworks of the sundering of bodies by the war, but also competing claims of medium specificity and inter-arts experimentation as central to modernism. The apparent contradiction of those accounts attests to “the paradoxically enabling trauma of productive loss” (126) traversing the unsettling of both generic and historical regularities throughout the nineteenth century. To position the war as ruptural cause of modernist culture is to occlude an understanding of the war itself as an effect of complex historical determinations stemming from the upheavals of modernity—those which shape as well the affective field in which artworks express the pain of transformation, and in which they become adequate to register the force of the war’s catastrophe. One must have suffered a long time to be adequate to the crisis of suffering, and have been greatly transformed to endure such transformation. When we read Hegel’s critique of Enlightenment and his philosophical transubstantiation of the French Revolution, we may be acutely aware that the pathos which also suffuses Beethoven’s Eroica is preparing the ground for those artworks of the twentieth century which take up ruptural traditions in the name of the new. Rasula cites Loy’s “Apology of a Genius”:
We come among you
innocent
of our luminous sores (127)
Among whom? one might ask. As Rasula will show, the genius of modernism is immersed in many thousands of years of cultural history, but it displays its wounds “among” the denizens of modernity. The sores of modernism illuminate the darkness of modernity like an underworld, by torchlight drawn from its own fires. Such a torch would be a prosthesis, supplementing the body’s lack, displaying its need, connecting it with the elements. The “excess of deficiency” (127) from which modernism suffers is bred in the bone of modernity, and its projects—whatever their explicit predecessors—stem in particular from the attunement of Jena Romanticism toward the dialectical overcoming of discrete artforms and genres.
In “Gathering Hay in a Thunderstorm” (Chapter 3), Rasula draws Aby Warburg’s research toward his Bilderatlas and his concept of pathosformel into contact with H.D.’s poetry and the meditations of her Tribute to Freud, in order “to explore the affective force of antiquity as a healing agent” (129). As the chapter weaves together H.D.’s vision of writing on the wall in Corfu with her dream of a caterpillar writhing under salt, with the intensities of her bond with D.H. Lawrence, and with the religious impulses of her sensibility, the depth and subtlety of Rasula’s psychoanalytic learning becomes apparent. There’s a sensitivity to the intersection of psychic trace and historical complex that imbues this material with a density of insight which the volume slows down to register. Meanwhile, the linking of H.D.’s case not only with Warburg’s art historical investigations but also the fissures of his dual identity as psychiatric patient and scholar of Renaissance art realizes the concept of pathosformel through the elaboration of its parameters. Warburg “sought the disclosure of otherness as such, in any form” (130), and Rasula takes the pursuit of this disclosure as an occasion for its advent: Warburg’s experience of his own body as akin to “a telephone girl during a storm or under artillery fire” (133) is fused not only with the “heraldic electricity” (159) of H.D.’s disposition, but also with the shock of cinematic experience recorded in Mann’s Magic Mountain and the harrowing cuts of the film Borderline, starring H.D. and Paul Robeson. Rasula limns the pathic intensity registered by Warburg in Renaissance paintings as a “sense of density evoked by the intractable body” (136) and lodged in works of art, reading the psychic distress at issue as manifest in the scholar’s life as much as in the concepts he develops. It’s the shiver that passes from one to the other that passes as well from Warburg to H.D., and that gives us to think modernism writ large as akin to a caterpillar writhing under the sprinkled salt of modernity—as an image of somatic convulsion. Citing Maeterlinck—“perhaps illnesses are the various and authentic poems of the flesh” (161)—the chapter offers a profound if understated meditation on the inextricability of illness and health, with culture caught at the crux of their chiasmus.
These opening chapters of Acrobatic Modernism enable us to imagine the quiver of the tightrope as it is traversed, or the sudden shudder of the fine line as one shifts to keep one’s balance above the void. The “acrobatic” is a matter of virtuosity, to be sure, but also of corporeal peril and exposure in the midst of the performance. The saltimbanque of Baudelaire’s “La Muse Vénale” not only shows off her charms, but does so through a “laughter soaked with tears that no one sees, / To split the sides of the vulgar.” The “hectic multiplicity” of modernism is riven by the very energies propelling its performances, such that “whether there’s a choice or not, modernism demands an acrobatic response to change, and change is the legislative circumstance of modernity” (11). Poised on the cusp of transformation, or undergoing its crux, the acrobat makes a living of the impossible, takes it as a test or “metabolic provocation” (12) productive of elaborate postures. Such performances take their toll, and Rasula’s title inspires attention, throughout, to the ways in which exposure to extremity—even when pulled off with aplomb— demands contortions as painful as impressive. “Historical mutation is the elective burden of modernism” (22) and artworks bear, as prostheses, the pain of the amputations they supplement, even those proceeding the birth of those who produce them.
Precedent becomes the closing theme of this book, as “the new” intersects with the question of how much precedent invention can include. A chapter on “The Renaissance of the Archaic” is preceded by a chapter on “The New Mythology,” and these form a diptych at the hinge of prehistory. The metaphor is meant to evoke Rasula’s discussion of the symbol:
In the original Greek, symbol refers to the two halves of a pledge split in two, so each half bears within it the potential for reunion. Moby-Dick is possessed of the perfect symbol: insofar as the white whale is symbolic, it’s because it is the living counterpart (and possessor) of Ahab’s lost leg. In that sense, then, a symbol emits phantom sensations, woeful registers of somatic penury. In addition to the spatial aspect of its object status, a symbol is also a temporal indicator. The sundered pledge attests to past truncation, portending the future reunion when the two halves of the pledge are reunited. (348)
Modernism is a sundered reunion with the deep past: reunion becomes the very act of severance that proclaims the new even as it claims a destiny in common with the archaic.
“The New Mythology” takes the landmark journal Transition as a signpost, dwelling on its publication of the “Work in Progress” that would become Finnegans Wake, with its sense of historical simultaneity wherein (as Siegfried Giedion claimed), “present, past, and future are not chopped off from one another but merge into one uninterrupted fabric” (296). But as usual, Rasula brings the usual suspects (Joyce) into contact with lesser-known figures, such as the German Surrealist Wolfgang Paalen or critic Carola Giedion-Welker, the latter becoming a kind of guide through both closing chapters. Giedion-Welker’s lucid commentaries on Joyce, Arp, Moholy-Nagy, Ozenfant and Jeanneret, Satie and others others illuminate the stakes of Dada, Constructivist, and Surrealist artworks and their archaic precedents. It’s her attunement to the problem of sensory ratios, the requirement of renovating human perception through mutations of proportion demanded by modernity, that Rasula particularly values in her perspective. “Reminiscence of the archaic,” she writes of Giacometti’s sculptures, “is this delicate awakening of the form from out of the plane of stone, this swelling up and down of the plane.” And of Arp she notes that the material is infused with “something growing, welling, gliding which admits neither of formal nor mental frontiers and fixations” (298). We might glean from such descriptions that, for Giedion-Welker, the reminiscence of the archaic in modernity involved a measureless formal flux or interior pressure transforming the dimensions of the work in accordance with historical forces traversing the present and connecting it with a distant past. What’s interesting in these passages is that the language is not one of rupture but of undulation, as if the deepest past were sculpting from within the immediacy of the present without the regulation of proportional laws.
The inspiration of the archaic suggests a return to origins, to inaugural moments, thus fusing the new with the old as that which was not old when it took place, and it is this simultaneity of taking place which accounts for how allegiance to precedent strictly entails commitment to the unprecedented: the first instance of what once was, right now. The incipient curvature Giedion-Welker sees in the awakening of modernist forms to archaic precedent (think of Gaudier-Brzeska) is manifest in the dynamic, rather than static, equilibrium urged by Piet Mondrian, the kinetic rhythm advocated by Naum Gabo, or the asymmetrical balance of typographical design adopted by Jan Tschichold (302). Rasula positions the values and inventions of Constructivism, its realization of the apparently abstract in the concrete practice of making, as part of the pursuit of a new mythology—and in this sense in continuity with the project of Jena Romanticism. “We admit,” Naum Gabo acknowledged, “that we do not what what ‘reason’ is, what ‘myth’ is, where free fancy begins, and where knowledge ends,” and it was this uncertainty about parameters of knowledge, perception, and imagination in modernity which forced a production of the new often inseparable from a recovery of the old. Gabo declared that “the aim of our time consists in creating a harmonious human being” (319), where the emphasis falls upon creating, since harmony could no longer be taken for granted. And indeed this specifies the terrain upon which Constructivism and Surrealism—apparently divergent or opposing movements—converged upon the same goal in different ways. “New innocence and new experience,” Rasula writes, “join to produce (from a Constructivist perspective) or to induce (in the Surrealist outlook) a new sentience” (346)—a new sentience for which the boundaries between reason and the irrational are as unclear as those between knowledge and myth.
In a sweeping final chapter, Acrobatic Modernism then considers “The Renaissance of the Archaic” such new sentience involved, again conjoining major figures (Georges Bataille, Maurice Blanchot, Charles Olson, Barnett Newman, Mark Rothko) with a host less familiar names, (Max Raphael, Anatole Jakovski, Andrea Caffi, Martha Graham, among many others). Abstract Expressionism anchors the chapter’s associative tour through investments in the paleolithic, and a trajectory comes into view from Constructivism and Surrealism into a postwar context for which avant-garde excavations of the archaic had themselves become historically mediated. “Prehistory” —that which comes before the beginning of record—comes to constitute an opening upon the way in which the archaic had been made new by modernism, as cave painting recalls the gestural inauguration of the unprecedented: art. The book draws toward a close with a moving meditation upon the hand print as prehistoric sign and modernist motif, wherein the marking of corporeal presence asserts or shadows or abstracts the being-there of the human in the midst of the ghostly apparitions of time’s passage. It’s through such associative gestures that Rasula is able to bring what seems to be unrelated into suggestive proximity, and this closing movement of the book’s final chapter might be regarded as itself a kind of methodological sign: any and all signs of what came to be called modernism are available for reconsideration of their significance, and of the way they snap the most profound depths of our history into altered focus.
Together, these books are a massive contribution not only to modernist studies but to our understanding of modernity. In their passage across two centuries, across the breadth of international modernism, across the arts and experimental practices located among their interstices, History of a Shiver and Acrobatic Modernism show us just how much typical scholarly protocols tend to occlude the profusion of modernist practices. In particular, the acrobatic agility of Rasula’s writing—a compositional style willing to risk immersion in the materials to the point of saturation—enables the kind of alacrity urged by a figure like Friedrich Schlegel: an associative field of intelligence and attention constantly mutating, expanding its limits, frequently turbulent but at times settling into regions of meditative continuity. These are books that display a ferocious determination to know or at least to gather as much as possible, yet also a light touch that makes so much research and learning amenable to enjoyment and play. To read them is a difficult pleasure, teeming as they are with so many encounters and new prospects. As we contemplate the vexed energies they trace, they draw us near the most distant, and they suffuse what we thought with knew with intimations of the unknowable.
While discussing the composition of these two books in a forthcoming volume of essays and conversations, Wreading: A Potential Intelligence (University of Alabama Press, 2021), Rasula notes, “The fact that these people were alive means a great deal to me.” You can tell. For it to mean a great deal that such people were alive requires us to encounter their works as refractory to the museum, to the catalog, to the backward gaze of the scholar. For it to matter that they were alive, they have to be brought to life. It means a great deal because the history of a shiver those lives transmit, of the luminous sores their works display, remains our own.

by George Shulman
Since the 2016 election, and during Donald Trump’s Presidency as well as its violent aftermath on January 6, commentators on the left have engaged in two related debates. One has concerned the danger posed by Trump’s rhetoric and policies, by his base, and by the extra-parliamentary right. This debate involves contrasting assessments of the future of the Republican Party, and of the durability of the hegemonic center that has ruled American politics from Reagan to Obama. Running parallel is a second debate on the left, and intensified since the summer, about the meaning of the Movement for Black Lives (M4BL) and the massive inter-racial protests it organized last summer, but also about the potential of the Democratic Party as a vehicle of social change. These debates involve judgments of the character of American political culture and claims about the fluidity or rigidity of its manifest polarization. At stake are contrasting visions of our political moment. One vision, influential if not dominant, implicit if not always explicit, circulates through Democratic Socialists of America and Jacobin, and has been articulated by notable commentators like Samuel Moyn and Corey Robin in The New York Times and The New Yorker. Since 2016 it has depicted our political moment as both reflecting and continuing an ongoing impasse in politics and ideology. I support a contrasting vision, which also circulates through activist and academic circles on the left, and which depicts our moment as a fraught interregnum bearing both a real danger of an authoritarian or fascist turn, and, incipient possibilities of radical change. While the trope of impasse presumes the reconstitution of the hegemonic center ruling American politics since the 1980s, the trope of interregnum imagines both breakdown and transformation.
I would begin by noting the elements of the orientation I am trying to capture with the trope of impasse. First, it has criticized ‘alarmism,’ and consistently minimized the sense that Trump’s presidency, his base, and the Republican Party posed dangers beyond historic patterns of harm. Second, it has minimized the extent and grip of racism, misogyny, and polarization in the political culture of whites and in general it discounts the power of political language and the potency of irrationality, in order to defend the premise that ‘common material interests’ (and demographic change) can and will underwrite a multi-racial, progressive, majority coalition. On the basis of that organizing fantasy, third, it attributes the character of the Democratic Party only to cowardice and corruption, bred by neoliberalism and elite complacency, and it has discounted how the party, as currently constituted, could undertake change more radical than tinkering. Fourth, it has imagined each party absorbing its radicalizing elements, thereby sustaining the hegemony of established elites. It expects that an ideological political center will be reconstituted, and that American politics will remain trapped in the deep structural impasse that it claims Trump merely manifested and never ruptured. The overall effect of such arguments, over the last five years, is to emphasize the undeniable inertial power of historical patterns and institutions, but diminish their contingency, fragility, and mutation. Such arguments minimize our sense of both danger and possibility, and magnify our sense of historical stasis. Though we hear an assumption that demographic change promises a brighter future, if only the Democratic Party supported truly progressive candidates, the repeated conclusion over five years is that the Trump moment and Biden’s election only continue the “interminable present”—the structural intractability and discursive paralysis—depicted by the academic left since the early 1990s.
We cannot definitively validate, or decisively disprove, these claims and anticipations, both because “evidence” also warrants contrasting interpretations, and because assessments of the strength or weakness of a president, a movement, or a party concern objects whose character and power depend on actions that can and do remake political reality, whether by unexpectedly shattering a consensus, contesting entrenched power dynamics, or mobilizing unforeseen support. By foregrounding that sense of contingency, I would raise questions about each element or step of the “impasse talk” I am trying to identify, and propose instead how the trope of ‘interregnum’ better grasps the danger and the possibility in our recent history.
My avowedly arguable premise is that politics cannot return to the neoliberalism and racial retrenchment of the last fifty years, and that post-Reagan conditions of political impasse cannot continue, either. Instead, I would propose that American politics has entered what Antonio Gramsci called an interregnum, in which the old gods are dying, the new ones have not yet been born, and we suffer ‘morbid symptoms.’ Though his Marxist teleology assured him which was which, we cannot be so confident about what is dying and what is emergent. For the last year manifested indigenous forms both of fascism, and of radical possibility, as enacted by M4BL and the multi-racial protests it organized and led. Each was incipient or inchoate, and each was amplified by COVID-19, one by the gross racial disparity and state abandonment, the other by manic denial of its mortal impact and political implications. Each rejected neoliberalism, each overtly named the centrality of race, each bespoke the extent to which liberal democracy has been hollowed out, each scorned the party system as failed representation, each refused the idiom of civic nationalism and its narrative of incremental progress, each depicted conditions of crisis and decisive choice. But the crystallization—or cooptation—of each emergent possibility is contingent, not only on organizing by white nationalists and abolitionists on streets, in localities, and by elections, but also on fate–ful choices by the Democratic Party about its policy and rhetoric.
To anticipate, I propose that changes in both cultural landscape and party politics preclude reconstitution of the impasse that has arguably characterized American politics at least Reagan, and instead have opened an interregnum in which mobilized and antagonistic political constituencies—70% of whites, in one party, increasingly committed to minority and racial rule, facing a party increasingly committed to multi-racial democracy—see decisive choices shaping antithetical futures. If the question posed by the developments on the right is how to distinguish the danger of fascism from minority rule committed to white supremacy, the question posed by developments on the left is whether the radicalization on the streets since last summer, and danger from the right, engender a significant modification of liberal nationalism on the order of a third reconstruction. I would thus intensify both danger and possibility by amplifying the contingencies—and the rhetoric—that can interrupt, inflect, or transform inertial patterns.
On the one hand, Trump was not repudiated in the 2020 election; he achieved a historic mobilization of working class, rural, and non-college educated voters to forge a coalition with explicit evangelical and capitalist elements, a long-sought Republican Party project, but he did so by disavowing creedal or civic nationalism, which had been the hegemonic rhetorical center that has long contained partisan difference. An explicitly anti-democratic and racially exclusionary Republican Party, no longer even evoking universalistic language, consistently won down ballot, protecting control of most states and redistricting, while retaining domination of the Supreme Court and the advantages bestowed by the constitution in the Senate and Electoral College. Roughly 70% of white voters, 40% of the electorate, deny legitimacy to the 2020 election, support the capitol invasion, and endorse not only voter suppression but overturning elections that Democrats win. Given the institutional grammar controlling elections, it is likely that a radicalized Republican Party will retake the Senate and perhaps the House in two years, and then win the Presidency in four years–unless the Biden administration produces tangible benefits clearly linked to electoral campaigns in states and nationally. Though a huge majority in public opinion polls support ‘bipartisanship,’ a default politics of ‘return to normal’ only allows the parliamentary obstruction that assures Republican electoral success. In turn, that success would cement an anti-democratic project of avowedly minority rule to protect authentic Americans from displacement, i.e. the native form of fascism that Du Bois and de Tocqueville–both seeing the imbrication of class rule, racial caste, and nationalism–called ‘democratic despotism.’ The newest iteration will amplify those inherited patterns, but in unprecedented ways it will abandon the universalist (creedal or civic) language that has both justified historic forms of domination, while also authorizing and yet containing protest against it.
On the other hand, experience of COVID-19 and last summer’s massive protests fostered notable shifts in how whites view both endemic racism and state action, opening unexpected and perhaps unprecedented possibilities for progressive politics. What some call a third reconstruction or new New Deal is now spoken of in ways that no one could have imagined even 6 let alone 12 years ago, and yet, importantly, it is also a political necessity. For the democratic coalition that elected Biden must address the suffering and rancor, as well as the political infrastructure and constitutional bias, that sustains its adversary, or it will become an ever-losing minority party despite its majority support. But given the polarization in American political culture –around race and gender, membership and immigration, the meaning of “America,” citizenship, and freedom, how can and should an openly social democratic and race-conscious approach be legitimated and narrated? That is the question of rhetoric, as Aristotle defined it: what are the available means of persuasion? Working through recent debates on the left will clarify possible answers.
The impasse argument
The first point of debate has been how to understand Trump’s electoral appeal and presidency, which has involved contention about naming -was Trump continuing conventional Republican goals (tax cuts and judges), or was ‘the F word’—fascism—appropriate to signal a mutation or intensification of inherited cultural and political patterns? These questions required judging the ways in which Trump simply repeated, or also modified, the white supremacy–and patriarchy–foundational in American history. One position feared the effects of ‘exceptionalizing’ Trump, which made him seem an anomaly in our history, rather than credit the racial and misogynist roots of his rhetoric and style, and rather than anchor his appearance in the failures of liberalism. The other position feared that ‘normalizing’ Trump would protect the ways that he represented a significant mutation of those historic patterns.
Against those who used the F word to signal those departures, two different kinds of claims were made, each normalizing Trump. One claim called Trump an inherently ‘weak’ president, as evidenced by his policy failures, whereas a contrary view traced how he was repeatedly thwarted by massive political mobilization. Likewise, by defining power only by what we “do” and not also by what we “say,” Trump’s actions were cast as conventional and ineffective, whereas a contrary view traced how overt racial rhetoric, performative misogyny, and the practice of the Big Lie were transforming inherited political culture and party politics. Anxiety about ‘fascism’ was thus dismissed on the grounds that Trump did not govern like European fascists and autocrats, rather than see him in relation to recurring but also mutating forms of what Alberto Toscano called “racial fascism,” entwining cultural mobilization, popular terrorism, and state violence.
The prevailing orientation, therefore, cast the “real” danger not as Trump or the right he was authorizing and mobilizing, but as the “alarmism,” even “hysteria” of those who used the F word. Why? Because the effect of “inflating” danger was to push the left to protect the regime of liberal democracy, as if it were the only and necessary alternative to fascism, whereas (and I agree) the failures and deep racial structure of liberalism in fact made Trump both possible and appealing. To reverse this argument’s logic, though, what is its effect? It dismisses those who see danger and precludes taking (the idea of) danger seriously. What is thereby being protected? If there really were danger from a growing and militantly anti-democratic right increasingly occupying an established political party, and if the U.S. had entered a version of a ‘Weimar moment,’ what would that mean? The left would have to re-imagine the cultural landscape (and working class) it has fantasized, and, it would have to decide if defending even the minimal terms of liberal democracy is a necessary to protect the possibility for radical possibilities. It would have to rethink the working class subject it is invested in sanitizing, rethink its assumption that hegemonic impasse will continue, and thus rethink its relationship to the loathed liberal object on which its future may depend.
The second point of debate involved the danger in the mobilization by the right, in increasingly networked and armed militias, in the alternate reality created by social media and FOX news, and in state and national sites of the Republican Party. The dangers have been consistently minimized by influential voices on the left, on the grounds that the extra-parliamentary right is not formally organized, and thus will be contained by the Republican Party. The capitol invasion and certification vote might have tested these claims, but influential judgment remains that the occupation ‘failed,’ as if that proved both the weakness of the right and the durability of the established order. Though the worst possible outcome did not materialize, that doesn’t mean the threat is not real and ongoing. The left faulted Biden for his fantasy of returning to normal that includes bipartisanship, but it has not traversed its own fantasy of the center holding until a progressive movement captures the Democratic Party and gains overt political power. Dramatizing a contrasting view, Richard Seymour responded to the capital invasion by inverting Marx: an “inchoate” and “incipient” fascism” has indeed appeared, as farce first; it can then reappear as tragedy. A first step has already occurred as the mobilized right has taken over and radicalized the Republican Party.
It is not consigned to irrelevance by demographics, as too many on the left assume; rather, Trump created a template for its resurrection. Indeed, his defeat further radicalized the party, even as it retained its grip on state and local governments. Given the electoral college, the rural bias in the Senate, voter suppression, and the composition of the Supreme Court, there is every reason to expect the party to remain committed to minority rule, and to electoral viability on terms that include overturning elections that Democrats win. No establishment element in the party is available for bipartisan consensus; every incentive encourages the party to obstruct Biden’s initiatives, diminish economic recovery, and prove that government is ineffective, thereby to feed the despair and rage that enable Republican majorities in Congress in two years, and a successor to Trump in four. Autocratic rule has been averted for the moment, but merely postponed, not forestalled. Alarm seems at the least prudent, and I would argue that prudence requires defending electoral (and so, liberal) democracy, not as an idealized alternative or revered object to defend against an alien form of despotism, but as a grossly flawed framework whose declared rights and recent advances nevertheless can authorize and enable emergent radical projects of democratization to develop further.
This broaches the third broad area of debate, concerning the character of public opinion and political culture. In simple terms, the election revealed that 72 million people, mostly white, across class lines, voted to reelect Trump–3 million more than in 2016, enough to have beaten Hillary in the popular vote and not only the electoral college. After the election, 80% of those voters remain convinced the election was stolen, a claim based on ‘disinformation’ that was taken as plausible because it confirmed prior racialized judgments about who is a legitimate citizen. Some of those voters were transactional, making a judgment on the basis of taxes and judges, but nevertheless, they knew they were voting for a candidate who refused to accept the peaceful transfer of power if he lost, as if Democrats could win only by fraud, i.e. by people of color voting. At issue is not only ‘denial of reality’ by enclosure within an alternate one, but mass investment in protecting white supremacy and patriarchy. The prevailing view of DSA and Jacobin would salvage this situation, to protect the vision of a class politics oriented by “material interest” rather than divided by the “identity politics” of race, gender, and nationalism. But for whites, class in the U.S. is lived through codes of race and gender, and by deep investments in both propertied individualism and nationalism. Indeed, a huge majority of whites has been wed to the death drive by the discourse of racial capitalism, aligning whiteness, work, and worth to masculinized self-reliance. Blocked grief at real losses has produced both the suicidal and manic features of melancholy. Rather than undergo mourning, many white men and women embraced death in the name of liberty, but they also are enraged, feel legitimized in their sense of victimization, and they are armed. The material realities of disease, precarity, and racial disparity must now include the invented reality of a stolen election, as well as the denial of reality embraced by the millions who voted for Trump. But the historic rationalism of the left, presuming the effectiveness of what Freud called the reality principle, prevents apprehension of the desires and fantasies–and so of the images and symbols–that constitute what class means in particular places and times.
I would call our historical moment an interregnum, therefore, partly because the historic marriage of citizenship and whiteness is being regenerated, not only as militias enact historic forms of popular sovereignty and local civic power, but also as the Republican Party increasingly recruits men and women of color into a newly emergent, multiracial and not only ethnic, form of whiteness. This anti-democratic form of ‘American democracy’ defensively asserts the individualism, popular sovereignty, and nationalism once taken for granted in the civic language that wed whiteness and citizenship, but now it is severed from even the pretense of universalist ideals and appeals. This zombie politics of the undead, this resurrection of American greatness may be dismissed as farce, but it will thrive and not truly die unless its premise—in gendered and racialized forms of individualism and resentment–is addressed, and unless its constitutional scaffolding is dismantled. This challenge has also prompted debates on the left about the Democratic Party.
The prevailing view, articulated by DSA and Jacobin, imagines a culture that is center-left in a readily accessible way, which implies that the only obstacle to a winning majority coalition is Democratic Party timidity, linked to the corrupt neo-liberalism of its established elites. If we recall that refusal to accept electoral norms has occurred before–when southern states seceded and then rejected open elections during reconstruction–it seems more plausible to say we have shifted from ‘polarization’ to a condition more like civil war, albeit so far a cold one, over antithetical visions of democracy and the future. Even if parliamentary stalemate persists, it reflects not so much structurally dictated foreclosure, as a condition of civil war whose outcome we cannot predict, because it is contingent on our action now.
In these cultural circumstances, the Democratic Party mobilized 8 million more voters and created the basis for a multi-racial coalition with some 30% of whites, more affluent and educated than not, and people of color across class lines. DSA and Jacobin still claim that Bernie Sanders could have won the election, despite the fact that even in the primaries he could not cross the 30% threshold, because he could not gain significant support from Black and Latinix constituencies (except in Nevada). The base of the Democratic Party, Black women, rescued Biden in the primaries because they credited the depth of racism and anxiety among whites across class lines, because they valued his appeal to competence, and, I would argue, because his profound (Catholic) understanding of grief linked mourning to public service in ways that really resonated with the Black church tradition. But in turn progressives and millennials still mobilized (in ways they did not for Hillary Clinton) because so many accepted Bernie Sanders’ dire judgment that we had indeed entered a Weimar moment in which the choice was really between Trump and democracy.
One incredible irony of our moment is thus that Biden’s reputation for moderation, his personal proximity to suffering, and his performance of a ‘common man’ version of a whiteness wed to decency not supremacy, were crucial to recruiting enough (suburban) whites to create a winning coalition with affluent progressives and people of color. Moreover, his first 100 days suggests that this persona may allow him to advance more progressive policies, perhaps a democratic version of Nixon going to China. Given our political culture, constitutional bias, and gerrymandering, the Democratic Party still needs both its moderate and its progressive wings if it is to fly, to use Cristina Beltran’s great metaphor, though this creates enormous parliamentary difficulty for progressive projects. And to complete the double bind, unless it produces benefits tangible to masses of people in the next two and four years, it is likely to be defeated electorally, but the actions that produce such benefits are likely to contradict the promises that are crucial to moderate voters.
Interregnum and Rhetorical Possibility
Rather than depict a durable center containing threats on the right as well as radical energies on the left, and rather than presume the readiness of working class Americans (across racial lines) to adopt a pointedly progressive political agenda, I see a darker and more dangerous situation in which a likely outcome is the victory of an openly anti-democratic Republican Party, anchored in an increasingly organized militia movement and a conspiratorial popular culture among the vast majority of whites, and recruiting enough people of color to appear nationalist rather than racist. Rather than moralize the character of the Democratic Party, I would emphasize that political culture among whites supports only some specific elements of the progressive or radical vision offered by the left, though to an uncertain degree some whites (across class lines) may be open to shifting affiliation. But tangible benefits are not self-evident in meaning and do not suffice to generate allegiance; rather, inferences from those benefits—that government can be effective for the many not the few, and that democracy is not a fraud—depends on the available means of persuasion. What are they? Which idioms might resonate, and with whom?
The symbiosis of Trump’s presidency and his base was made possible by the conjunction of defensive nationalism, racial retrenchment, and neoliberal precarity, the dominant strands in American politics since Reagan, which set the limitations of Obama’s self-defeating and disappointing presidency. But in ways the left has not credited, this conjunction reflects the failure of prior populist and progressive projects to address how citizenship is racialized standing and capitalism is always-already racial. The repeated failure of American social reformers to sever citizenship from whiteness, to show the price that whites and not only blacks pay for white supremacy, and thereby to join a class politics to an abolition project, is the ongoing condition enabling this iteration of American-style fascism. Conversely, a politically effective and durable response to Trump and his white base must address both precarity and structural racism, as twinned not separate. Progressives must show that separating whiteness and citizenship brings tangible benefits to those disposed by zero-sum racial logic to see only loss. But we also must explain what those tangible benefits mean–narrate their meaning–in ways that reattach profoundly alienated people—not only working class whites but millennials across class and race lines—to democratic ideals and practices they understandably deem fraudulent and/or exclusionary. Those ‘values’ are not manifestly valuable in a time of rampant cynicism, but must be turned from empty nouns into active verbs by political poesis and praxis that vivifies and enlarges their historic (and limited) meaning. Politics has entered an interregnum, though, not only because of danger on the right, but also because the conjunction of COVID and M4BL organizing has created just that possibility, by linking precarity and race in democratizing ways.
How might different ways of politically and rhetorically linking precarity and race address the danger of an emboldened and increasingly organized right? Aziz Rana, Robin Kelley, and many M4BL advocates have argued that the crisis in liberal nationalism and its creedal narrative, witnessed on the right and the left, is an opportunity to conceive a democratic politics no longer defined and contained by the nation-state. M4BL, drawing on traditions of black radicalism, is thus seen as a model of how social movements should sever projects of social justice even from a progressive version of civic nationalism and its redemptive narrative, to assemble instead coalitions that shape politics locally and influence policy nationally. On this view, radical social change requires not an over-arching national narrative, but a movement of movements, coalitions forged by transactional and strategic relations around intersecting issues, contiguous interests, and regional projects. The great benefit of this approach is to contest the settler colonialism presumed and erased by progressive versions of civic nationalism, and to instead foreground the patiently prefigurative politics that slowly but surely builds another world, a durable and vibrant res publica, within and against this one. Such ‘horizontalism’ may also offer a resilient practice of survival under conditions of a cold civil war, when political persuasion seems impossible, and mutual aid and mobilization seem paramount.
These arguments are credible and appealing, but I fear they cede state power to a mobilized right intent on crushing sanctuary cities, anti-racism insurgency, climate change activism, queer politics, and critical race curricula, let alone social democratic attempts to increase social equality and address racial disparity. They cede state power because they relinquish a large-scale (say national) effort to seek a majoritarian hegemony on behalf of a democratic horizon of aspiration, to legitimate equality, popular power in participatory practices, and through elections and truly representative institutions. I would argue that social transformation requires more than a coalition of constituent movements, which are always at risk of acting as narrowing interest groups; it requires hegemony, to denote the symbolic legitimation and organization of political power that at once advances and protects the constituencies it brings into relation as a majoritarian formation. Such hegemony requires symbolic or figurative language, an organizing vision and historical narrative, to explain circumstances, invoke a ‘we,’ and stipulate ‘what is to be done.’ For democratic ideas and participatory practices are not self-evidently desirable or legitimate; by praxis and imaginative poesis we turn empty nouns into embodied verbs, visible realities, rhetorically compelling objects, and durable affective attachments.
On the assumption that radical social change requires a persuasive idiom with broad appeal, my avowedly arguable proposition is for progressives to articulate a “third reconstruction” that, in Baldwinian terms, publicly reckons with the historical legacy, institutional features, and cultural meaning of white supremacy, while in Gramscian terms, symbolizes democratic renewal through a ‘national-popular’ idiom aspiring to hegemony. Because the toxic character of civic life and prevailing devaluation of public goods is inseparable from endemic racism, a third reconstruction is not only a program of ‘reparations’ directed to the ‘wealth gap’ suffered by Black communities, but is also the means and the signifier of a broadly democratic reconstitution of social life. That reconstitution requires the use of state power and public programs to break the grip of oligarchy and caste, but its democratic integrity depends on ongoing ‘movement’ in every locality and across of range of issues, to bear witness to historic injustice and present injuries, to sustain non-state infrastructures of mutual aid, to pressure elites, and to create stages on which people can see themselves assembled, enjoying civic life and public things. But as the freedman bureaus during the first reconstruction indicate, the survival, let alone vitality of any ‘democracy-from-below’ requires a state that challenges local tyrannies and supports insurgencies, which in turn requires a ‘national-popular’ idiom that shows the relevance of democratic ideas to people rightly cynical about them, and that recruits (some or enough of) those who inhabit the “non-intersecting” reality that is the legacy, not only of Trump, but of the failed liberalism that made him possible.
Rather than recuperate the tired teleological narrative of progress, the trope of a “third” reconstruction emphasizes two prior but “splendid” failures, as Du Bois put it, to suggest a revolutionary experiment to make anew, the contingency of any victory or accomplishment, and the necessity for ongoing popular struggle with entrenched forms of power. We cannot know if such language could achieve hegemony until and if it is genuinely attempted. In this interregnum, when we do not know what is in fact dying–is it white supremacy or democratic possibility?–drawing on ‘national-popular’ or vernacular idioms seems necessary to reckon finally with the past, project a potentially common horizon, and thereby protect the very idea of a democratic, multi-racial politics. Failure does not mean a return to neo-liberal impasse, but an opening for an aspirational fascism to shift from incipience and farce to resurgence and tragedy.
George Shulman teaches political theory and American Studies at the Gallatin School of New York University. In 2010, his second book, American Prophecy: Race and Redemption in American Politics, won the David Easton Award for best book in political theory. He is currently working on a book entitled Life Postmortem: Beyond Impasse.

This review has been peer-reviewed by the b2o editorial board.
by Anton Jäger and Jan Overwijk
On December 5th, 2019, London’s Conway Hall hosted an illustrious reunion. Michael Hardt and Antonio Negri – authors of the 2000 classic Empire, itinerant celebrities of the academic left – came to London to revisit their theses in a “world of Trump” (Hardt and Negri 2019a). “Twenty years on”, the announcement read, “globalization remains a central issue of our era, but commentators are conducting its postmortem, as forces across the political spectrum herald the return of national sovereignty” (Hardt and Negri 2019a). A lot had indeed changed in twenty years, the authors admitted. Across the world, evangelists of globalization found themselves in a state of retreat, embattled by Brexiteers, Orbánists, and other antiglobalists, led forth by the likes of Bolsonaro, Trump, and Duterte (Eichengreen 2018; Norris and Inglehart 2016). With supposed “populists” heading states from Budapest to Delhi, raising tariff barriers and restricting labor mobility, had Empire stood the test of time?
There was a time when Empire occupied the center of global political theory. “Even if it doesn’t deliver the goods,” a reviewer charged in 2001, “Empire should inspire a multitude of empirical investigations and practical political projects” (Henwood 2001, 12). Others were less enthused: a member of the American LaRouchist movement described Negri as a “terrorist controller” who became “a leading ideologue of the new decasualization” (Celano 2001, 16). Despite such early pushback, the phrases deployed in Hardt and Negri’s book still occupy a stable place in the left’s vocabulary” – “multitude”, “cognitive capital”, “deterritorialization”, “post-Fordism” – and have found their way into scholarly language (Kioupkiolis 2016, 138-139). Interestingly, Hardt and Negri’s theory also seems to have been granted a paradoxical new lease on life after the failure of left populism in the 2010s. After ten years of experimenting with parties, institutions, elections, and representation the left finds itself sent back to a position resembling early 2000s horizontalism, but without facing a triumphantly cohesive neoliberal bloc.
No thinkers provided a more trenchant diagnosis of this previous period than Hardt and Negri. Yet no thinkers also more clearly exemplified the limits of the previous horizontalist critique of the Washington Consensus than the authors of Empire – limits to which the left populist moment was all too attentive in its focus on party building and associative activity. The dogged return of the Hardt-Negri thesis thus speaks to a deeper contradiction in their oeuvre. While few theorists offered a more powerful theory of the new gods of fin de siècle capitalism – both economic and political – they had far less to say about the ‘old gods’ that stalked the neoliberal world, from the spread of general market dependence, the retrenchment of mid-century social rights, to the declining bargaining power of labor. On a surface level the hypothesis of Empire was so plausible as to be unassailable – the spreading of flexibility and creativity through the entirety of the capitalist labor market, and the digital ideologies this spawned. Hardt and Negri also offered a potent vision of the new modes of anti-representative politics that flourished on this new economic terrain, and how capital reconstituted both itself and the labor process. On a deeper level, Empire equally leaned into the most implausible of all hypotheses: that the fight for an old-style political economy and decommodification had to be abandoned for Marxism to remain viable, that old dogmas were only just that: dogmas, and that regression could be recast as progression.
As the world returns to the squares and the “multitude” resurfaces, this article revisits the project begun with Empire. Although cognizant of the advancements and insights offered by Empire and the broader, anti-institutional mood it was part of, it claims that Hardt and Negri’s theory of the multitude, indexed to a specific understanding of capitalist logics and a Spinozist ontology, still retains a fatal ambiguity. That ambiguity deserves revisiting today, in a time when the left populism first proposed by Ernesto Laclau and Chantal Mouffe and later enacted by Podemos, La France Insoumise, and Syriza has waned and Hardt and Negri’s movementism is undergoing a revival.[1] While the 2010s swore by theorists such as Laclau and Mouffe’s “organizational” tendencies, the 2020s open a chapter continuous with Hardt and Negri’s horizon (Cunliffe 2020, 122). This article thus cautions both politically and theoretically against a hasty return to Hardt and Negri’s trilogy of four after the close of the populist decade, and urges us to move beyond it while maintaining some of its key insights. In this sense, it calls neither for uncritical acceptance nor unconditional rejection. We argue that even today still, much of value can be found in Hardt and Negri’s oeuvre, even if that value is often too one-dimensional.
Any reckoning with Hardt and Negri’s legacy must move from the abstract to the concrete, peering at the foundations propping up the political theory: their ontology. From Empire (2000) to Commonwealth (2018), both authors understood the transition from the Fordist phase of capitalism to its post-Fordist phase primarily as one of a “multitude” coming into its own. But Hardt and Negri take this faith in the productive capacities of the global working class far beyond Mario Tronti’s (2019) original, post-operaist “reversal of perspective” (Shukaitis 2015, 3). In the 1960s, Tronti sought to correct classical Marxism’s overly strong emphasis on the autonomous development of the productive forces as the principal determinant of historical progress (Balestrini 2020). Instead of envisioning history as a chain of events in which a reactive working class pre-empts capital’s maneuvers, Tronti’s operaismo understands labor as the prime historic agent, to which capital is forced to ceaselessly respond. Post-Fordism, on this count, is not so much driven by new business opportunities for capital as by a need for capital to contain the struggle of organized labor through a new regulation regime – an endogenous, rather than an exogenous, shock. Like Boltanski and Chiapello (2007) in The New Spirit of Capitalism therefore, Hardt and Negri argue that the post-Fordist mode of regulation must be viewed as capital’s response to the revolts of May 1968. The soixante-huitards, as Paolo Virno (2004, 111) notes, demanded the abolition of wage labor but instead got the abolition of the stable job. That capital is merely a reactive force, then, does not mean that it cannot be historically effective.
This Trontian worldview informs Hardt and Negri’s elegy to the concept of proletarian resistance. “Resistance”, Hardt and Negri write, “is actually prior to power” (2001, 360). What is distinctive about Hardt and Negri’s workerism, however, is that they do not primarily understand the agency of labor as a historical force but as an ontological power. Hence their nominal displacement: instead of “labor” or “the working class”, they speak of “the multitude”, inspired by Spinoza’s original multitudo. In its simplest formula, the multitude represents “the power to act”, an ontological principle of self-organization, a purely immanent source of “creative positivity” (Negri 1999, 79; Hardt and Negri 2009, 179-180; 2001, 61). The multitude forms the sole “constituent power”, the only creative agent that produces both itself as well as its historic antagonists, the “constituted power” that is capital, sovereignty and Empire. Capital is thus not so much a freestanding counterforce to labor but a historical aberration of the multitude itself – a “failure to realize our own power” as Benjamin Noys puts it (Noys 2010, 112; see also Hardt and Negri 2001, 312).
More concretely, the multitude under post-Fordism makes up the collective subject of cooperative immaterial laborers under Empire. “Empire”, meanwhile, is understood as the global social order organized around “biopolitical production”, or the production of living labor and subjectivity (Hardt and Negri 2001, 24). With its post-Fordist mode of regulation, Empire thus forms the attempt of capital to capture the value that the multitude always already produces in its very mode of being and becoming. Empire’s stress on networked, collaborative and flexible production—what Hardt and Negri, following Maurizio Lazzarato (1996) call “immaterial labour”— necessarily mirrors the decentralized, cooperative creativities of the multitude, since capital must always follow labor as the sole source of value. In this sense, the post-Fordist moment can rightly be said to be a further realization of the productive capacities of the multitude, which finds itself in a feedback loop with the common: it produces the common in common through the common (Hardt and Negri 2009, 123, 148; 2017, 98). A principle of pure relationality, the multitude is this very feedback loop. Or to use Hardt and Negri’s Deleuzian language, it is the relation that pre-exists the relata.
The pre-existence of labor as a creative force also drives its primal agency. “[T]he deterritorializing power of the multitude”, Hardt and Negri (2001, 61) contend, “is the productive force that sustains Empire”. The post-Fordist formation of Empire here appears as the historical end result of the ontological pressures of the multitude, forcing capital to battle on the multitude’s home terrain of total immanence. At first glance, this may appear as a problematic proposition. It appears that, in ontologizing Mario Tronti’s sociological reversal of perspective, Hardt and Negri pre-decide historical and empirical questions concerning the development of capitalism in ontological terms. For it is not at all empirically obvious that the labor conditions in post-Fordism are the result of the dynamism of the multitude rather than of a power grab of capital in the face of stagnating accumulation in the capitalist core in the 1960s and 1970s. Moreover, Hardt and Negri explicitly eschew the type of ontology that builds in a metaphysically coercive strain of teleology: “there are no final ends or teleological goals written in history” (Hardt and Negri 2004, 221). Instead, they follow the Marxist principle that theory follows practice (Hardt and Negri 2004, 140). History and ontology therefore appear to be pulling in opposite methodological directions: the one pointing to a timeless tension between “Empire” and the “multitude”, the other situating that tension in a distinct temporal setting with history as its facade.
Hardt and Negri navigate this problem by distinguishing between a historical and an ontological multitude – in Spinozist jargon, a multitude of “actuality” versus one of “possibility”. Whereas the latter shapes an “absolute freedom” by acting in the eternity of the perpetual present, the former signals the politics required to constitute the multitude in the image of its absolute aspirations. Without falling into a Hegelianism, one can easily see these as a multitude for itself and a multitude in itself. The distinction, Hardt and Negri hurry to add, is merely analytic: the two dimensions of the multitude cannot ultimately be separated. The historical multitude, for instance, only recognizes itself in its political project based on its ontological potential. “The multitude, then, when we put these two together”, Hardt and Negri conclude, “has a strange double temporality: always-already and not-yet” (2004, 222). By joining these two faces of the multitude, Hardt and Negri explicitly refuse a false dilemma between history and ontology and keep their eyes fixed on both at once. They then infuse their materialism with just enough historical contingency to steer clear of the philosophic vice of a grand teleology. As Kam Shapiro (2004, 294) puts it: “It is here, in the space between the potential and the actual […] that Hardt and Negri interject the teleological strain of their materialism”.
Some tricky questions remain, however. It is difficult to comprehend, for instance, how a Spinozist monism that collapses yet separates the historical and the ontological does not simply end up muddying the two. There are, after all, still two countervailing tendencies in Hardt and Negri’s Spinozism: does the arrival of Empire and post-Fordism represent the liberation of the ontological by the historical? This fits well with the Spinozian picture in which the multitude is a vital force of excess that blooms through history like a flower slowly bursting through the asphalt. But this vision is explicitly denied by Hardt and Negri’s insistence on the priority of history (2004, 140), on the Marxian methodological principle that theory should always follow social reality. What, then, is history? Is it a contingent organization of materials that informs empirical sociology or is it a passive receptacle for the play of the ontological powers singled out by the Spinozists? If this question is rejected as a false dilemma, then one might ask: is the fact that historical Empire is the exact mirror image of the ontological multitude merely a momentous coincidence?
Hardt and Negri’s question is never resolved. Rather than pre-deciding on the question of what entity or force forms the motor of history, Hardt and Negri’s confusion of the ontological and the historical makes it undecidable who or what is the prime mover in capitalism. This confusion stretches out over several dimensions: ontologically speaking, it remains unclear what constitutes the difference between Empire and the multitude, or, between post-Fordism and the labor force it subsumes. Empire, for Hardt and Negri (2001, 327), represents Deleuze and Guattari’s “smooth space defined by uncoded flows, flexibility, continual modulation”, a fully immanent network that sustains all relations (Hardt and Negri 2001, 327). In contrast to “sovereignty”, which is imbued with a transcendent logic, post-Fordist capital functions through what they call, again in reference to Deleuze and Guattari, an immanent “axiomatics” (Hardt and Negri 2001, 327). “The primary characteristic of such an axiomatic”, Hardt and Negri write, “is that relations are prior to their terms”. This means, shockingly, that Empire has the exact same conceptual structure as the multitude: it is the relation that precedes the relata. Empire and the multitude thus become ontologically indistinguishable.
Adding to the confusion, Hardt and Negri argue that this indistinguishability between capital and labour is itself a product of history. Post-Keynesian capital, they maintain, survives in a permanent state of crisis: its modus operandi is the exploitation of disequilibrium and the unruly forces it discharges. As a result, it becomes increasingly difficult to grasp whether a crisis came “from above” or “from below”, whether the fall in profit was a ruse of capital or resistance from the multitude, whether rebellion or recuperation (Cooper 2011, 135). In an ironic twist, therefore, little to nothing remains of the original Trontian reversal of perspective. Both ontologically and historically, it has become impossible to say whether the current phase of capitalism results from the agency of labor or that of capital; ontologically speaking, they are both forces of pure “relationality” on the plane of immanence; historically speaking, it is radically uncertain on which empirical force one should pin crises.
Despite adversity, Hardt and Negri maintain that the multitude represents the sole ontologically productive principle. Empire itself, they claim, “is not a positive reality” (Hardt and Negri 2001, 361), but merely a “parasite”, an “apparatus of capture that lives only off the ontological vitality of the multitude” (Hardt and Negri 2001, 62; 2019b, 83). Our concluding hypothesis is therefore that in this multifaceted confusion of the historical and the ontological as well as the multitude and Empire, Hardt and Negri ultimately go with the overpowering thrust of their Spinozian monist ontology. By this picture, the multitude is the causa sui, the liberating force of excess that pushes its way through history, now driving capital into the fully immanent Empire as the last vestige onto which capital is forced in anticipation of Commonwealth. The latter is Hardt and Negri’s term for communism, which, incidentally, Negri defines as “the negation of all measure, the affirmation of the most exasperated plurality—creativity” (1999, 33). However powerful the image, it brings with it a risk to misunderstand the precarious, flexible and networked labor conditions of post-Fordism as the deepest producing-desires of the working class – and thus to downplay the continuities between pre-Fordism and post-Fordism. It is to this risk that we will now turn.
Empire’s consequences were never exclusively philosophical. Besides its claims in ontological and philosophical registers, the implications of Hardt and Negri’s argument extend far into sociology and Marxist studies more generally, leading into social movement studies, political sociology, and political theory. Most of these fields of discussion can be centered around their description of a new, distinct accumulation regime that began in the 1970s. Hardt and Negri have consistently described the advent of their “polytechnic” work as part of a distinct, new historical phase of capitalist growth. During the late-Fordist age, they claim, workers used their historical advantages and pushed beyond the “dynamic stabilization” (Tronti) of the post-war period (Smith 2019, no page). Borrowing from cybernetics and systems theory, Tronti’s concept indicated the capacity of Italian capital to harness seemingly militant demands for wage increases and public sector expansion to their benefit, channeling popular energy into increased capital accumulation. Once it was clear that the interests of labor and the interests of capital began to diverge, however, capital went on the offensive and steadily deconstructed the post-war settlement. This could not be done without acknowledging the legitimacy of some of the revolts that had taken place within that system itself, which drove the demands for increasing spontaneity, creativity, and bottom-up input. Rather than the result of falling growth rates, Hardt and Negri argue, labor militancy itself drove declining profit margins and urged a different model of governance.
A recurrent response to this deconstruction has been a version of left melancholy, lamenting capital’s supposed breach of contract after the Trente Glorieuses. But rather than lamenting the death of the post-war compromise, Hardt and Negri see a liberation from a corporatist cage which can stimulate even stronger militancy. Such activity was heralded in the Italian “hot autumn” of 1968-69, when workers ignored the dictates of union and party and began to agitate on their own terms. In ending this “dynamic stabilization”, a newly disorganized mass of casual workers became available in the interim, who would shun the large representative pillars which had structured mass working class politics throughout the twentieth century. A new “multitude” was becoming visible in the interstices of this old world, less beholden to organizational dogmas and open to institutional experimentation. Although it shared a structural location with the older, industrial proletariat, its set-up was also constitutively different, less tolerant of leaders, representation, and mediation, and less centered on the hierarchical, industrial workplace. The new class in the social factory tracked a broader systemic shift across capitalist economies. The model of the factory at the heart of Fordism separated a male sphere of production from a female sphere of consumption, the former’s commodification reliant on patriarchal decommodification in the latter (Winant 2019). Capital’s push to post-Fordism and the consequent “feminization of work”, in turn, transformed the whole of society into the factory, forcing workers to hire themselves out to a variety of employers and adopt an inviting, entrepreneurial pose (Hardt and Negri 2009, 133). “Neoliberalism” became the preferred mode of management for this new welfare world. After the tense maneuvering between capital and labor in the inflationary 1970s, an “entrepreneurial multitude” gradually came about, less collectivist than its industrial predecessor but still politically militant, and potentially more emancipatory.
In its own time this vision also generated a familiar range of critiques from Marxists. Normatively, they questioned Hardt and Negri’s emphasis on labor’s supposedly deterritorializing powers and their key claim: that labor militancy rested on a supposed refusal for measurement (Negri 1999, 33). Earlier Marxists have mainly faulted Hardt and Negri for their account of the transition and for neglecting problems of industrial overcapacity in the current economy – rather than workers who wanted too large a segment of the social product, it was a global glut of manufacturing goods that drove capital’s profit rates down in the late 1960s (Brenner 2006, 2018). At the heart of Hardt and Negri’s chronicle, however, lies a deeper ambiguity: the substantial and eerie continuities between pre-Fordism and post-Fordism. These problems can be traced back to Hardt and Negri’s conceptualization of the Fordist regime itself. In their insightful passages, Hardt and Negri did acknowledge the political preconditions for this Fordist moment. Rather than an inevitable social formation, Fordism was often a political battle for decasualization and formal labor contracts, fought between workers and management in the 1920s.
Before 1918, most labor was casual, underpaid, and precarious by nature; it was only when political struggles over these working conditions pushed towards decasualization and permanent contracts that a corporatist settlement was reached. As studies by Charles Maier (1975) and Marcel van der Linden (2014) have shown, most corporatist arrangements rebranded as “Fordist” were the result of intense revolutionary activity from 1918 to 1945, as socialist and communist parties made their first forays into bourgeois governments and began to use state power to coerce capital into the general interest (Maier 1975; van der Linden 2014, 9-21). “Fordism”, in this sense, was less of a natural stage for capitalism than a political imposition from below and above, as recent studies by Noam Maggor and Stefan Link (2011; 2018; 2020) have pointed out – an attempt to shortcut international competition and capital development without dependency, growing a solid labor force which could be kept in the factory and disciplined into consumption (see also Buck-Morss 2002). Rather than an evolutionary stage inherent in capitalism’s DNA, Fordism was a unique political product which arose out of workers’ struggles rather than being imposed on them. In no way was Fordism thus a natural development for capital, a fact that is acknowledged by Hardt and Negri but never properly thought through (Link 2018; Buck-Morss 2002; Link 2011, 2020). When viewed from the perspective of capital’s short-term interests, after all, labor protection, decasualization, welfare rights, and formal contracts are no more than legal and political barriers in the free flow of capital and its maximum valorization in production. As John Clegg notes, “in a capitalist order of fully specified property rights, it is wage labor rather than slave labor that is the anomaly” (Clegg 2015: 303). Completely “enforceable labor contracts”, in this sense, would “be the dream of many an employer”, allowing them to extract surpluses without having to honor any contractual obligations (Clegg 2015, 303).
This prehistory of post-Fordism sensitively reshuffles the stages of capitalism implicit in Hardt and Negri’s story. Rather than a completely new historical situation, the post-Fordist era has seen the return of phenomena reminiscent of a pre-welfarist capitalism. Precarious labor conditions, loss of control over labor time, or the offloading of market risks have all reappeared vigorously, now coupled to a new ideology of human capital development. A return to self-entrepreneurship and self-employment form the legal counterpart of this shift, heralded by Hayek and other neoliberal ideologues. Organized capitalism, in this sense, was an interlude, not an evolutionary successor.[2] This similarity should induce healthy caution against Hardt and Negri’s periodization. What looks like the new is rather a resurrection of the old, now motivationally enforced through a radically “embedded” form of neoliberalism, organized by states, intergovernmental bodies, and carefully constructed trade treaties (see Slobodian and Plehwe 2020).
This critique has both descriptive and normative ramifications. Descriptively, it relativizes the transition from pre-Fordism to Fordism from an ontological development to a contingent process mediated by political struggle. Normatively, this analysis casts doubt on Hardt and Negri’s assertion of labor’s supposedly deterritorializing powers, culminating in the prospect of commonwealth as the “negation of all measure” (Negri 1999, 33). Rather than a tool for employers, measurability and rationalization were often a demand pressed by workers who sought better contracts, clarified working hours, and higher pay rates. This became clear in the first bill for the 8-hour day and the setting of wage scales in Belgium, Germany, and France after the First World War. Likewise, late nineteenth century statistical research that uncoupled poverty from innate character and instead linked it to social forms of unemployment, though doubtless an instrument of state discipline and biopower, simultaneously effected a pushback against charity-based poverty relief and pried open a political field of labor market regulation and social security (Desrosières 1998, 262). More than a refusal to be “measured”, measurability was a potent response to market-dependence and workplace discipline – the insistence to enumerate the exact amount of labor paid rather than remain in the dark. As Max Henninger notes, “we have an interest in taking the categories developed in the Marxist critique of political economy more seriously than Negri seems to do, for the simple reason that if we don’t ‘do the math’ ourselves, others will do it for us” (Henninger 2007, 177; see also Morozov 2017). Capital was in large part rational when forced to be so from below or above, whether a militant working class a domineering developmental state.
Unsurprisingly, the metaphysical and historical ambiguities and inconsistencies reverberate through the post-Operatist duo’s politics. In this context, a reckoning with the influence of cybernetic theory on left-wing thinking has also remained overdue. Taken in by a new digital ideology of verticality and absence of hierarchy, Hardt and Negri built on the promises of the terrain created by the end of “organized capitalism”, where large-scale institutions such as parties and unions were replaced with looser networks and assemblies. As Hardt and Negri put it in Multitude: “once again, a distributed network such as the Internet is a good initial image or model for the multitude because, first, the various nodes remain different but are all connected in the Web, and, second, the external boundaries of the network are open such that new nodes and new relationships can always be added” (2004, xv). Here, “immaterial labor” thus “seems to provide the potential for a kind of spontaneous and elementary communism” (Hardt and Negri 2001, 294). The emancipatory switching of cybernetic languages has thus played a key role in this ambition, with computerized “societies of control” offering their own unique “line of flight” or “exodus” (Deleuze 1992). Yet, as contemporary critics continue to point out, cybernetics was never a neutral science and cannot be so today. Strangely, there are two contradictory risks involved, attesting to cybernetics’ complex logic and development: one of control and one of anti-control. First of all, with cybernetics implicated in war time strategy and post-war management, its in-built assumption of entropy and tendency toward homeostasis blunts the tools of critical analysis and smuggles in neoclassical assumptions about perfect capitalist equilibria (Galison 1994; Tiqqun 2020). On this account, offered most forcefully by Peter Galison (1994), cybernetics cannot simply be dissociated from its heritage of behaviorism, old-school rationalization and control. Rather than recognizing the persistence of hierarchy and domination in the new digital workplace, Hardt and Negri took the self-presentation of the neoliberal bloc at face value and saw the digital as a less vertical mode of organization.
Contrary to these worries of persistent control, there exists the danger of importing the “Californian Ideology” (Barbrook and Cameron, 2015) into a supposedly emancipatory program. This celebration of anti-control runs from old libertarian fantasies through 1960s counterculture into the ideology of Silicon Valley today. Underneath the rhetoric patina of horizontality and participation, this ideology thus hid an increasingly classical capitalism in which cybernetics simply imported market mechanisms into the realm of state management itself. Attempts at “repurposing” these new organizational logics – part of the general internet euphoria typical of the early 2000s – obscure this essential co-originality between cybernetic management and capitalist profit imperatives, the one driving the design of the other. And rather than superseding the immobile monolith of the party, the cybernetic swarm simply affirms and reproduces the disorganization and refusal of general will formation implicit in an atomized market. A mere fetishism for physicality – “nothing can beat the being together of bodies and the corporeal communication that is the basis of collective political intelligence and action”, as Hardt and Negri postulate recently – will not solve this organizational deficit (cited in Lovink 2016, 19; Gardiner 2020, 1-15). In the face of the paradoxical legacy of cybernetics, it is clear that there are no easy answers when it comes to politics in communication-heavy societies. The threat remains palpable however, that by buying into this “cybernetic illusion”, Hardt and Negri rather threaten to liquidate the only historic forces ever capable of coercing capital into a less adversarial mode.
A similar problem of self-presentation holds for the concept of “cognitive capital” or its cognates recurrent in the Hardt and Negri corpus (Boutang 2011; Vercellone 2007). These theories can be traced to earlier debates in the 1980s and 1990s, when the disappearance of the industrial proletariat led to theorizing about a new “non-class of non-workers” who would supervise an increasingly automated industrial landscape (Gorz 1982, 82). André Gorz’s work remains a prime point of reference here. Himself enamored with Hardt and Negri in his late life in the 1990s, Gorz and Negri claimed that the “crisis of measurability” inherent to the post-Fordist regime meant that labor itself had become impossible to standardize and all activities could now conceivably count as “work” (Marazzi 2008, 43). Workers outside of stable contracts spend their entire lives perfecting CVs and reskilling capacities or reframing every inch of human activity as enhanced human capital—all under the imperative to become as reprogrammable, networked and adaptive as the new cybernetic machines that now streamline the workplace. They thereby rendered the very notion of “socially necessary labor time” a pitiful anachronism.
Since it was no longer possible to satisfyingly measure labor performance in strict clock hours, a permanent grant would provide the only natural political response to a measurability crisis, completing the neoliberal dissolution of the waged worker. This was three years after Gorz proclaimed that “as a system, socialism was dead,” together with its “philosophy of work and history.” If the left still “stood for the emancipation of the workers,” he claimed, this would turn them into the spokespersons for “those 15 percent who still define themselves chiefly by their work” (Gorz 1994, vii). Negri usually followed Gorz on this score. “Flexibility and mobility of labor force”, he claimed in 2001, “are irreversible: The question is not to oppose the new organization of labor, but to guarantee a salary and freedom for the post-Fordist worker.” Basic income schemes remain a classical alternative here, which would allow casual contracts to survive while offering workers a minimum means of sustenance. It is a logical train of thought if one sees the negation of measure as the fulfilment of a liberating ontological movement.
A second, connected question concerns the key concept mobilized in Empire—“immaterial labor”. In Hardt and Negri’s view, the new multitude’s mode of production was less centered on the large scale, industrial factory but on the small-scale, flexible value chains of a globalized world. It also implied a change of personnel from a proletariat into a “cognitariat”, which worked with information rather than producing physical objects. As capitalist production shed its basis in concrete, physical objects, production was now more fleeting and moved into the confines of the human brain, or even into the network of cooperating brains—the social brain (Boutang 2011). Following the ontological push of the multitude, measurable labor-power had become immeasurable “invention-power”. This shift, Hardt and Negri claim, has had momentous consequences for Marx’s classical value theory. Loyalty to this theory would imply the view that labor can be measured in neat, homogeneous slices of time, which is then repaid in monetary form. Such a model of the labor theory of value was clearly premised on the figure of the factory clock, which herded workers to their posts at a time in the morning only to end by emptying at a designated ring of the bell.
Around this Fordist set-up the post-war welfare state was constructed, centering male producers who spent wages earned from material production. Post-Fordist labor markets, in which workers surf from one job to the other desperately searching for gigs, hardly conform to the same model. They also severely complicate the claim to “measurability” posited in the classical labor theory of value. As Hardt and Negri note, in a world where time discipline has become diffuse, the workplace has dissolved into an encompassing ‘social factory’ and workers are not enumerated with the same wage scales, what future is there for a labor theory of value in the classical mold? Instead of relying on the intrinsically Fordist measurement unit of “labor time”, the age of the new entrepreneur celebrates more ethereal activities and efforts. This crisis of immeasurability has received a new lease on life in a burgeoning “platform capitalism” literature, which sees a return to new decentralized forms of domination through networks, rather than the semi-military forms of discipline associated with Fordist factory (Wood 2020; Standing 2016; Huws 2019).
Yet critics have also continued to question the novelty of this “cognitariat” in recent years. As Charles Post notes, Hardt and Negri’s “immaterial labor” tends to “confuse highly material labor – work in the telecommunications industry creating and maintaining the infrastructure for computerization” with “forms of mental labor” such as “designing machinery and work-systems” (Cummings and Post 2016, 251). Rather than debunking Marx’s value theory, the paying of wages for “immaterial” activities is simply an extension of capitalist practice, not a complete qualitative break. The same continuity has been applied to Hardt and Negri’s reworking of Marxian value theory. Michael Heinrich has similarly cautioned against Hardt and Negri’s innovation. Although the transition to a service economy has undeniably rewired European economies and initiated a switch from tradeables to non-tradeables, this has not put an end to classical processes of value creation. “What is relevant”, Heinrich counters, “is the act of exchange, not the fact that physical objects are being exchanged. “Services, after all, “can also be exchanged and therefore become commodities”, and “the difference between a material product and and ‘immaterial’ service consists solely of a different temporal relationship between production and consumption: the material product is first produced and subsequently consumed (a bread roll should be consumed on the same)” (Heinrich 2012: 44).
Heinrich’s point provides a potent tonic against “the frequently stated argument” that with the “transition from an industrial to a service economy” or in the left-wing variant of Hardt and Negri— the transition from “material” to “immaterial” production—Marx’s value theory has become outmoded” (Heinrich 2012, 44). In regular economics registers, this shift has been explained in terms of a move towards non-exportables and services, part of the new “information economy” that implies a rewiring of classical economic registers (Castells 2011). Hardt and Negri’s incessant stress on the immeasurability of immaterial labor has been a powerful and welcome sociological gesture—one thinks of intellectual property, intangible assets and brand management—but should never tip over into denying the necessity of measurement as a moment in the realisation of value. Rather than a supersession of old capitalist logics, then, the advent of the computer or the cybernetic machine has not fundamentally displaced the question of class composition or the basics of class conflict, it has merely induced new cybernetic strategies for “governing” or “navigating” capitalism’s unruly contradictions.
If the twenty-first century looks uncannily more like the nineteenth than the twentieth, where does that leave us with Hardt and Negri’s multitude? Stripped of its linguistic charms, Empire’s subject looks more painfully familiar than it might: a planetary proletariat with no recourse to mass institutions or statist safety nets, slowly losing its claim to the “making” class due to deindustrialization. In essence, the new “multitude” thus reveals itself as the cybernetically managed proletariat of yore, stripped of its organizational encasing and as cruelly market-dependent as its nineteenth-century predecessor, but without the cage of “integration” (as Horkheimer put it) of a previous disciplinary era, indicating working class submission to the planning state (Abromeit 2011; Horkheimer 1978). Piece work, putting-out systems, and unsalaried labor have all seen a return in the era of neoliberalism, now engineered through algorithmic devices rather than despotic overseers. Yet the steady automation of middle management or the disappearance of the foreman in this new “digital Taylorism” do little to decrease the relevance of the nineteenth-century models Hardt and Negri are quick to reject (Leberecht 2015). In this sense, the “multitude” still offers a surface reading of a disorganized new global proletariat. Should the rise of precarious labor, sharply formulated, not rather be considered as an example of downright “class war from above”, rendering Hardt and Negri’s redeeming narrative “nothing less than ideology “ (Palmer 2014: 40)?
Such an argument for putative continuity should not obscure real differences between the pre- and post-Fordist phase of capitalism. Hardt and Negri are fully correct to insist on the new techniques of management and steering which have been implemented since the late 1960s, when capital saw a chance to break free from the post-war compromise and reclaim prerogatives over investment. In terms of political leadership, the new regime did come with a new hegemonic order – indicated by Boltanski and Chiapello’s “projective city” (2007), the justificatory regime of the “third spirit of capitalism.” Networks function as the watchword of this new city, a normative space which interpolates workers to ‘surf” the decentralized market signals as “agile”, “lean”, “employable” agents (Bernes 2017, 122; Thrift 2005). The summum bonum of the cybernetic city is the virtue of “connexionism”: the extension of the network to the benefit of all. As with Foucault’s neoliberal “governmentality”, precarious market dependence reminiscent of the nineteenth century now figure in a new strategic field in which subjects are motivated to accept their material condition under the banner of self-entrepreneurship. This is also what distinguishes digital Taylorism from its analogue predecessor: not so much a radical change in the precarity of labor conditions, but in the celebration of this precarity as “gamified”, fluid existence (Neilson and Mezzadra 2019, 82-83; Slobodian 2020). What used to run through the soft power of impersonal market coercion now is increasingly glorified through the even softer attractions of human capital development. Capital’s political encasing has thus become less top-down, hierarchical, and vertical than in the managerial age. Yet none of these normative diagrams should lead one to overstate their importance in the face of the essential continuity with the capitalism analyzed by Marx’s generations, in which the capitalist macrocosm spanned only one part of the globe (Mattick 2018, 8-9).[3]
This fact has become ever clearer to our post-2008 world, in which a global surplus population faces an increasingly stagnant capitalism unable to absorb its services. Notions such as the “multitude”, in turn, do little to elucidate the specific modalities of market dependence all workers experience and how these stratify labor markets across lines. Anno 2019, humanity inhabits an almost fully proletarianized planet: nearly 60% of the world is currently employed in wage relations with a sizable portion of the remaining 40% in partial or complete market-dependency. What was still a condition confined to European workers in the late nineteenth century – foreclosed by the safety valve of colonial emigration – is now a planetary fait accompli (Jäger 2019, 1-22).
Capitalism’s universalization should however caution against deriving a new political stand to this order. Across the global South, market-dependent producers eke out a living without employers, selling wares on the streets or marketing themselves. Ever since urbanization’s decoupling from development and development’s decoupling from growth, this surplus population has not ceased to grow (Benanav 2019, 2014; Benanav and Clegg 2010). But there is a danger of taking this new subject as a prepackaged agent rather than a truly “deterritorialized” anti-subject deserving of legal rights. As Mike Davis notes, speculations about “a new politics of ‘multitudes’ in the ‘rhizomatic spaces’ of globalization remain ungrounded in any real political sociology” (Davis 2020, 7). Rather than focusing on the differing scales of market dependence in the new global economy, Hardt and Negri took the cyber-proletariat as a given and transposed it into an ontological category (Dyer-Witherford 2015). While the attempt to find a new idiom to collect and unite all those wretched of the earth—including those not employed in wage labor—must be applauded, there is a definite risk involved in the task. As Davis (2020, 7) sharply claimed, “imprudent coronations of abstractions like the ‘multitude’ as historical subjects simply dramatize a poverty of empirical research” and do little to point at potential conflicts of interest between sections of the wage dependent classes.
Rather than a new phase of ontological prowess, the new multitude thus tends to appear as the result of a failed Fordist integration which has reverted back to the classical age – a radically embedded neoliberal capitalism in which capital is longer an agent of growth and thrives on state predation. Likewise, Davis cautions against celebrations of spontaneity and casualness which come with these “ideologies of informality” (Van Ballegooijen and Rocco 2013, 1794-1810; Scott 1999; DeLong 2007). Rather than arguing for cash transfers or microcredit for the slums, the classically “Fordist” demand for labor rights, coupled with transformative post-growth programs, should still be at the center of an anti-neoliberal left. To claim the proletariat is “fading away” in the face of the “increasing heterogeneity of work situations and, thus, of social conditions”, as sociologists in the information age often do, elides the fact that “informal workers… tend to be massively crowded into a few major niches where effective organization and “class consciousness” might become possible if authentic labor rights and regulations existed” (Davis 2000, 185 (f)). Overall, “it is the lack of economic citizenship, rather than livelihood heterogeneity per se, that makes informal labor so prone to clientelist subordination and ethnic fragmentation” (Davis 2000, 185 (f)) More than a new political subject, the new “multitude” thus risks tumbling into its very opposite: a floating signifier in desperate search of material grounding in our social reality. At worst, it is a symptom of the disorganization of the populist age in which the measurement techniques of focus groups, real time polls and approval ratings struggle to delineate “the people”. These metrologies have become the face of the multitude’s supposed “immeasurability” (Csigo 2017; Cooper 2011; Feher 2018).
This strategy would require more than invocations of an “entrepreneurial multitude” which survives in the grottoes of globalization, and revisit earlier questions of social rights and decommodification (Hardt and Negri 2018, 146). “The main issue in the informal sector”, Davis notes, “is normalization of the rights and protections of labor, not property” (Davis 2000, 185 (f)). Such a vision would depart from the accelerationist optimism implicit in the Negrite vision, which celebrates the new informal masses as harboring an exclusively new emancipatory promise. Instead, even the oldest dogmas of social democracy, from labor rights to public provision, are “as good as ever”.[4] The closing of the left-populist decade, symbolized by the successive defeats of the Sanders, Syriza, and Corbyn coalitions, has made this point even clearer: rather than stick to an horizontalism, left populists began by returning to the party and rethinking the organizational basics of a previous age. Although they failed, the questions they asked had been left neglected and underused, distracting leftists from the task that the twentieth century originally posed – and which Hardt and Negri sought to bury in 1999.
*
Coming at the tail end of a series of anti-police protests and the storming of the Capitol, early 2021 offers a unique vantage point to assess the valences of Empire. At the close of the neoliberal 1990s, Hardt and Negri’s work offered creative and penetrating insights into the changing nature of labor under capitalism and the ramifications of the neoliberal settlement. It spoke to a disenchanted left traumatized by the counter-revolutionary wave of the 1980s and 1990s, which pulverized the structures of an organized left in the Third World, Europe, and the US, and liquidated the fragile counter-powers built up during the red century. Empire was a new theory for new times, forcing the left to strategies on new terrain. As a holistic theory of politics and social change, its omissions still risk underplaying the continuities between pre- and post-Fordist capitalism and reads an erroneously emancipatory dynamic into a mode of cybernetic management now sold as human capital development. This historical sloppiness and slipperiness stem from a series of metaphysical blunders, where cybernetic techniques of labor control and new strategies of accumulation are recast as an ontological subject reaching its final state. Its practical consequences remained equally suspect: the “multitude” refuses a politics and sociology of class articulation and skirts over real differences in today’s proletarian landscape, abandoning the sphere of production and measurability to a new illiberal bloc (Slobodian 2018; Körösényi, Illés, and Gyulai 2020). As the left-populist decade ends and movementism regains its attraction, Empire indeed seems to offer a useful point of retreat for a newly disillusioned left. One must wonder, however: what is gained by racing from one cul-de-sac into another?
Bibliography
Balestrini, Nanni. 2020. The Golden Horde: Revolutionary Italy, 1960-1977. New York: Seagull Books.
Barbrook, Richard, and Cameron, Andy. 2015. The Internet Revolution: From Dot-com to Cybernetic Communism. Amsterdam: Institute of Network Cultures.
Benanav, Aaron. 2014. “A Global History of Unemployment: Surplus Populations in the World Economy, 1949-2010,” PhD Thesis (2014), University of California, Los Angeles.
Benanav, Aaron. 2019. “Demography and Dispossession: Explaining the Growth of the Global Informal Workforce, 1950-2000.” Social Science History, 1-25.
Benanav, Aaron. 2020. Automation and the Future of Work. London: Verso Books.
Benanav, Aaron, and Clegg, John. 2010. “Misery and Debt: On the Logic and History of Surplus Populations and Surplus Capital.” Endnotes 2: no page.
Boltanski, Luc, and Chiapello, Ève. 2007. The New Spirit of Capitalism. London, New York: Verso Books.
Boutang, Yann Moulier. 2011. Cognitive Capitalism. Cambridge; Malden: Polity Press.
Brenner, Robert. 2006, Economics of Global Turbulence. The Advanced Capitalist Economies from Long Boom to Long Downturn. London: Verso.
Buck-Morss, Susan. 2002. Dreamworld and Catastrophe: The Passing of Mass Utopia Between East and West. Cambridge, MA: The MIT Press.
Castells, Manuel. 2011. The Rise of Network Society. London: John Wiley & Sons.
Celano, Paulo. 2001. “Toni Negri, Profile of a Terrorist Ideologue.” Executive Intelligence Review: 16-17.
Clegg, John. 2015. “Capitalism and Slavery.” Critical Historical Studies 2:2 (Fall): 281-304.
Cooper, Melinda. 2011. “Complexity Theory After the Financial Crisis: The Death of Neoliberalism or the Triumph of Hayek?” Journal of Cultural Economy: 371-385.
Cooper, Melinda. 2011. “Marx Beyond Marx, Marx Before Marx: Negri’s Lucretian Critique of the Hegelian Marx.” In Reading Negri: Marxism in the Age of Empire, edited by Pierre Lamarche, Max Rosenkrantz and David Sherman, 127-148. Chicago; LaSalle: Open Court.
Csigo, Peter. 2017. The Neopopular Bubble: Speculating on “the People” in Late Modern Democracy, Budapest: Central European University Press, 2017.
Cunliffe, Phillip. 2020. The New Twenty Years’ Crisis: A Critique of International Relations, 1999-2019. Montreal: McGill-Queen”s Press.
Davis, Mike. 2000. Planet of Slums. London: Verso Books.
Davis, Mike. 2020. Old Gods, New Enigmas: Marx”s Lost Theory. London: Verso Books.
Eichengreen, Barry. 2018. The Populist Temptation: Economic Grievance and Political Reaction in the Modern Era. New York: Oxford University Press.
Feher, Michel. 2018, Rated Agency: Investee Politics in a Speculative Age. New York: Zone Books.
Desrosières, Alain. 1998. The Politics of Large Numbers: A History of Statistical Thinking. London; Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press.
Galison, Peter. 1994. “The Ontology of the Enemy: Norbert Wiener and the Cybernetic Vision.” Critical Inquiry 21(1).
Gorz, André. 1991. Capitalism, Socialism, Ecology. London: Verso Books.
Hardt, Michael, and Negri, Antonio. 2001. Empire. Cambridge, MA; London: Harvard University Press.
Hardt, Michael, and Negri, Antonio. 2003. Labor of Dionysus: A Critique of the State-Form. Minneapolis: University of Minnesota Press.
Hardt, Michael, and Negri, Antonio. 2004. Multitude: War and Democracy in the Age of Empire. New York: Penguin.
Hardt, Michael, and Negri, Antonio. 2009. Commonwealth. Cambridge, MA; London: Harvard University Press.
Hardt, Michael, and Negri, Antonio. 2017. Assembly. Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Hardt, Michael, and Negri, Antonio. 2019a. “Empire, Twenty Years On”, see https://conwayhall.org.uk/event/michael-hardt-and-antonio-negri-empire-twenty-years-on/
Hardt, Michael, and Negri, Antonio. 2019b. “Empire, Twenty Years On.” New Left Review 120 (November-December): 67-92.
Heinrich, Michael. 2012. An Introduction to the Three Volumes of Karl Marx”s Capital. New York: NYU Press.
Henninger, Max. 2007. “Doing the Math: Reflections on the Alleged Obsolescence of the Law of Value under Post-Fordism.” Ephemera 7(1): 158-177.
Henwood, Doug. 2001. “Blows against Empire.” Left Business Observer 96 (February): no page.
Huws, Ursula. 2019. Labour in Contemporary Capitalism: What Next? London: Springer.
Jäger, Anton. 2019. “Back to Work: Review of David Graeber”s Bullshit Jobs.” nonsite: 1-22.
Kioupkiolis, Alexandros. 2016. Radical Democracy and Collective Movements Today: The Biopolitics of the Multitude versus the Hegemony of the People. London: Routledge.
Körösényi, Andras, Illés, Gábor and Gyulai, Attila. 2020. The Orbán Regime: Plebiscitary Leader Democracy in the Making. London: Routledge.
Cummings, Jordy, and Post, Charles. 2016. “Rethinking Precarity and Capitalism: An Interview with Charlie Post.” Alternate Routes 27: 248-260.
Lazzarato, Maurizio. 1996. “Immaterial Labor.” In Radical Thought in Italy: A Potential Politics, edited by Paolo Virno and Michael Hardt, 133-147. Minneapolis: University of Minnesota Press.
Leberecht, Tim. 2015. The Business Romantic: Give Everything, Quantify Nothing, and Create Something Greater Than Yourself. New York: Harper & Collins.
Linden, van der Marcel. 2014. “San Precario: A New Inspiration for Labor Historians.” Labor Studies in Working-Class History of the Americas (March): 9-21.
Link, Stefan. 2011. “Rethinking the Ford-Nazi Connection.” Bulletin of the German Historical Review 49 (Fall): 134-141.
Link, Stefan. 2018. “The Charismatic Corporation.” Business History Review 92 (Summer): 85-115.
Link, Stefan. 2020. Forging Global Fordism: Nazi Germany, Soviet Russia, and the Contest over the Industrial Order. New York: Princeton University Press.
Lovink, Geert. 2016. Social Media Abyss: Critical Internet Cultures and the Force of Negation. London: Polity.
Maier, Charles. 1975. Recasting Bourgeois Europe: Stabilization in France, Germany and Italy in the Decade After World War I. New York: Princeton University Press.
Marazzi, Christian. 2008. Capital and Language: From the New Economy to the War Economy. Los Angeles: Semiotext(e).
Morozov, Evgeny. 2017. To Save Everything, Click Here: The Folly of Technological Solutionism. London: Public Books.
Negri, Antonio. 1999. “Value and Affect.” Boundary2 26(2): 77-88.
Neilson, Brett and Mezzadra, Sandro. 2019. The Politics of Operations: Excavating Contemporary Capitalism. New York: Duke University Press.
Norris, Pippa, Inglehart, Ronald. 2016. “Trump, Brexit, and the Rise of Populism: Economic Have-Nots and Cultural Backlash.” Harvard Kennedy School Faculty Research Working Paper Series: 1-31.
Noys, Benjamin. 2010. The Persistence of the Negative: A Critique of Contemporary Continental Philosophy. Edinburgh: Edinburgh University Press.
Palmer, Bryan D. 2014. “Reconsiderations of Class: Precariousness as Proletarianization.” Socialist Register 50: 1-40.
Shapiro, Kam. 2004. “The Myth of the Multitude.” In Empire’s New Clothes: Reading Hardt and Negri, edited by Paul Passavant and Jodi Dean, 291-317. New York; London: Routledge.
Shukaitis, Stephen. 2015. The Composition of Movements to Come: Aesthetics and Cultural Labour After the Avant-Garde. London: Rowman & Littlefield.
Slobodian, Quinn. 2020. Globalists: The End of Empire and the Birth of Neoliberalism. New York: Harvard University Press.
Slobodian, Quinn. 2018. “You Live in Robert Lighthizer”s World Now.” Foreign Policy (August 6), no page.
Slobodian, Quinn, and Plehwe (eds.), Dieter. 2020. Nine Lives of Neoliberalism. London: Verso Books.
Smith, Jason. 2020. Smart Machines and Service Work: Automation in an Age of Stagnation. Chicago: Reaktion.
Standing, Guy. 2016. The Precariat: The New Dangerous Class. London: Bloomsbury.
Thrift, Nigel. 2005. Knowing Capitalism. London: Sage.
Tiqqun. 2020. The Cybernetic Hypothesis. Cambridge, MA: Semiotext(e) and MIT Press.
Tronti, Mario. 2019. Workers and Capital. Translated by David Broder. London: Verso Books.
Van Ballegooijen, Jan, and Rocco, Roberto. 2013. “The Ideologies of Informality: Informal Urbanisation in the Architectural and Planning Discourses.” Third World Quarterly 34: 1794-1810.
Vercellone, Carlo. 2007. “From Formal Subsumption to General Intellect: Elements for a Marxist Reading of the Thesis of Cognitive Capitalism, in Historical Materialism.” Historical Materialism 15(1): 13-36.
Warde, Alan. 1985. Consensus and Beyond: The Development of Labour Party Strategy Since the Second World War. Manchester: Manchester University Press.
Wood, Alex. 2020. Despotism on Demand: How Power Operates in the Flexible Workplace. New York: Cornell University Press.
Winant, Gabriel. 2019. “Hard Times Make for Hard Arteries and Hard Livers” Deindustrialization, Biopolitics, and the Making of a New Working Class.” Journal of Social History 53(Fall): 107-132.
[1] For contrasts with the “populist” decade, see Laclau (2005).
[2] As Charles Post (in Cummings and Post 2016, 251) notes, “the ‘Golden Age’ was… exceptional in the history of capitalism… the product of a combination of a long period of rising profitability (1933-1966) and a militant labor movement across the industrialized world. Workers had threatened the foundations of capitalist rule (France and Spain in the mid-1930s, France and Italy immediately after World War II, France in 1968, Portugal 1974-1975) or severely disrupted capitalist accumulation in mass strike waves in the mid-1930s, immediate post-war years and again between 1965-1975. Capital was forced to make major concessions to labor.”
[3] As Mattick (2018, 8-9) notes, “when Marx wrote Capital, capitalism was hardly the world’s primary system for the production and distribution of goods (even in England there were still more domestic servants than industrial workers), though it could be argued that at least in Europe and North America it was already socially dominant, in the sense that its institutions were central enough to social life to determine their continuing growth in importance as society continued to evolve. By abstracting from the complex range of features characterizing the actual societies of his time to focus on what he took to be basic to capitalism as such, Marx was able to explain both the evolution towards a more completely capitalist society and specific, apparently essential, features of that evolution.”
[4] A phrase used by Michael Foot to celebrate Tribune’s twentieth anniversary (Warde 1982, 85).

by Seamus Deane
In its drive for universal dominion, the most barbaric global force of the last seventy years has been American foreign policy. Among its most notable creations has been American domestic right-wing nationalism. By extension, this has been reproduced, as part of the enormous projection of American power, as similar domestic nationalisms in numerous parts of the globe. So exact has this process of reproduction been that the leaders of these ‘populist’ movements bear an uncanny resemblance to one another, boiler-plate reproductions of a composite of gangsterism, deceit, violence, ignorance, racism, baroque evangelical religious convictions and a matching derision for expertise (a contemporary mode of anti-intellectualism), plus billionaire support and well-honed social media skills. They include Trump, Netanyahu, Johnson, Bolsonaro, Modi, Berlusconi, Salvini, Orbán, Erdoğan, Kaczynski, Sisi — to name but a few.
The USA had been producing Republican grotesques for some decades —Nixon, Reagan, the elder Bush, but then, like fully evolved mutations of a political climate change, emerged two paragons in excelsis of the type – George W. Bush and Trump. The sun belts and the bible belts had combined to produce the first three of these for the Republican party. Trump, though, went further; he fused them with the rust belt(s) and made bigotry, racism, resentment, the celebration of economic inequality, the most active core values of an under-educated and brainwashed electorate. These became renovatory for a party that needed to find some species of ideology to bolster its practices of gerrymander, voter suppression and non co-operation that, since Newt Gingrich and Karl Rove, had become daily exercise routines for a Republican Party, determined by every possible means to ward off the threat of demographic change. These populist movements also bear strong family resemblances – fundamentalist religious furies, bug-eyed on the same issues, like hostility to abortion, immigration, support for internal domestic and for international violence; white racism, always front and centre, imperial fantasies, enmities old and new – Russia, China, Iran, Islam,’socialism’ –and a global economic system run like a protection racket.
‘We can’t predict the future but we can always change the past’ is an old joke but works also as a rationale for many historians. The past American century could do with some revisionism; otherwise, it would be possible to believe that the astonishing power and incompetence of the US military and political classes have had no rival since the Fall of Rome. Unopposed in the air, the US has spent twenty years in Afghanistan, seventeen years in Iraq, in Syria openly since 2014, bombing non-stop in all. We can only roughly count in multi-millions the civilian deaths inflicted by the USA, starting in 1950, from Korea to Vietnam, Laos, Cambodia, across Asia to the ruined Middle East – not to mention Central and South America. American presidencies are primarily remembered in the wider world for catastrophic war: Truman (atomic war on Japan, pulverizing of North Korea), Johnson (chemical warfare, (plus white phosphorus and napalm), Vietnam), Reagan (Central America), Bush Snr. (Panama, Iraq), Clinton (Serbia, Iraq), Bush Jnr. (Iraq, Afghanistan), Obama (Afghanistan, Libya, Syria, Yemen, Somalia, Pakistan) and the proxy wars of its criminal allies, Israel (Gaza, Lebanon) and Saudi Arabia (Yemen).
One can show this policy of warmongering has been long established, especially among what we call western democracies – Britain, France, the USA – as they have feasted, since the mid nineteenth-century, on the remains of the decaying Spanish, Ottoman and Austro-Hungarian Empires and have taken, by force and duplicity, the natural mineral resources of the Middle East, especially oil. The fall of the Soviet Empire has stimulated comparable political appetites. Wearing the bib of NATO, the US has been, since 1989, digesting several former Soviet republics. The right-wing nationalism of Ukraine, for instance, has served as an especially piquant sauce while a cold-eyed Putin, on the other side of the table, is compelled to watch this steady mastication of the remnant of the former USSR and the Warsaw Pact countries. With Yugoslavia dissolved, Serbia bombed, NATO and the EU expand almost in lockstep in the process of incorporating the former enemy and its ‘near abroad’, now ringed by US military bases and heavily infiltrated by the CIA. Only the Covid-19 plague has prevented the proposed display of minatory American/ NATO military games in the regions where the Soviets once destroyed the spectacular Nazi military machine.
Perhaps the radical switch to global domination came with World War I when European interstate wars were magnified into a global struggle. More specifically, it came with the refusal of the US Senate in 1919 to ratify Woodrow Wilson’s proposed League of Nations on the grounds that the USA refused to be dragged into wars on behalf of others. It would choose its own wars and when it did, they would be global. Or one might say, as Carl Schmitt did, that the change came with the Kellogg-Briand pact of 1928 or, to give its full title, General Treaty for the Renunciation of War as an Instrument of National Policy. That was interlinked with the Stimson doctrine of 1932 which declared that the USA had, according to the 1928 pact, the right to decide the justice or injustice of any territorial change anywhere in the world. Schmitt pointed out that this global interventionism had been repudiated by the USA only a lifetime earlier, in 1861, when the UK recognized the Confederacy as a ‘belligerent faction’ in the American Civil War. Such recognition was itself an intervention. Intervention had by 1932 become a more doctrinal affair, with global range and yet its legitimacy was confined by Stimson to the decision of one nation alone.[1]
So as the low dishonest decade of the 30s dawned, the system of international law was decisively shifted from its former European to an American base; interstate agreements and the ‘bracketing’ of war were, by fiat, globalized. War, as such, had been criminalized at the Versailles Treaty of 1918. The then most recent civil war in Russia, begun by the Whites and supported warmly but not competently by the UK, produced a polity the very principles of which challenged the legitimacy of the Great Power States in particular.
At first, it appeared that Europe was the decisive zone of struggle across the fifty years of war and inter-war. But, in the long run, it was not. The increasingly possible German turn to the left after WWI was halted by the brutal Freikorps murders of Rosa Luxembourg and Karl Liebknecht in 1918. Contrastingly, the ominous turn to the right in Germany was finally facilitated in 1933, when the fragile Weimar republic was transferred by the vain and treacherous von Hindenburg to Hitler’s Nazi grip for safe keeping.[2] The long French turn to the alt-right had begun with the Dreyfus case of 1894-1906; when Charles Maurras was sentenced to life for treason in 1954, he declared his punishment was revenge for Dreyfus, served cold after sixty years. Right and left in France had long been in dangerous equipoise. Only a year separates the firing-squad executions of Marc Bloch by the Nazis and Pierre Laval by De Gaulle’s government. Both died with ‘Vive la France!’ on their lips. Pétain just beat de Gaulle to the punch in that instance. A close-run thing in both Germany and France.
Yet these tragic national moments quickly lost much of their dramatic force, especially in the ‘near abroad’ retrospect of the European Community. The angles of intrastate and interstate frictions began to alter in the larger and yet more shriveled spaces of the Cold War. Hitler’s fanatical concentration on the Russian front was the one element of his strategic approach that survived his defeat and became American doctrine. The USSR, fellow- and pre-eminent victor in the War, had been the real enemy of the USA all along. The question had been, which would destroy Germany first? The answer was the USSR, but not before being irretrievably weakened by its losses, its demographic profile an indicator of the catastrophic long-term damage it suffered then.[3]
National post-war conflicts revealed the intramural war that had been strategically conducted in secreto in 1939-45 and became manifest thereafter in the Cold War. Its first battle was to decide who got the credit for winning World War II. Some of it had to be ceded to Russia; but was it Soviet or Mother Russia? The latter, who had beaten the last world conqueror, Napoleon, had (the story went) done it again, despite then Czarist, now Stalinist, tyranny. But, alas, it was the Soviets who appeared at Yalta and there were powerful communist parties in France and Italy. Communist contributions to the defeat of fascism in those countries were first downplayed by the domestic right and then almost erased by the exemplary and brutal US intervention in the Italian 1948 elections. (The Irish embassy in Rome co-operated in relaying American dollars to the Vatican for the support of Catholic candidates.) The past had to be rewritten for the sake of the future.
Yet the great damage the Americans sought to do to the communists in Europe was almost superfluous, since the Soviets did it for them with their robotic repression and their manufacture of atheistic boredom outmatching the US manufacture of consumerism and kitsch religious fervor. The Americans were able to begin the Cold War by obliterating North Korea in 1950, secure in the belief that most of Western Europe had by then been made safe for democracy and capitalism; in the Iberian peninsula, for dictatorship and capitalism. Eastern Europe and the Balkans were anaesthetized. The geo-political balance was not only kept but reinforced during the ‘trente glorieuses’ years of prosperity, 1945-75, even through the breakdowns and massacres of the fading Anglo-French empires, (India-Pakistan, Kenya, Nigeria, Rhodesia, Algeria, Indo-China). Colonies re-coagulated into the Third World. The Cold War reached its peak of tension in the Cuban crisis of 1963. As the Soviet Union twitched towards its demise, Western Asia (now the Middle East) began to overtake it as the focal point of global struggle. America’s Israel began its wider wars for domination; apartheid and genocide, well-learned in Nazi Germany, now practiced in the lone surviving fascist state, were re-programmed as democracy and defence of the Western promontory in the East. Israel’s America outfaced the new Great Beast, Islam, its ramshackle, mostly Arab, autocracies and their vast lakes of oil, with fleets of weapons from the Pentagon and televangelistic ravings, once anti-semitic, now pro-Israeli, on the Jewish role in the End Days on the new sound-track as the bombs rained down.
Perhaps the idea that has infiltrated most deeply behind democratic defences, partly because they had decayed or been exposed or had often simply been pretences, was that bureaucratic and discursive modes of government were of their nature not only given to moral emptiness but were actually devoted to the creation of it. In its first and still most influential modern articulation by Carl Schmitt, in the Germany of the 1920s and early 30s, this first appeared as a clarifying analysis, parading the virtue of decisionism as a power to overcome Weimarian chaos but, in addition, as a theory of power, envisioned as a surgical act that cleared the functioning of a body politic blocked by endless discussion . This is often and rightly regarded as a defence of dictatorship but it is perhaps even more effective in its negative force as the claim that deliberative democracy cannot but abandon basic moral instincts in order fully to be itself.[4] Although the stain of that accusation spread quite slowly within Europe and the USA, it began to accelerate in the sixties, precisely when democratic protest against the Vietnam war, against sclerotic authority, seemed to have gained democracy a high prestige. The reaction was quick. Ronald Reagan, elected as governor of California, promptly carried out his notorious assault on the Berkeley campus, staff and city itself (1967-69). He was one of the first populists, ruthless, vacuous, a commercial for American capitalism as the main attraction with Religion as the B-movie and a Las Vegas-Biblical rhetoric for both. Further, a remarkable shift within academic discourse began in that decade and continues still. In brief it involved a deflection into the American academy and political world of the negativing power of Carl Schmitt’s thought. This deflection was achieved by the adoption by a kind of whining ricochet of Carl Schmitt via the writings and teachings of Leo Strauss in a concerted ambush on modernity and the Enlightenment.
Quite how this took place is an intricate story. An early recruit into the anti-modernity narrative was Edmund Burke. A predominantly Catholic, Irish and Jesuit commentary replaced utility with prudence as the key term in his thought and his revolutionaries became the subhuman others by whom the Christian civilization was suborned at its centre. [5] Stalinism also played its feral role in the standard refiguring of the Russian revolution as a replay of the French; the interpretive rein was tightened to restrain all revolution, revolution as such, from destroying that mass of inarticulable belief which, for the Straussian version of the plebs, was their zone of the ignorant sublime while the governing elite communicated actual knowledge by esoteric semaphore.[6] One problem was that those—like, say, Allan Bloom—who most loudly lamented the disappearance of the deep truths of tradition were themselves the most pernicious betrayers of it. If one can speak of an American or any other kind of titular national ‘Mind’, it only reveals how much time the author wasted in reading the ‘classics’ that are ostensibly to save it. [7] But the very vulgarity of this discourse is what made it so amenable to such political ends as it was used for in the days of Wolfowitz and Cheney and their ilk during the bloody wars, by no means ended yet, of the Bush administration. The ever-expanding ‘war on terror’ has, on top of slaughter, produced an unexampled exodus of people from Western Asia and the Middle East, victims of the terror of a war which was itself the most intense instalment yet in a long series of assaults already decades long. Launched by lies, supported by sycophants, equipped with weaponry whose users rejoiced in its unmatched destructive and annihilating range, the war pulverized helpless populations, their homes, the infrastructure of their cities, hospitals and mosques. Their remnants fled to the refugee camps, the snail-trail of misery left by the passage of the American war-machine. Now the region is dominated by carious, aftermath political regimes and sectarian civil wars, while Europe’s shores seethe with displaced immigrants. The bombing of Libya by NATO made it a war zone, opened Africa wide to the ISIS created in Iraq. The Taliban have returned in Afghanistan, the Shia crescent from Iran to Syria has consolidated, Yemen has became an apocalypse under Saudi bombs and in the midst of all, Trump, after a series of assassinations and displays of random force, has suddenly announced America First and started to withdraw, leaving behind Bush’s initial and now unimaginable mess.
After WWII, Alexandre Kojève envisaged history ending in the arms of a Kantian federated Europe; but it turned out to be only what we now know as the EU, finally relieved of the UK. And the series of judicial coups that marked the development of the EU, confirmed that its democratic deficit was more the consequence, maybe even the aim, of policy rather than some unfortunate side- effect.[8] Francis Fukuyama, at the end of the Cold War imagined it ending in a neo-liberal capitalist paradise, finally relieved of political conflict.[9] At least, after the latest attempt at world domination by the USA (which we might date to 1991), after the financial crisis of 2008, the Pandemic of 2019 –, and the anti-Enlightenment of the Internet age, no-one, apart from all the evangelicals who set off like commuters for their daily incandescence, is going to announce the end of history in any foreseeable future.
Perhaps we can again take direction from the Old Right. Carl Schmitt, claimed that, since the declaration of the Monroe Doctrine in 1813, the USA has been caught up in a dialectic of interventionism and isolationism.[10] Right now, with the end of the Trump presidency, perhaps an isolationist phase has set in; in a tectonic shift, the manic right has begun to be consumed in its own negation. With the 2021 invasion of the Capitol perhaps the USA, weary of invading everywhere else, has decided, to the world’s relief, finally to invade itself.
Seamus Deane is Professor of Modern History and American Literature at University College, Dublin. He has published two books of poems, Gradual Wars and Rumours.
[1] Carl Schmitt, The Nomos of the Earth in the International Law of the Jus Publicum Europaeum trans. and annotated by G.L.Ulmen (New York: Telos Press Publishing, 2006), 279, 296-99. See the recent plea for a return to a truly liberal foreign policy in the USA: David C. Hendrickson, Republic in Peril: American Empire and the Liberal Tradition (New York: Oxford University Press, 2018), 161-210, 216-17. But the endless whitewashing of the ‘new international order’, including the UN, as a juridical operation that began with the Kellogg-Briand pact continues apace. See Oona Hathaway and Scott Shapiro, The Internationalists: How a Radical Plan to Outlaw War Remade the World (New York: Simon and Schuster,2017).
[2] See Christopher Clark, Iron Kingdom: The Rise and Downfall of Prussia, 1600-1947 (London: Penguin Books, 2007), 655-58.
[3] Tony Wood, ‘Russia Vanishes’, London Review of Books (6 December, 2012), 39-41. Adamson, David M. and Julie DaVanzo, Russia’s Demographic ‘Crisis’: How Real Is It?. Santa Monica, CA: RAND Corporation, 1997. https://www.rand.org/pubs/issue_papers/IP162.html.
‘Today Russia is experiencing rapid population aging that will accelerate in the next two decades. The patterns and trends of population growth and aging in Russia have been strongly affected by such catastrophic events as the two world wars, the civil war, and famines. These catastrophes have distorted the population age-sex structure. For example, due to huge losses during the World War II, Russia has the lowest male-to-female ratio in the world, especially among the elderly. The irregularities of the age-sex pyramid will have an impact on the rate of population growth and aging for several decades.’
[4] Schmitt, Political Theology: Four chapters on the Concept of Sovereignty (Chicago; University of Chicago Press, 2004,[1922]), 62. In his polemical account of the conservative thought of Donoso Cortés, he says that for Cortés, ‘Liberalism…existed…only in that short interim period in which it was possible to answer the question “Christ or Barabbas?” with a proposal to adjourn or appoint a commission of investigation.’
[5] See my ‘Burke in the United States’ in The Cambridge Companion to Edmund Burke ed. David Dwan and Christopher J. Insole (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2012), 221-32.
[6] Leo Strauss, Natural Right and History (Chicago: University of Chicago, 1953). The opening pages in particular of this work show Strauss’s strong affinity with Schmitt; For example, pp.5-6: ‘genuine choice is nothing but resolute or deadly serious decision. [It] is akin to intolerance rather than to tolerance. Liberal relativism has its roots in the natural right tradition of tolerance…but in itself it is a seminary of intolerance.’
[7] Allan Bloom, The Closing of the American Mind (New York: Simon and Schuster, 1997)
[8] On Alexandre Kojève’s aide-mémoire The Latin Empire: Outline of a Doctrine of French Policy’, see Thomas Meaney, ‘Fancies and Fears of a Latin Europe’, New Left Review, 107, (Sept/Oct 2017), 117-30. See Perry Anderson, ‘The European Coup’, London Review of Books (17 December, 2020), 9-23.
[9] Francis Fukuyama, The End of History and the Last Man (New York: Free Press, 1992).
[10] Schmitt, Nomos of the Earth, 253-55.

by Elissa Marder
I think it would be a real mistake to imagine that we are now entering “life after Trump.” Although Trump’s presidency did rupture something in American life by ushering in a scary new day for American fascism, the roots of Trumpism took hold long before Trump took office, and the impact of the Trump-effect is far from over. The Trump era has taken us dramatically and I suspect irrevocably Beyond the Reality Principle. The possibility of “life after Trump” would need to be an actual reckoning with the painful realities that face us (climate change, the enduring legacy of slavery, the carceral system, poverty) rather than a nostalgic wishful hope that we can simply return to the way things supposedly were “before.” Joe Biden won the election not by being Biden but by not being Trump. The idea that Biden could simply “make America a democracy again” is itself a fantasy that invests in some of the very same myths about American political life that Trump exploited for his own populist, racist, and fascist ends. Trump not only violated political norms, institutions, science, facts, and trust but was rewarded for doing so by the Republican leadership and by more than 72 million American voters.
We need to take up the challenge of understanding why Trump’s assault on the reality principle was so effective and so appealing to so many. Why—after more than four years of his abhorrent rhetoric and political tactics, has political resistance to him—from both the left and the more traditional right—been so feeble? 72 million US citizens voted for Trump. Some of those people fully embrace his toxic rhetoric and his warped world view. Others claim to have made a rational decision to vote for him by pointing to his economic policies or his support for American businesses. In fact, however, given his blatant and triumphant disregard for the truth, facts, the constitution, and the rule of law, one could not vote for Trump without also voting against the reality principle. Every vote for Trump was also a vote against truth.
In this domain, the opposite of truth is not a lie, but a wish. Trump peddles magical thinking and weaponizes Freudian dream logic. Unlike most other fascist leaders, he doesn’t give a damn about politics, policy, or ideology. He doesn’t believe in anything other than his own perverse infantile fantasy of phallic infallibility. But what we must work to understand is how and why his grandiose and simplistic pronouncements touched so many people so very deeply.
Denial is his super-power. His refusal—or inability—to respect any prohibition, restriction, or limitation of his own will-to-power apparently enthralled his admirers. His seemingly unlimited capacity to demand that the world bend to his infantile view of it inspired his followers to join him on the path beyond the reality principle. He made those people feel that he recognized their distress and that he—and he alone—could make it go away. Most of his promises were absurd: Mexico will pay for the wall; the coronavirus will vanish by Easter. But it is as if the very absurdity of these promises only further cemented his power. He dared to express impossible wishes. Trump’s grip on his own fantasy is like a twisted reversal of the Lacanian dictum not to give way on one’s desire. He never ever concedes to the reality principle. It is through the prism of this denial that he touched so many. We must take the measure of the despair, anxiety, shame, helplessness, and fear that underlies a vote for Trump. 72 million people voted for him because he promised them a way of escaping, denying, or avoiding some aspect of reality that had indeed become unbearable. There is an important truth to be reckoned with here: what if those people needed his absurd promises precisely because certain aspects of reality have become unthinkable and hence unbearable. The omnipresent specter of climate change and global warming, for example, cannot be processed by individual psyches because there is little—if anything—that individual people can do to stop the devastation that hovers on the horizon. Quotidian survival requires that we deny the magnitude of that devastation. In the case of climate change, denial of reality only accelerates and exacerbates the very reality that it aims to deny. The thread that connects all of Trump’s supporters (whether they are white supremacists, white collar capitalists or workers in obsolete industries) is a need to ward off acceptance of a loss that is disavowed because it is felt to be unbearable. Trump apparently relieved people of the responsibility and the burden of facing reality. His utterances are both absolutely (and impossibly) performative and completely unreal. His shamelessness absolves people of their shame.
Trumpism not only altered the terms of American political discourse by undermining truth, facts, science, expertise, precedent, norms, decency, and trust but he also waged an assault on reality itself. We need to understand how he transformed his own personal denial of reality into a collective fantasy that effectively altered the political landscape. His denial of reality did in fact create a new reality. It is this new reality—the reality of “fake news” and “alternate facts”—that has become the hallucinatory norm.
Everything Trump says is literally incredible. “Like you wouldn’t believe” is one of his favorite phrases. One doesn’t need to have a psychoanalytic sensibility to appreciate the double-edged dreamlike duplicity of this expression. Meant as a variation of one of his standard hyperboles (everything he touches can only be the greatest, biggest, the most tremendous, etc.) the expression “like you wouldn’t believe” openly avows that the reality being hyped requires an act of belief precisely because it is unbelievable: it is beyond the reality principle.
Trump deploys reversal as a political tool. He contests every bit of reality that threatens to expose his lies and misdeeds as “fake news” and then disseminates his own false counterclaims via social media and conservative TV. Over time, the infusion of so much noise (flooding the zone with shit as his aide Steve Bannon famously put it) has transformed the public sphere into a vertiginous hall of mirrors. All news is potentially “fake news” so there is no news. The internet is the perfect delivery device for disinformation. It soaks up distorted wish fulfillments and amplifies them through endless replication.
As in a dream, there is no negation on the internet. Disinformation is always already viral: viral communications cannot be destroyed, negated, or contained. They can only be refuted by the presentation of “evidence” that comes from a reality that has no bearing whatsoever on the life of what transpires in the viral dreamscape.
Trump is not merely an aberration of American political life; he is also a symptom of it. He reflects at us the image of what we have become and exposes the wishfulness and the denial in those (like me) who still harbor sentimental fantasies about the checks and balances that supposedly guarantee democratic institutions, the court system, and the rule of law. Over the past weeks, it has become a commonplace for people to observe that this election “stress-tested” the electoral process and that “the guard rails” have held. But from what I saw, we just got lucky. The disaster may not have been averted, merely postponed.
So now we find ourselves in an odd limbo. We have moved so far Beyond the Reality Principle during the Trump years that it is difficult to imagine a possible return to what intellectuals now quaintly refer to as the norms of political life. Personally, I don’t think that there can be a return to a world before Trump. That world no longer exists, if indeed it ever did. Instead, we need to invent another relation to reality; one that is neither bound to “cruel optimism” (to invoke Lauren Berlant’s felicitous phrase) nor paralyzed by the necessity of recognizing the limits of personal and state sovereignty.
As far as I’m concerned, this post-election season has been like a bad dream from which we have yet to awaken. This last and most recent phase is like the dream-within-the-dream when you dream that the nightmare is over but it’s not. Because none of the things that we have seen go down in the last month should be thinkable or possible. So just because the worst possible outcome didn’t fully materialize doesn’t in fact mean that the threat is not real and ongoing. The world that awaits us demands that we traverse that fantasy and awaken to the challenges of imagining a different and more livable new reality.