I’ve been thinking a lot about pessimism recently. Eugene Thacker has been deep in this material for some time already. In fact he has a new, lengthy manuscript on pessimism called Infinite Resignation, which is a bit of departure from his other books in terms of tone and structure. I’ve read it and it’s excellent. Definitely “the worst” he’s ever written! Following the style of other treatises from the history of philosophical pessimism–Leopardi, Cioran, Schopenhauer, Kierkegaard, and others–the bulk of the book is written in short aphorisms. It’s very poetic language, and some sections are driven by his own memories and meditations, all in an attempt to plumb the deepest, darkest corners of the worst the universe has to offer.
Meanwhile, the worst can’t stay hidden. Pessimism has made it to prime time, to NPR, and even right-wing media. Despite all this attention, Eugene seems to have little interest in showing his manuscript to publishers. A true pessimist! Not to worry, I’m sure the book will see the light of day eventually. Or should I say dead of night? When it does, the book is sure to sadden, discourage, and generally worsen the lives of Thacker fans everywhere.
Interestingly pessimism also appears in a number of other authors and fields. I’m thinking, for instance, of critical race theory and the concept of Afro-pessimism. The work of Fred Moten and Frank B. Wilderson, III is particularly interesting in that regard. Likewise queer theory has often wrestled with pessimism, be it the “no future” debates around reproductive futurity, or what Anna Conlan has simply labeled “homo-pessimism,” that is, the way in which the “persistent association of homosexuality with death and oppression contributes to a negative stereotype of LGBTQ lives as unhappy and unhealthy.”[1]
In his review of my new book, Andrew Culp made reference to how some of this material has influenced me. I’ll be posting more on Moten and these other themes in the future, but let me here describe, in very general terms, how the concept of pessimism might apply to contemporary digital media.
*
A previous post was devoted to the reticular fallacy, defined as the false assumption that the erosion of hierarchical organization leads to an erosion of organization as such. Here I’d like to address the related question of reticular pessimism or, more simply, network pessimism.
Network pessimism relies on two basic assumptions: (1) “everything is a network”; (2) “the best response to networks is more networks.”
Who says everything is a network? Everyone, it seems. In philosophy, Bruno Latour: ontology is a network. In literary studies, Franco Moretti: Hamlet is a network. In the military, Donald Rumsfeld: the battlefield is a network. (But so too our enemies are networks: the terror network.) Art, architecture, managerial literature, computer science, neuroscience, and many other fields–all have shifted prominently in recent years toward a network model. Most important, however, is the contemporary economy and the mode of production. Today’s most advanced companies are essentially network companies. Google monetizes the shape of networks (in part via clustering algorithms). Facebook has rewritten subjectivity and social interaction along the lines of canalized and discretized network services. The list goes on and on. Thus I characterize the first assumption — “everything is a network” — as a kind of network fundamentalism. It claims that whatever exists in the world appears naturally in the form of a system, an ecology, an assemblage, in short, as a network.
Ladies and gentlemen, behold the good news, postmodernism is definitively over! We have a new grand récit. As metanarrative, the network will guide us into a new Dark Age.
If the first assumption expresses a positive dogma or creed, the second is more negative or nihilistic. The second assumption — that the best response to networks is more networks — is also evident in all manner of social and political life today. Eugene and I described this phenomena at greater length in The Exploit, but consider a few different examples from contemporary debates… In military theory: network-centric warfare is the best response to terror networks. In Deleuzian philosophy: the rhizome is the best response to schizophrenic multiplicity. In autonomist Marxism: the multitude is the best response to empire. In the environmental movement: ecologies and systems are the best response to the systemic colonization of nature. In computer science: distributed architectures are the best response to bottlenecks in connectivity. In economics: heterogenous “economies of scope” are the best response to the distributed nature of the “long tail.”
To be sure, there are many sites today where networks still confront power centers. The point is not to deny the continuing existence of massified, centralized sovereignty. But at the same time it’s important to contextualize such confrontations within a larger ideological structure, one that inoculates the network form and recasts it as the exclusive site of liberation, deviation, political maturation, complex thinking, and indeed the very living of life itself.
Why label this a pessimism? For the same reasons that queer theory and critical race theory are grappling with pessimism: Is alterity a death sentence? Is this as good as it gets? Is this all there is? Can we imagine a parallel universe different from this one? (Although the pro-pessimism camp would likely state it in the reverse: We must destabilize and annihilate all normative descriptions of the “good.” This world isn’t good, and hooray for that!)
So what’s the problem? Why should we be concerned about network pessimism? Let me state clearly so there’s no misunderstanding, pessimism isn’t the problem here. Likewise, networks are not the problem. (Let no one label me “anti network” nor “anti pessimism” — in fact I’m not even sure what either of those positions would mean.) The issue, as I see it, is that network pessimism deploys and sustains a specific dogma, confining both networks and pessimism to a single, narrow ideological position. It’s this narrow-mindedness that should be questioned.
Specifically I can see three basic problems with network pessimism, the problem of presentism, the problem of ideology, and the problem of the event.
The problem of presentism refers to the way in which networks and network thinking are, by design, allergic to historicization. This exhibits itself in a number of different ways. Networks arrive on the scene at the proverbial “end of history” (and they do so precisely because they help end this history). Ecological and systems-oriented thinking, while admittedly always temporal by nature, gained popularity as a kind of solution to the problems of diachrony. Space and landscape take the place of time and history. As Fredric Jameson has noted, the “spatial turn” of postmodernity goes hand in hand with a denigration of the “temporal moment” of previous intellectual movements.
From Hegel’s history to Luhmann’s systems. From Einstein’s general relativity to Riemann’s complex surfaces. From phenomenology to assemblage theory. From the “time image” of cinema to the “database image” of the internet. From the old mantra always historicize to the new mantra always connect.
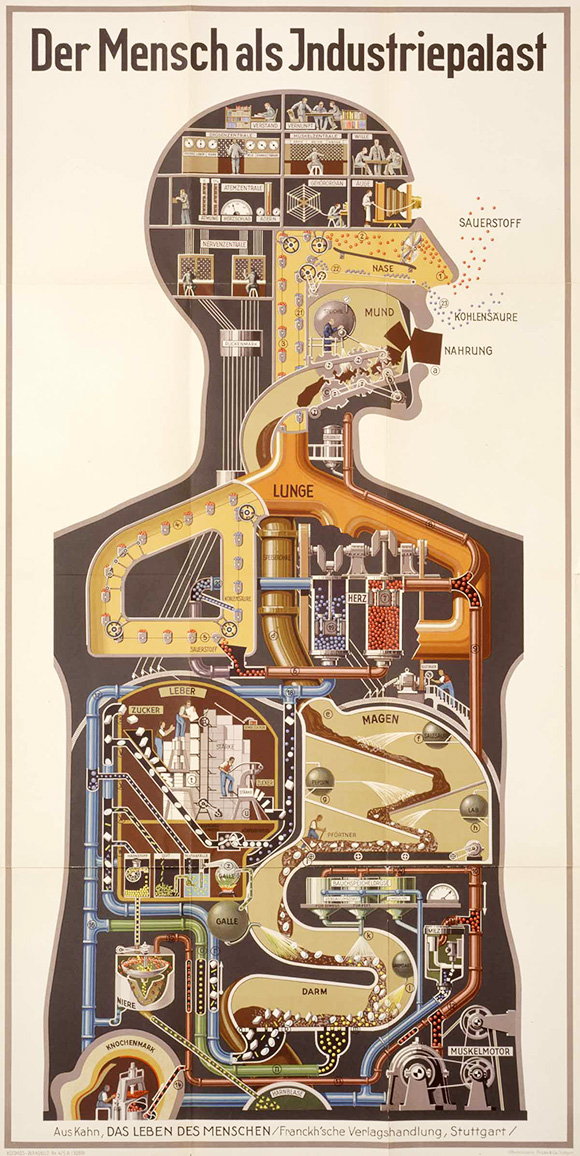
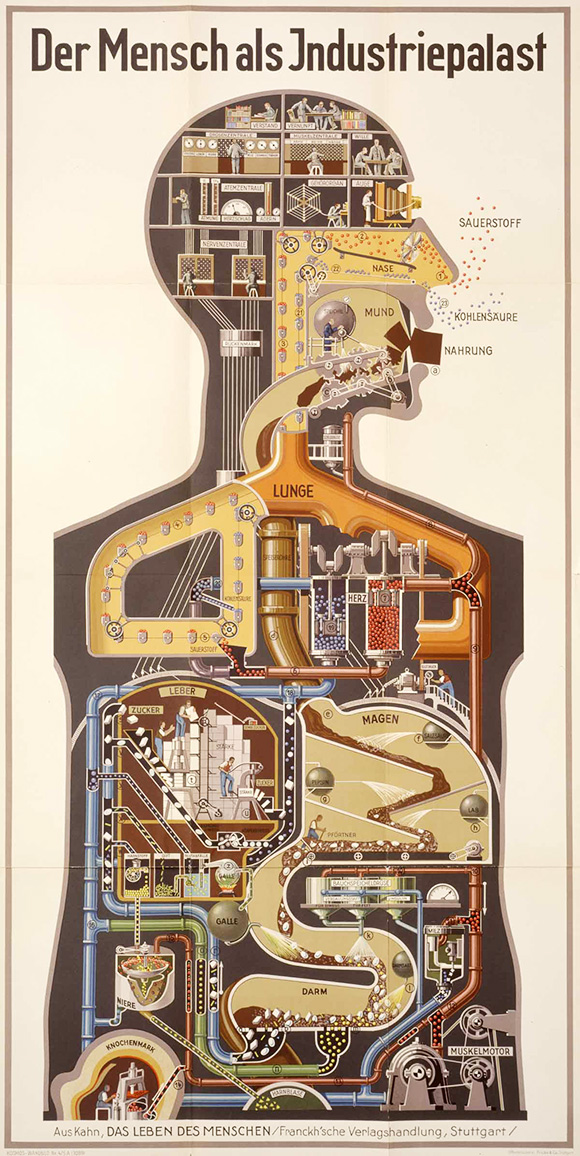
During the age of clockwork, the universe was thought to be a huge mechanism, with the heavens rotating according to the music of the spheres. When the steam engine was the source of newfound power, the world suddenly became a dynamo of untold thermodynamic force. After full-fledged industrialization, the body became a factory. Technologies and infrastructures are seductive metaphors. So it’s no surprise (and no coincidence) that today, in the age of the network, a new template imprints itself on everything in sight. In other words, the assumption “everything is a network” gradually falls apart into a kind of tautology of presentism. “Everything right now is a network…because everything right now has been already defined as a network.”
This leads to the problem of ideology. Again we’re faced with an existential challenge, because network technologies were largely invented as a non-ideological or extra-ideological structure. When writing Protocol I interviewed some of the computer scientists responsible for the basic internet protocols and most of them reported that they “have no ideology” when designing networks, that they are merely interested in “code that works” and “systems that are efficient and robust.” In sociology and philosophy of science, figures like Bruno Latour routinely describe their work as “post-critical,” merely focused on the direct mechanisms of network organization. Hence ideology as a problem to be forgotten or subsumed: networks are specifically conceived and designed as those things that both are non-ideological in their conception (we just want to “get things done”), but also post-ideological in their architecture (in that they acknowledge and co-opt the very terms of previous ideological debates, things like heterogeneity, difference, agency, and subject formation).
The problem of the event indicates a crisis for the very concept of events themselves. Here the work of Alain Badiou is invaluable. Network architectures are the perfect instantiation of what Badiou derisively labels “democratic materialism,” that is, a world in which there are “only bodies and languages.” In Badiou’s terms, if networks are the natural state of the situation and there is no way to deviate from nature, then there is no event, and hence no possibility for truth. Networks appear, then, as the consummate “being without event.”
What could be worse? If networks are designed to accommodate massive levels of contingency — as with the famous Robustness Principle — then they are also exceptionally adept at warding off “uncontrollable” change wherever it might arise. If everything is a network, then there’s no escape, there’s no possibility for the event.
Jameson writes as much in The Seeds of Time when he says that it is easier to imagine the end of the earth and the end of nature than it is to imagine the ends of capitalism. Network pessimism, in other words, is really a kind of network defeatism in that it makes networks the alpha and omega of our world. It’s easier to imagine the end of that world than it is to discard the network metaphor and imagine a kind of non-world in which networks are no longer dominant.
In sum, we shouldn’t give in to network pessimism. We shouldn’t subscribe to the strong claim that everything is a network. (Nor should we subscribe to the softer claim, that networks are merely the most common, popular, or natural architecture for today’s world.) Further, we shouldn’t think that networks are the best response to networks. Instead we must ask the hard questions. What is the political fate of networks? Did heterogeneity and systematicity survive the Twentieth Century? If so, at what cost? What would a non-net look like? And does thinking have a future without the network as guide?
_____
Alexander R. Galloway is a writer and computer programer working on issues in philosophy, technology, and theories of mediation. Professor of Media, Culture, and Communication at New York University, he is author of several books and dozens of articles on digital media and critical theory, including Protocol: How Control Exists after Decentralization (MIT, 2006), Gaming: Essays in Algorithmic Culture (University of Minnesota, 2006); The Interface Effect (Polity, 2012), and most recently Laruelle: Against the Digital (University of Minnesota, 2014), reviewed here in 2014. Galloway has recently been writing brief notes on media and digital culture and theory at his blog, on which this post first appeared.
Back to the essay
_____
Notes
[1] Anna Conlan, “Representing Possibility: Mourning, Memorial, and Queer Museology,” in Gender, Sexuality and Museums, ed. Amy K. Levin (London: Routledge, 2010). 253-263.